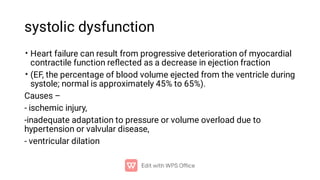
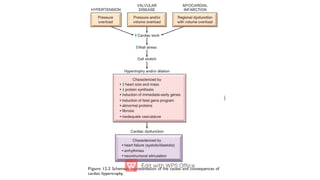
Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs or can only do so with elevated filling pressures. It is commonly caused by chronic heart conditions that damage the heart muscle over time like heart attacks, hypertension, and valve diseases. There are two main types of heart failure - systolic and diastolic dysfunction. Systolic dysfunction refers to the heart's inability to contract properly, while diastolic dysfunction means the heart cannot relax and fill with blood adequately. Left-sided heart failure most often stems from issues like ischemic heart disease, hypertension, or valve problems that impair the left side of the heart. The clinical effects include blood backing up in the lungs and poor perfusion of tissues.

![Congestive heart failure (heart failure)
•
•
•
•
•
Heart failure is defined as the condition in which a heart cannot
pump blood to adequately meet the metabolic demands of
peripheral tissues, or can do so only at elevated filling pressures.
It is the common end stage of many forms of chronic heart disease
like in valve disease or hypertension or IHD ,myocardial infarction [MI]
. However, acute hemodynamic stresses, such as fluid overload,
abrupt valvular dysfunction, or myocardial infarction, can all
precipitate sudden CHF.
types – systolic dysfunction
_ diastolic dysfunction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heartfailure-221230182023-211ee7d8/85/heart-failure-pdf-2-320.jpg)