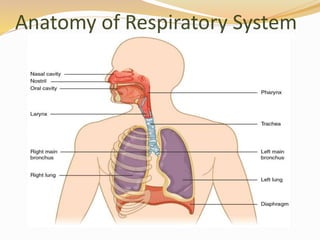
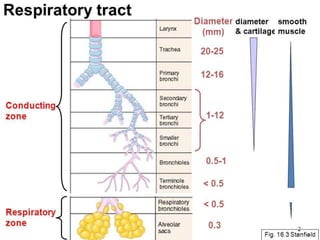
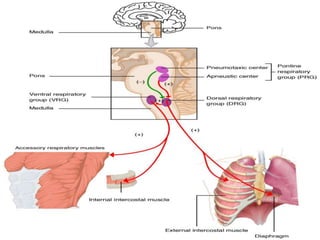
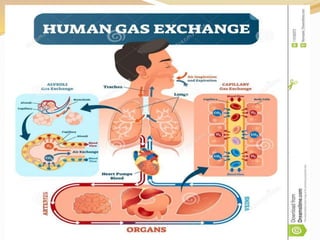
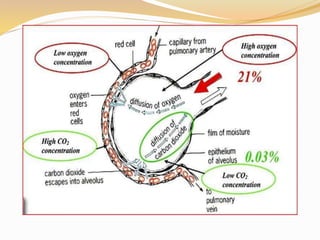
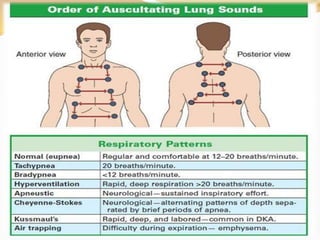
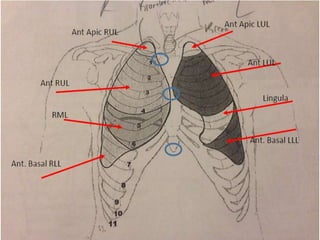
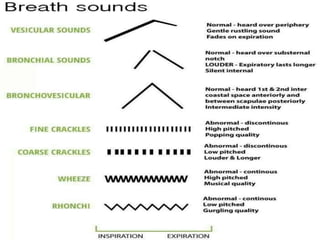
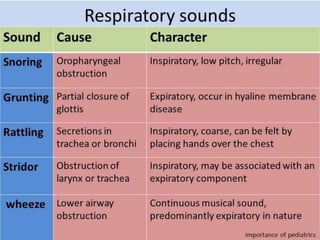
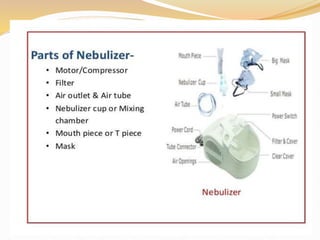
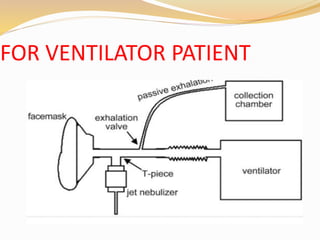
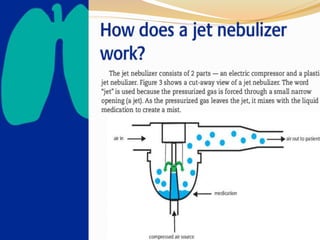
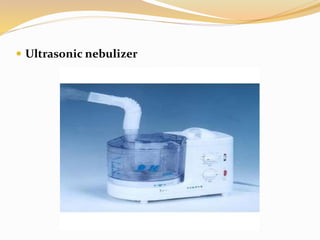
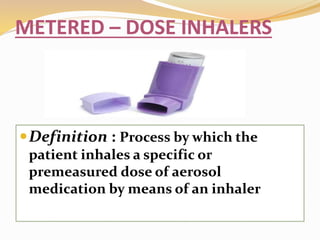
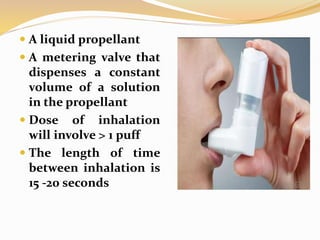
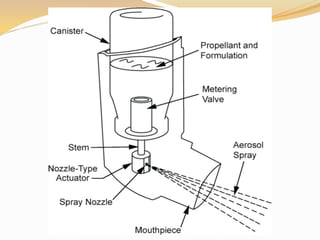
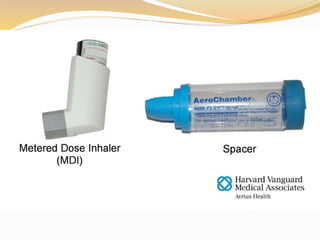
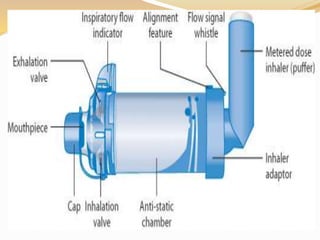
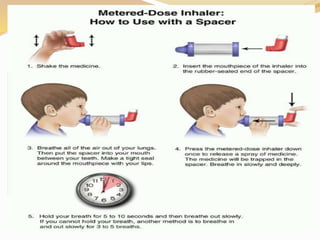
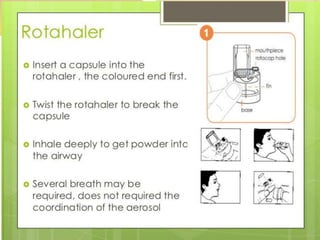
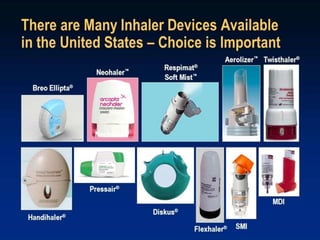
Inhalation therapies deliver drugs directly to the lungs for localized treatment of respiratory disorders, offering benefits such as rapid response and reduced adverse effects compared to oral administration. The document outlines various inhalation methods, including steam inhalation, nebulization, and metered dose inhalers, as well as the medications used and their indications. It also details the procedures for using each type of inhaler, including patient positioning, monitoring, and equipment maintenance.