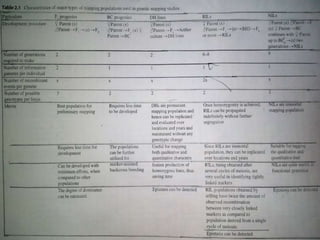
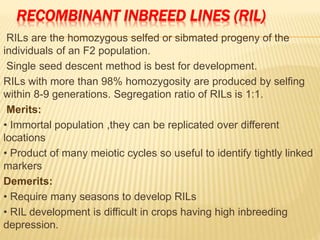
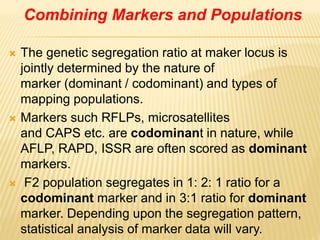
This document discusses different types of mapping populations used in genetic mapping. It describes F2, backcross, double haploid, recombinant inbred line, and near isogenic line populations. For each type, it provides details on how they are developed and their advantages and disadvantages. It also discusses how marker segregation ratios differ depending on the population type and marker dominance. The document recommends using short-term mapping populations initially for preliminary mapping but developing long-term populations like recombinant inbred lines for global mapping projects.