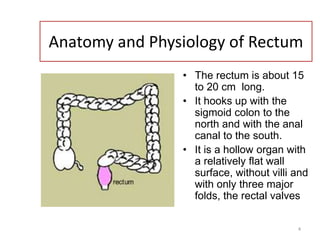
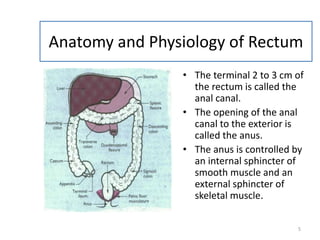
This document provides information about suppositories and pessaries. It begins with an introduction to suppositories and their uses. It then discusses the anatomy and physiology of the rectum as the site of administration for many suppositories. Several methods of suppository preparation are described, including hand molding and compression molding. Ideal properties of suppository bases are outlined. The document covers types of bases such as oleaginous, hydrophilic, and water dispersible bases. It also discusses formulation components like antioxidants, emulsifying agents, and preservatives.














































![COMPRESSION MOLD SUPPOSITORIES [ COLD COMPRESSION]
Mix theobroma oil and drug
Mixture is forced into a mold under pressure , using a wheel
operated press
Mold is removed , opened , replaced
On large scale , cold compression machines are hydraulically
operated by water – jacketed cooling and screw fed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suppositoriespessaries-240223090928-d631d2c8/85/SUPPOSITORIES-PESSARIES-Pharmaceutics-ppt-51-320.jpg)
![Advantages:-
Suitable for thermo labile drugs.
No possibility of settling of the insoluble solids in
base.
Disadvantages:-
Rate of production is low so not suitable for large
scale.
Air get entrapped in the mass which leads to
oxidation of ingredients.
COMPRESSION MOLD SUPPOSITORIES [ COLD COMPRESSION]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suppositoriespessaries-240223090928-d631d2c8/85/SUPPOSITORIES-PESSARIES-Pharmaceutics-ppt-52-320.jpg)















![Stability testing
• Cocoa butter suppositories on storage , BLOOM
i.e they form a white powdery deposit on the
surface
• This can be avoided by storing them at uniform
cool temperatures and by wrapping them in foils
• Fat based suppositories harden on storage [ shift
in melting range to become more stable
polymorphic form of base ]
• Softening time test and DC can be used to test
stability](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suppositoriespessaries-240223090928-d631d2c8/85/SUPPOSITORIES-PESSARIES-Pharmaceutics-ppt-68-320.jpg)






