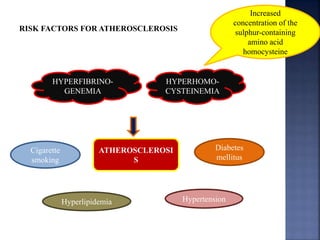
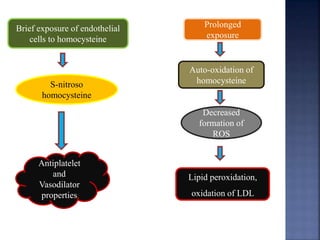
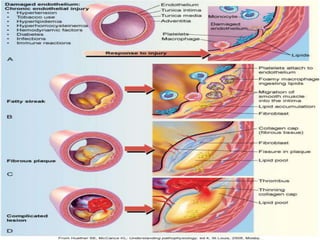
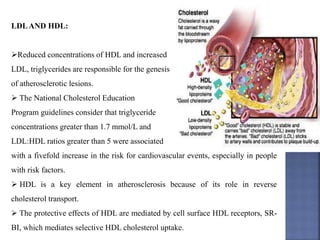
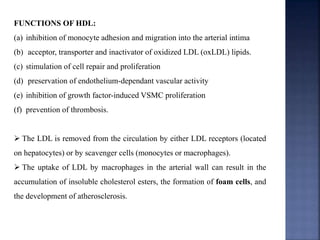
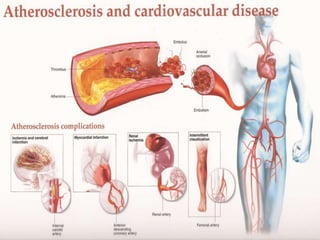
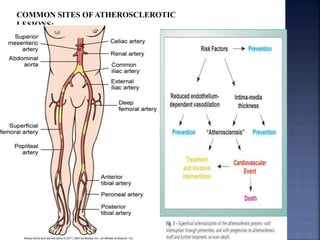
Atherosclerosis is the hardening and narrowing of arteries caused by plaque buildup within the arterial wall. Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. Over time, plaque hardens and narrows the arteries. There are three main types of atherosclerotic lesions: fatty streaks consisting of lipid-filled foam cells, fibrous plaques made of extracellular lipid and connective tissue, and complicated lesions with features like hemorrhage and ulceration. Risk factors for atherosclerosis include diabetes, hyperlipidemia, smoking, and hypertension. Genetic factors can also influence a person's risk by impacting lipid metabolism, coagulation, blood pressure regulation, and other