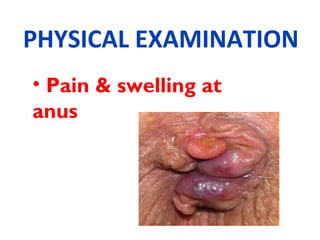
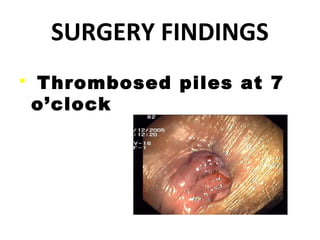
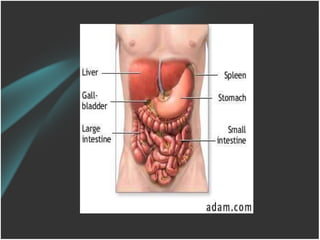
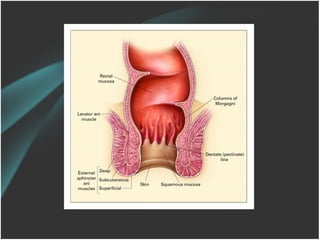
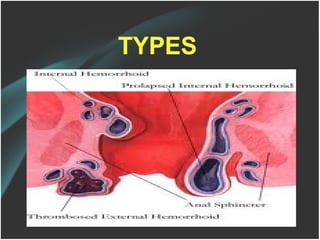
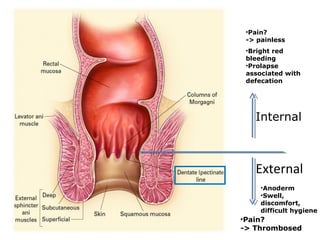
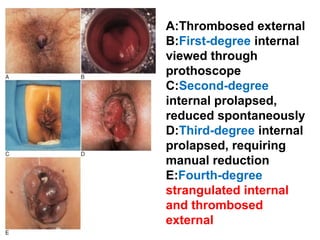
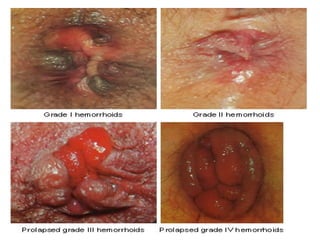
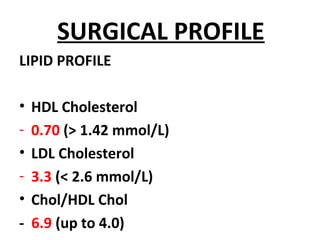
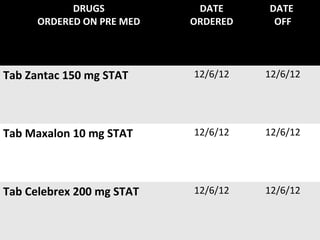
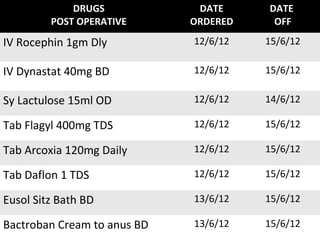
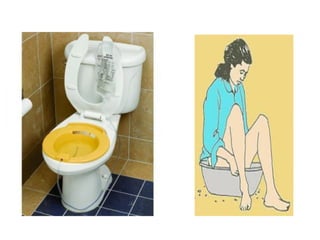
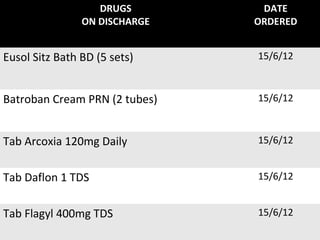
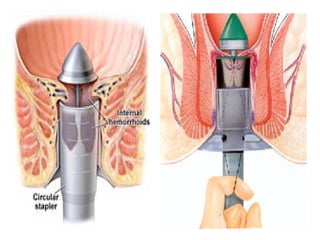
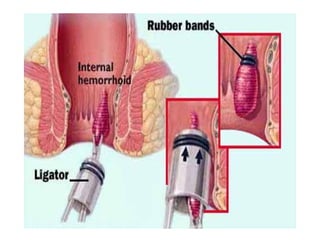
The document discusses a care conference for a patient diagnosed with thrombosed piles who underwent a haemorrhoidectomy. It provides details of the patient's medical history, surgery findings, nursing diagnoses, medications, and objectives of the care conference which are to discuss haemorrhoids including causes, symptoms, grades, complications, and post-operative nursing care.