Embed presentation
Downloaded 311 times


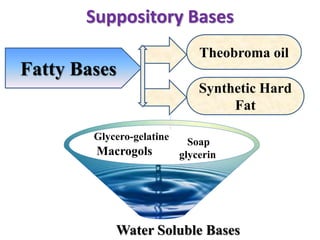

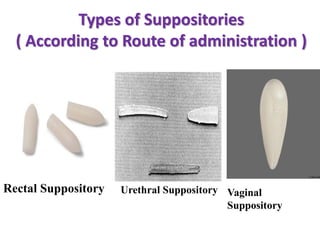

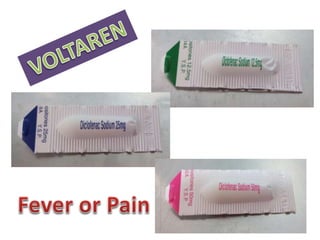
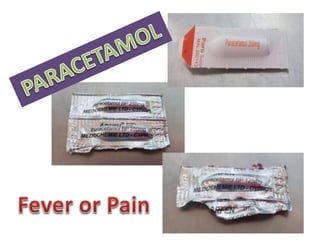
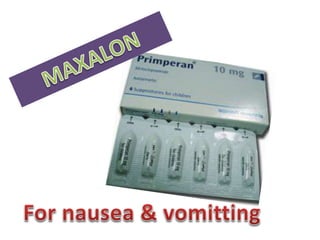
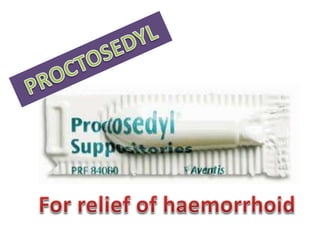

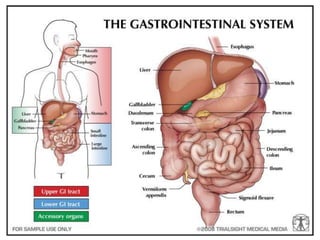
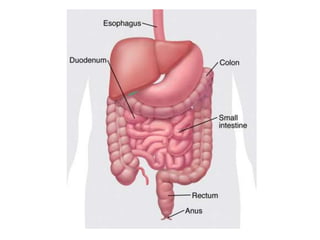
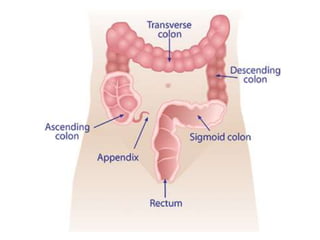
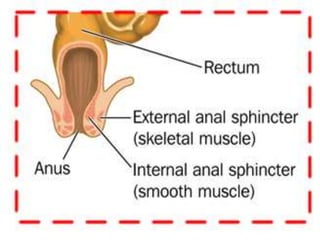


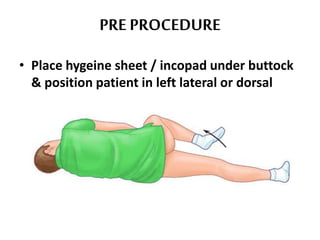

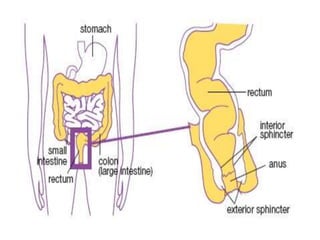
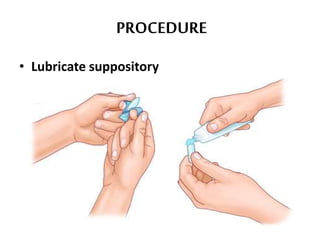
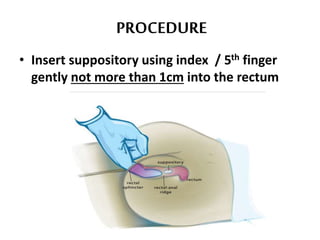
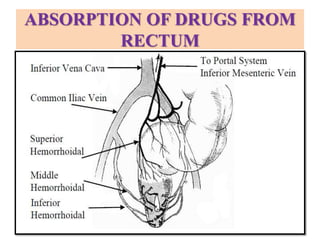
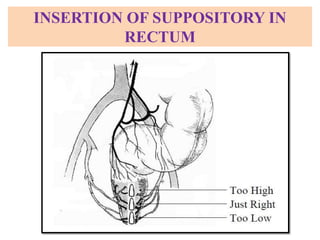




This document defines suppositories as cone-shaped solids or semi-solids intended for insertion into body orifices like the rectum, vagina, or urethra. Suppositories melt or dissolve in the body, releasing medication locally or systemically. Ideal suppository bases melt at body temperature, are non-toxic, compatible with medications, and release the drug readily while being easy to handle and stable over time. The document discusses rectal, urethral, and vaginal suppositories and the advantages of avoiding first-pass metabolism. It provides steps for properly administering a rectal suppository including positioning, lubricating, gently inserting the suppository, and post-procedure care.
































