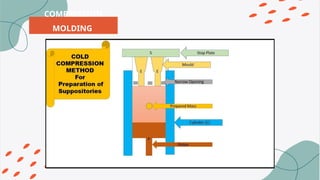
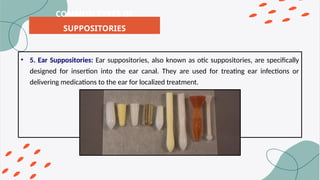
The document provides detailed information on the preparation and use of suppositories, which are solid medications administered rectally, vaginally, or urethrally for various medical purposes. It outlines methods of preparation including hand rolling, compression molding, and fusion molding, along with guidelines for proper use and hygiene. It also lists different types of suppositories and their specific uses, emphasizing the importance of following precautions and consulting with a doctor if symptoms persist.