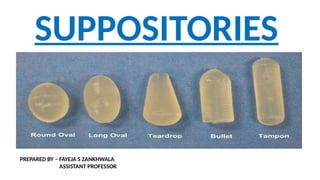
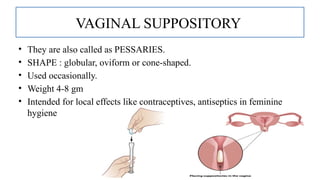
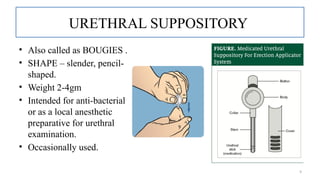
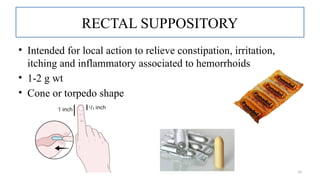
The document provides a comprehensive overview of suppositories, detailing their definitions, classifications, and formulations. It discusses the advantages, disadvantages, ideal properties of bases, and various methods of preparation. Additionally, it outlines the evaluation criteria for ensuring quality in suppository manufacturing.



























![COMPRESSION MOLD SUPPOSITORIES [ COLD COMPRESSION]
Mix theobroma oil and drug
Mixture is forced into a mold under pressure , using a wheel
operated press
Mold is removed , opened , replaced
On large scale , cold compression machines are hydraulically
operated by water – jacketed cooling and screw fed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suppositories-241205075431-4d4b272f/85/SUPPOSITORIES-VAGINAL-RECTAL-NASAL-EAR-32-320.jpg)
![Advantages:-
Suitable for thermo labile drugs.
No possibility of settling of the insoluble solids in base.
Disadvantages:-
Rate of production is low so not suitable for large scale.
Air get entrapped in the mass which leads to oxidation of ingredients.
COMPRESSION MOLD SUPPOSITORIES [ COLD COMPRESSION]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suppositories-241205075431-4d4b272f/85/SUPPOSITORIES-VAGINAL-RECTAL-NASAL-EAR-33-320.jpg)







