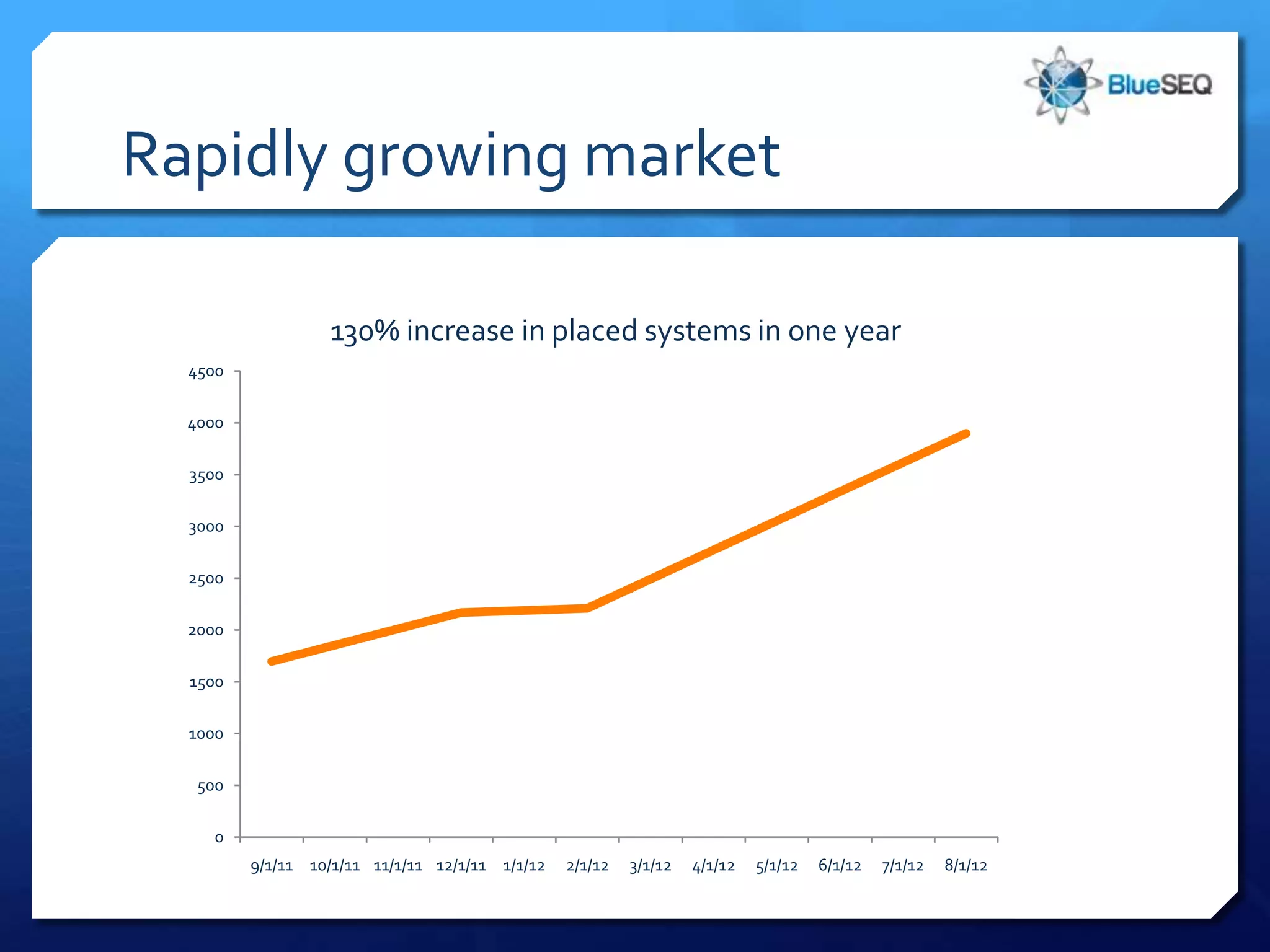
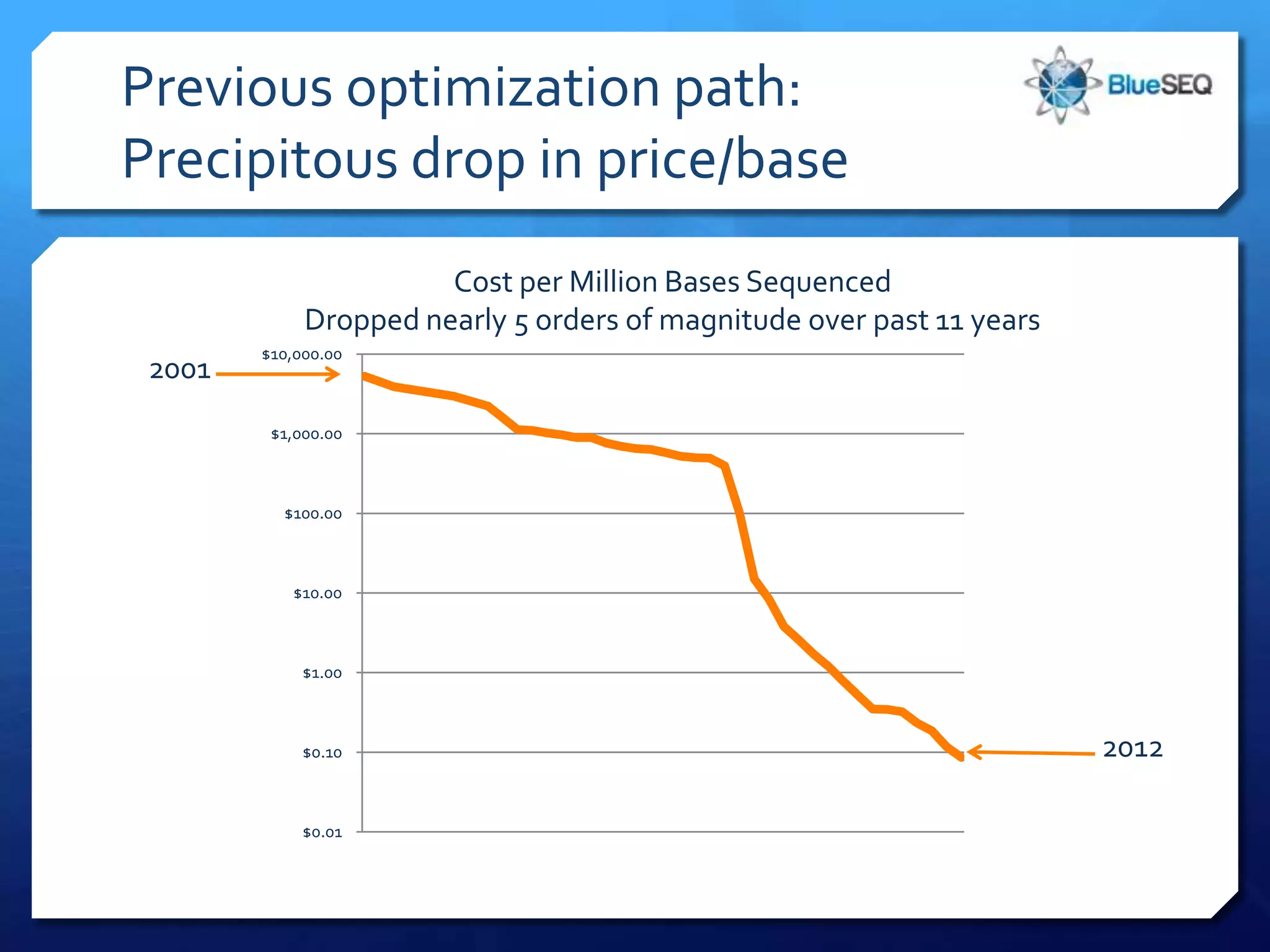
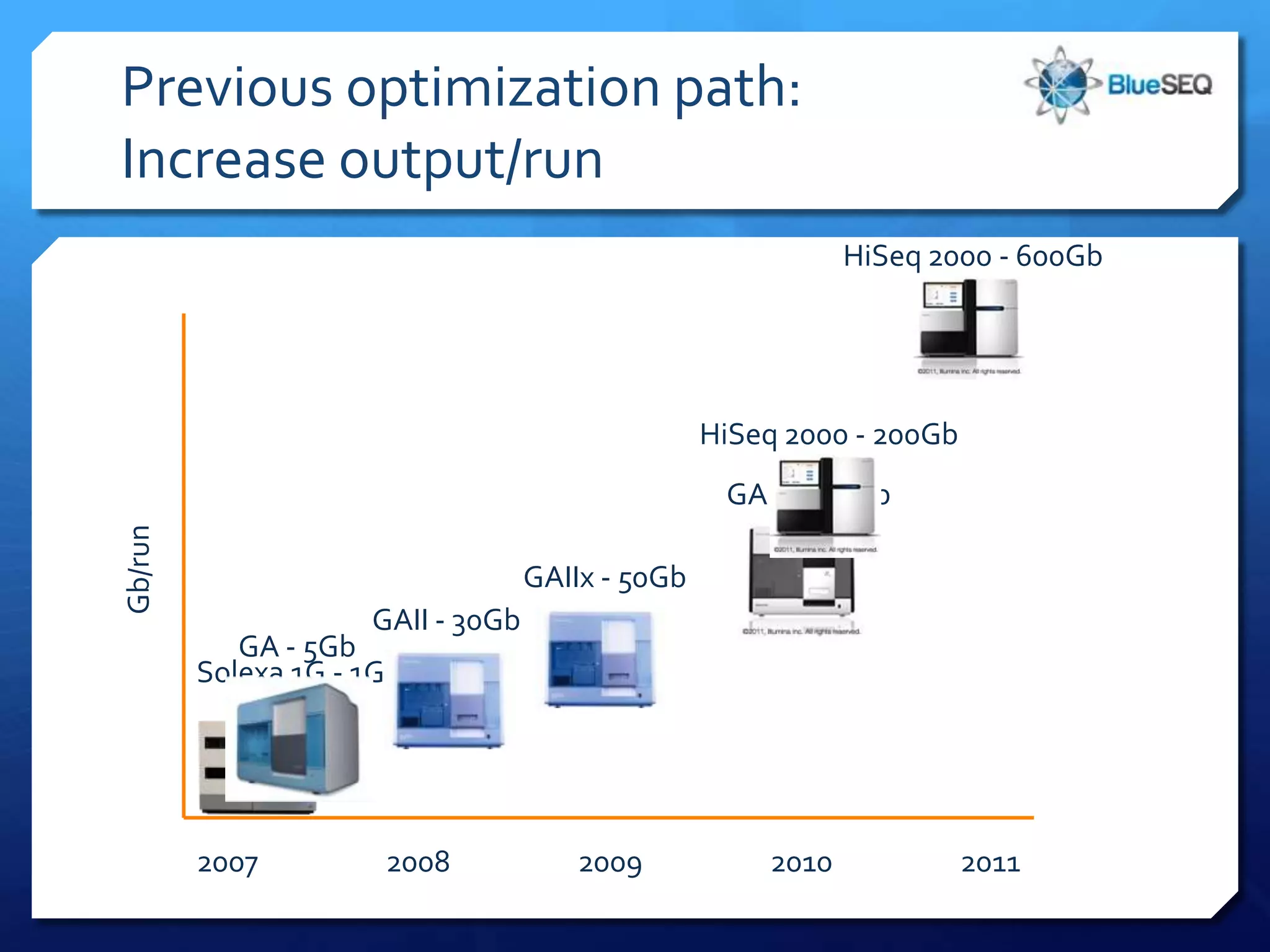
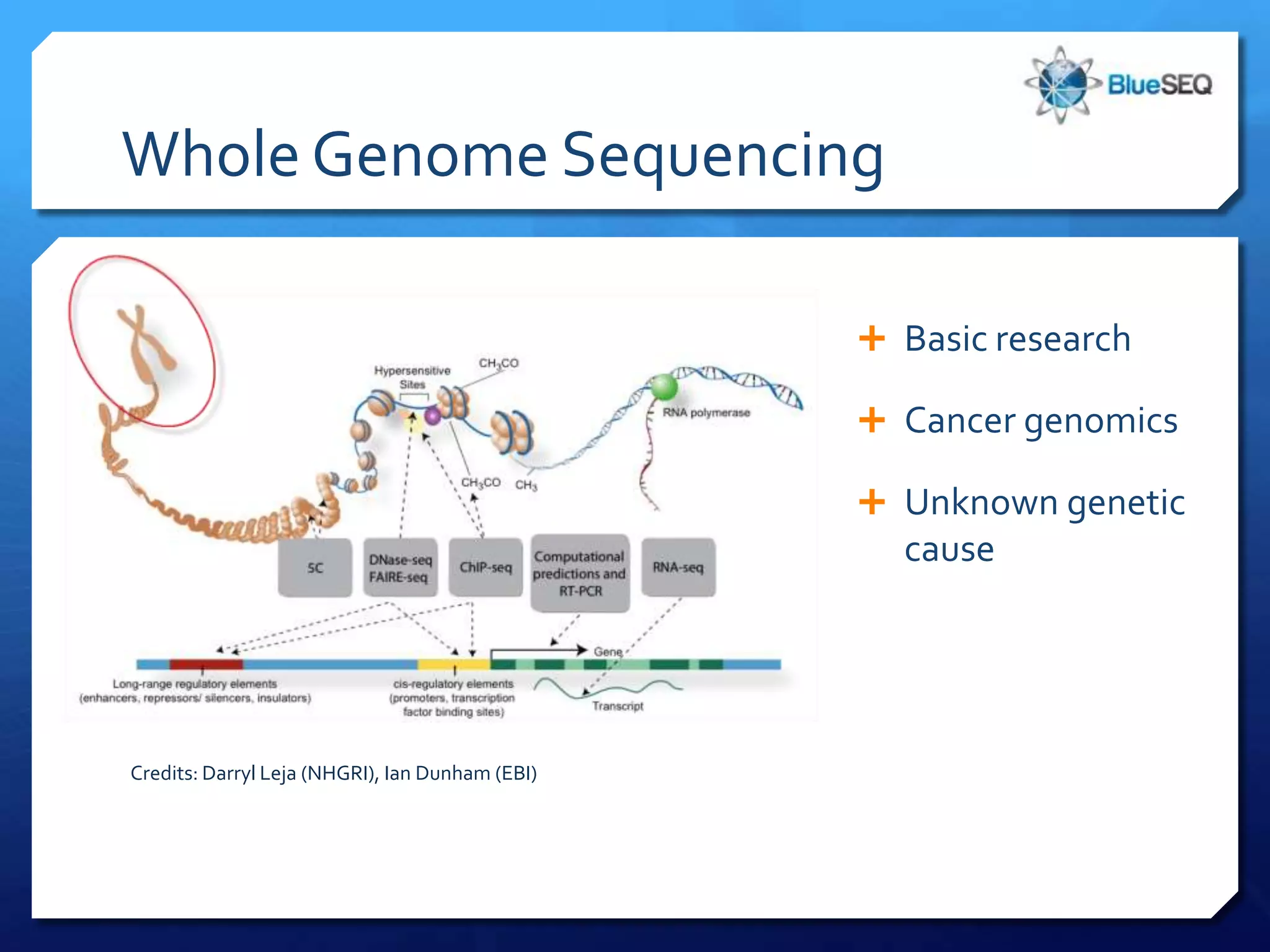
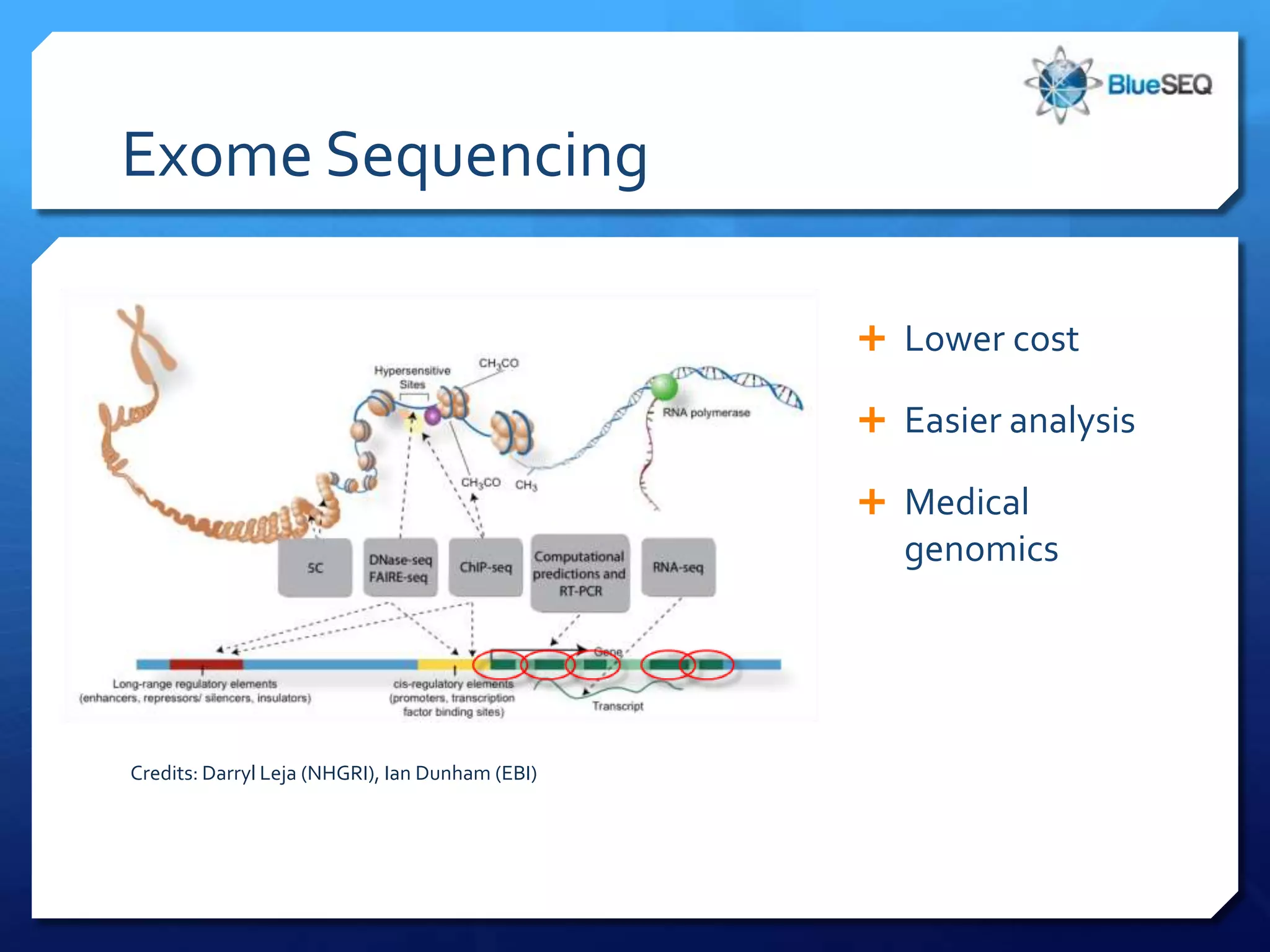
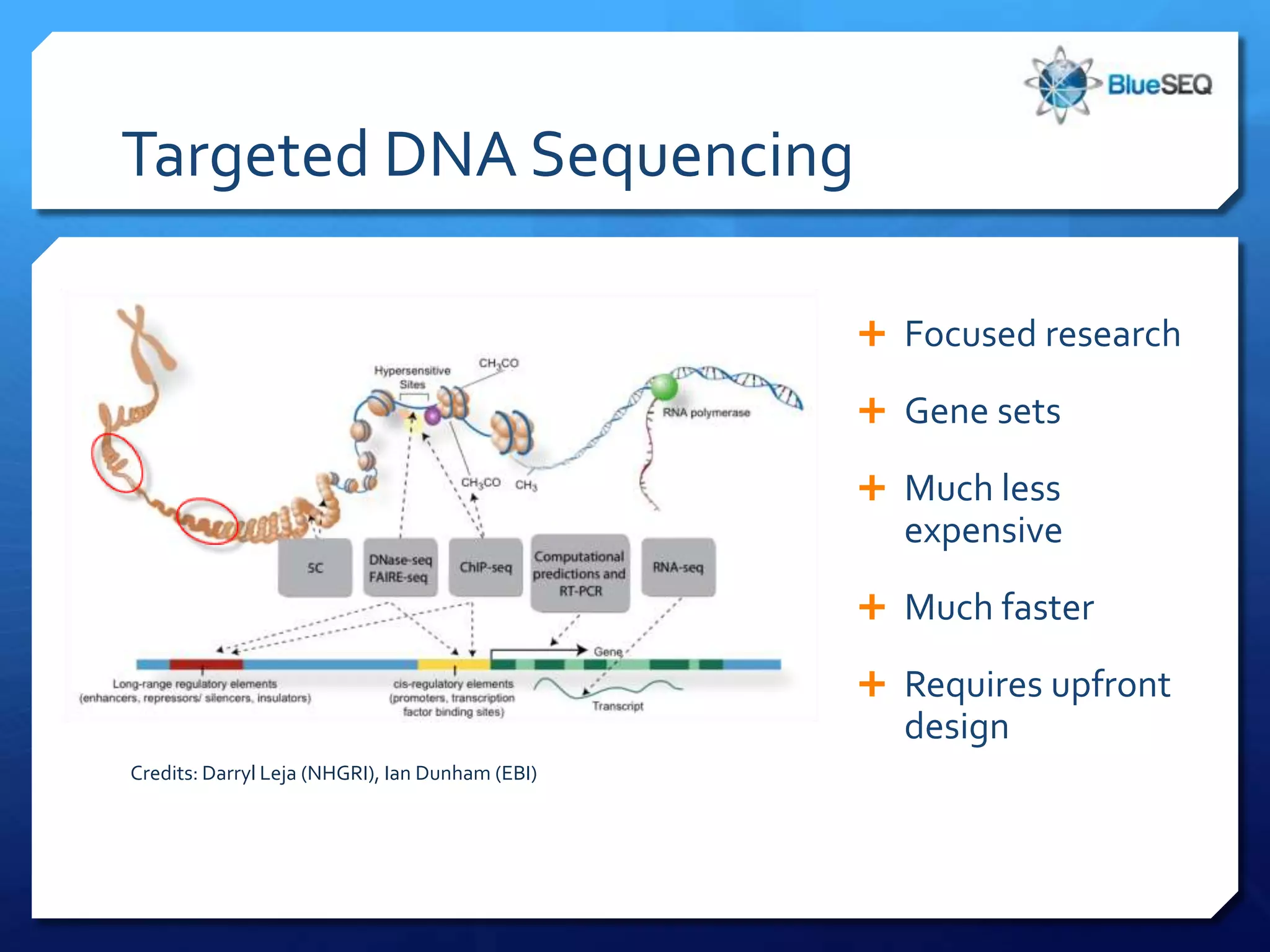
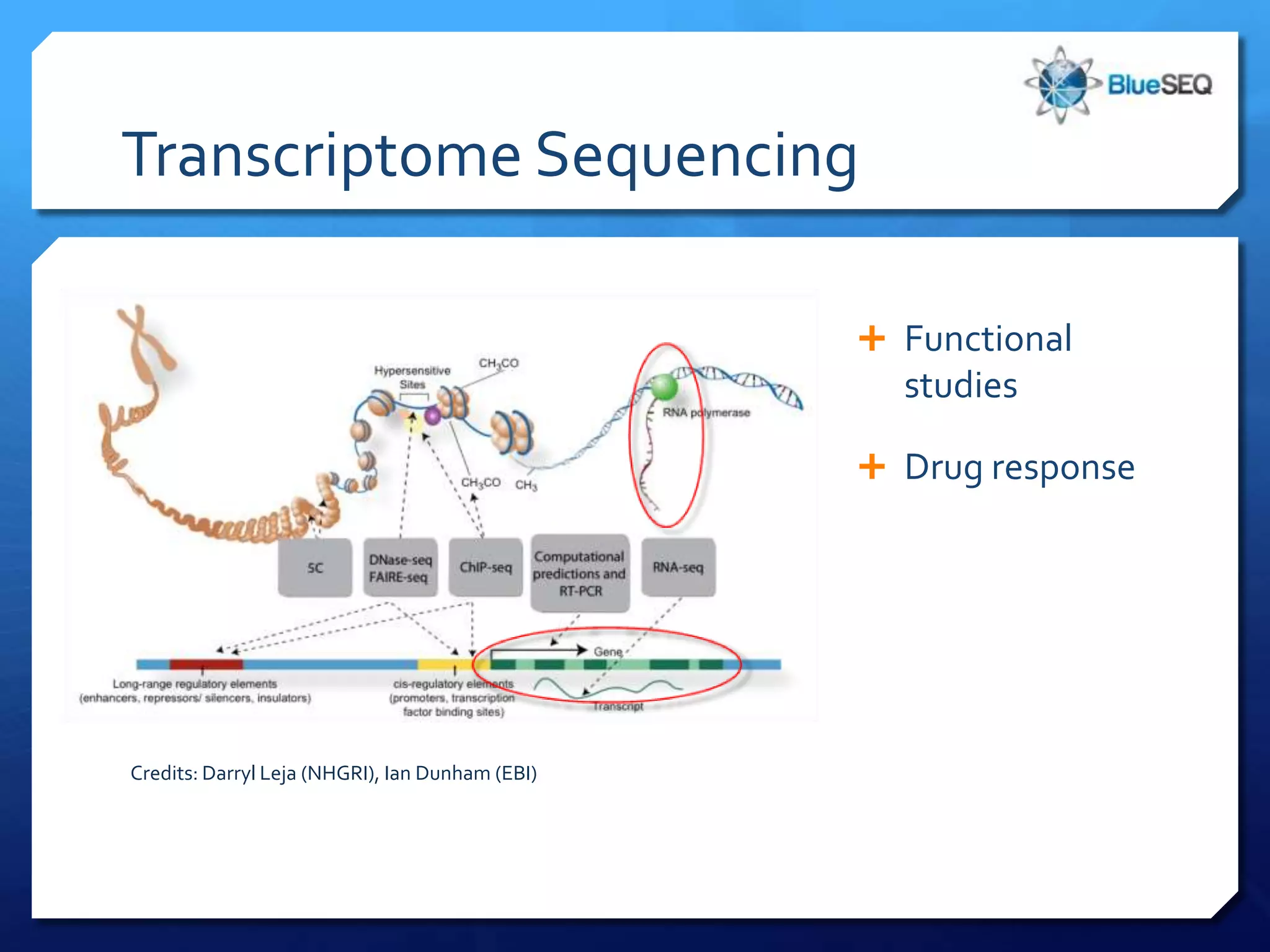
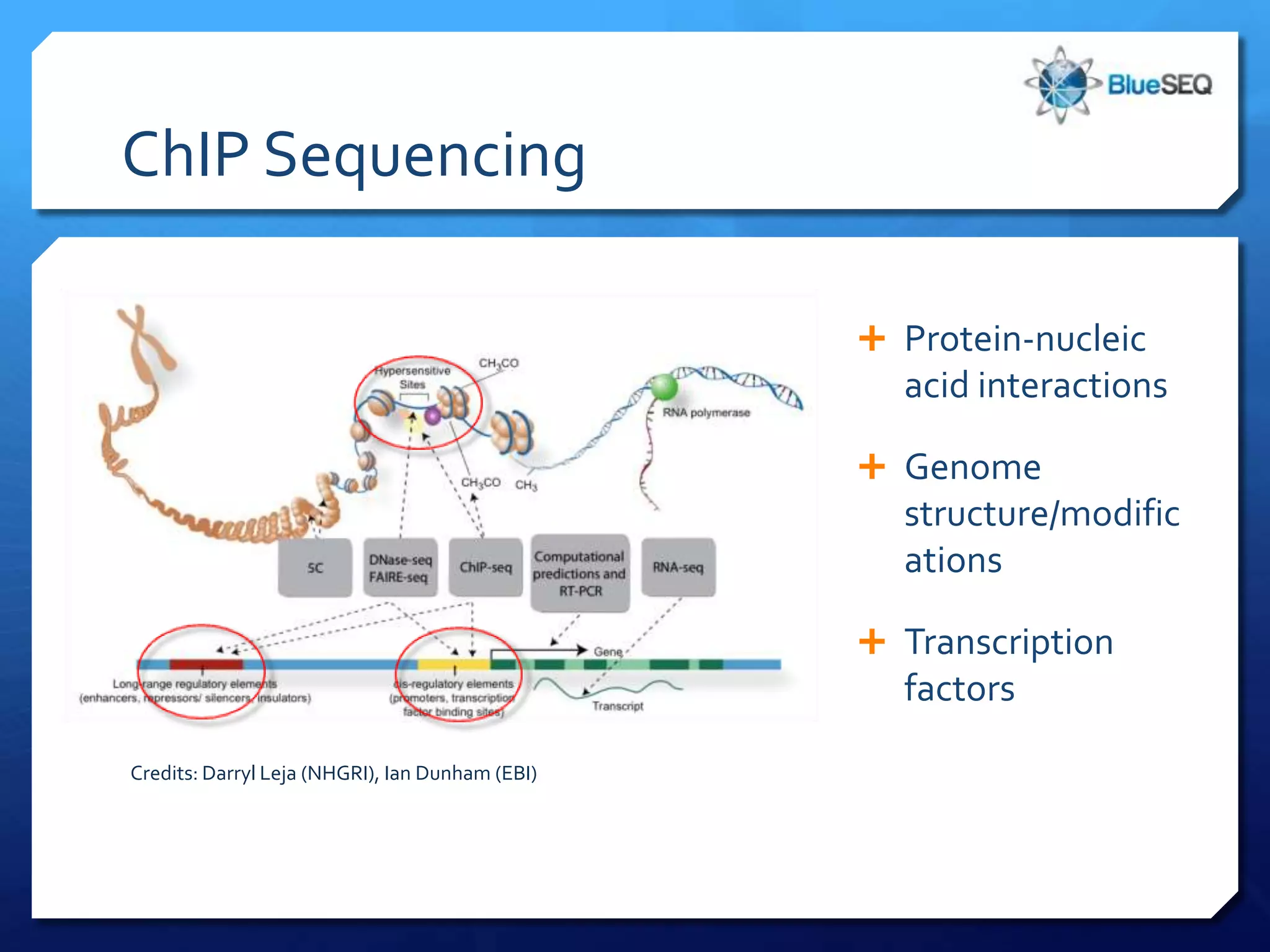
The document discusses the advantages and future of next-generation sequencing (NGS). It notes that the NGS market has grown rapidly, with costs and runtimes decreasing significantly over time. Current optimization aims to further lower costs and runtimes while increasing ease-of-use. NGS allows for hypothesis-free and versatile experimental design. A diverse set of applications are discussed, including whole genome sequencing, exome sequencing, and metagenome sequencing. The document predicts that new platforms will offer cheaper, quicker, and longer sequencing. Future applications may include single-cell sequencing and direct detection of base modifications.