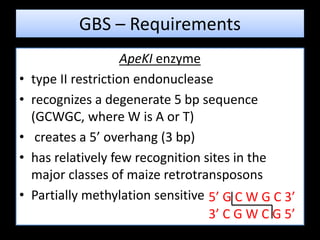
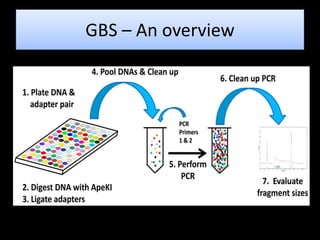
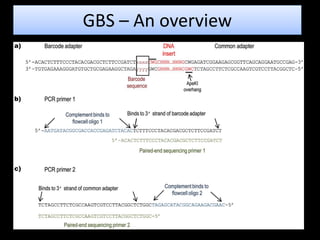
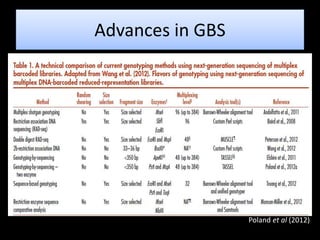
The document discusses genotyping by sequencing (GBS), a molecular technique that enhances breeding cycles by allowing efficient DNA polymorphism discovery and marker assaying with reduced costs and sample handling. It details the process and requirements for GBS, including DNA extraction using specific enzymes and the design of adapters for sequencing. Additionally, GBS aids in significant SNP discovery and studies related to genetic diversity, genomic selection, and phylogenetics without needing prior genome knowledge.