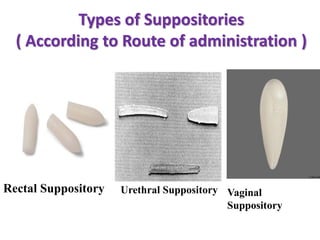
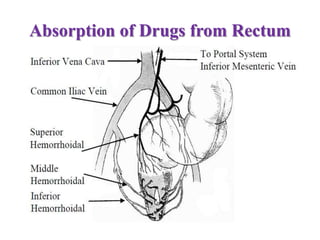
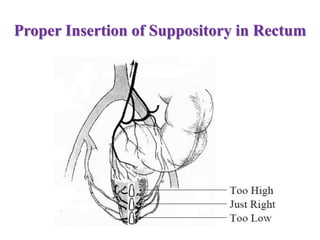
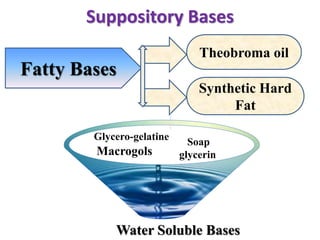
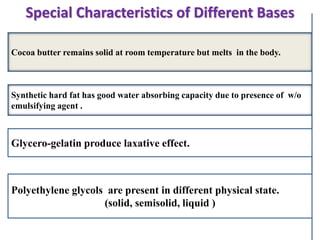
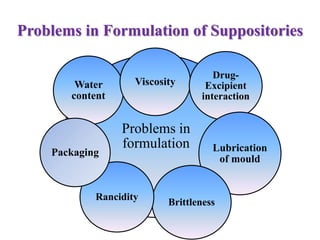
This document defines suppositories as solid or semi-solid dosage forms intended for insertion into body orifices like the rectum, vagina, or urethra. Suppositories are classified by their route of administration and melt or dissolve in the body to exert local or systemic effects. Ideal suppository bases melt at body temperature, are non-toxic, compatible with drugs, and release drugs readily while being easy to handle and stable during storage and molding. The document discusses various suppository bases, preparation methods, packaging, and commercial products.