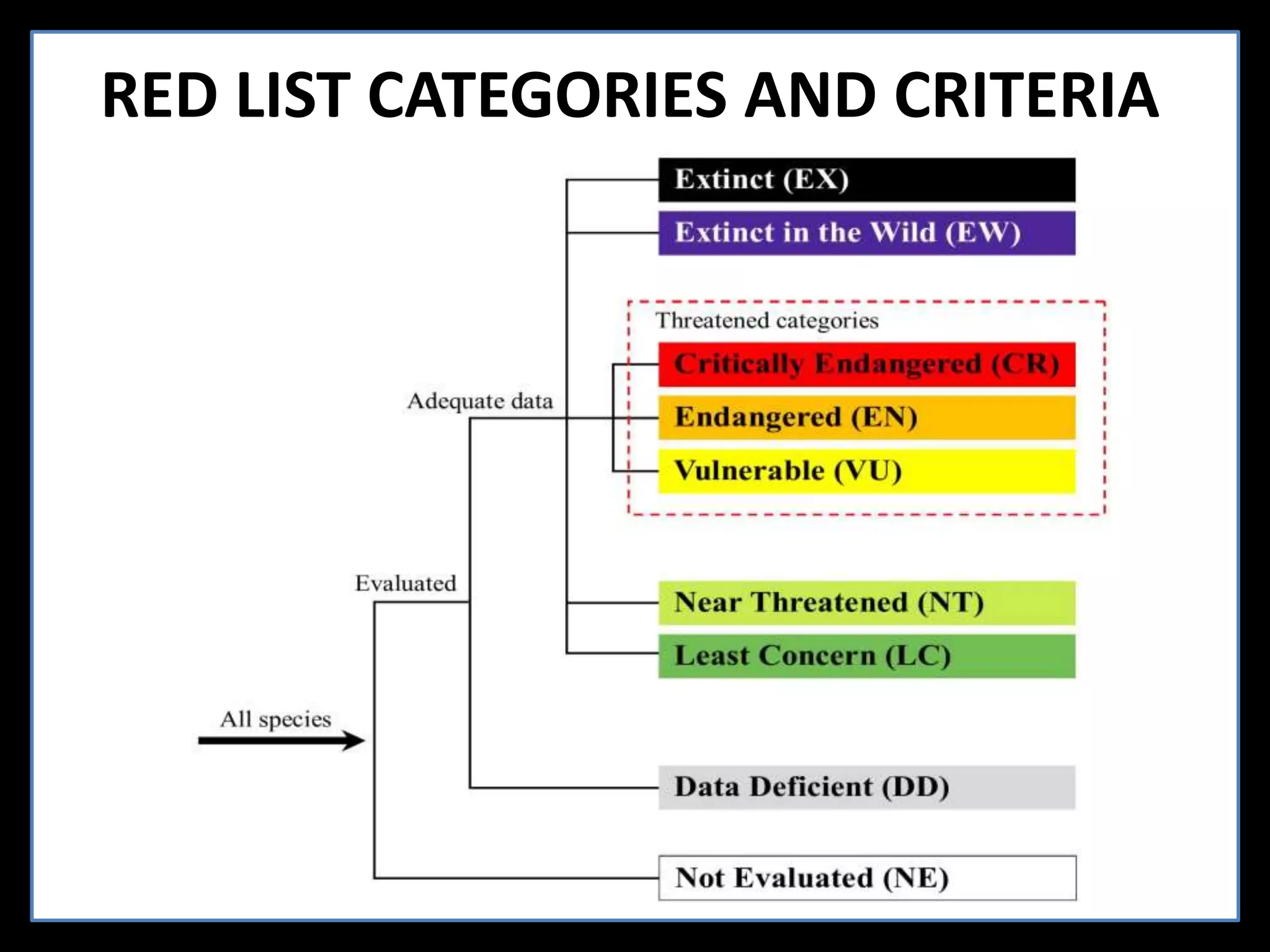
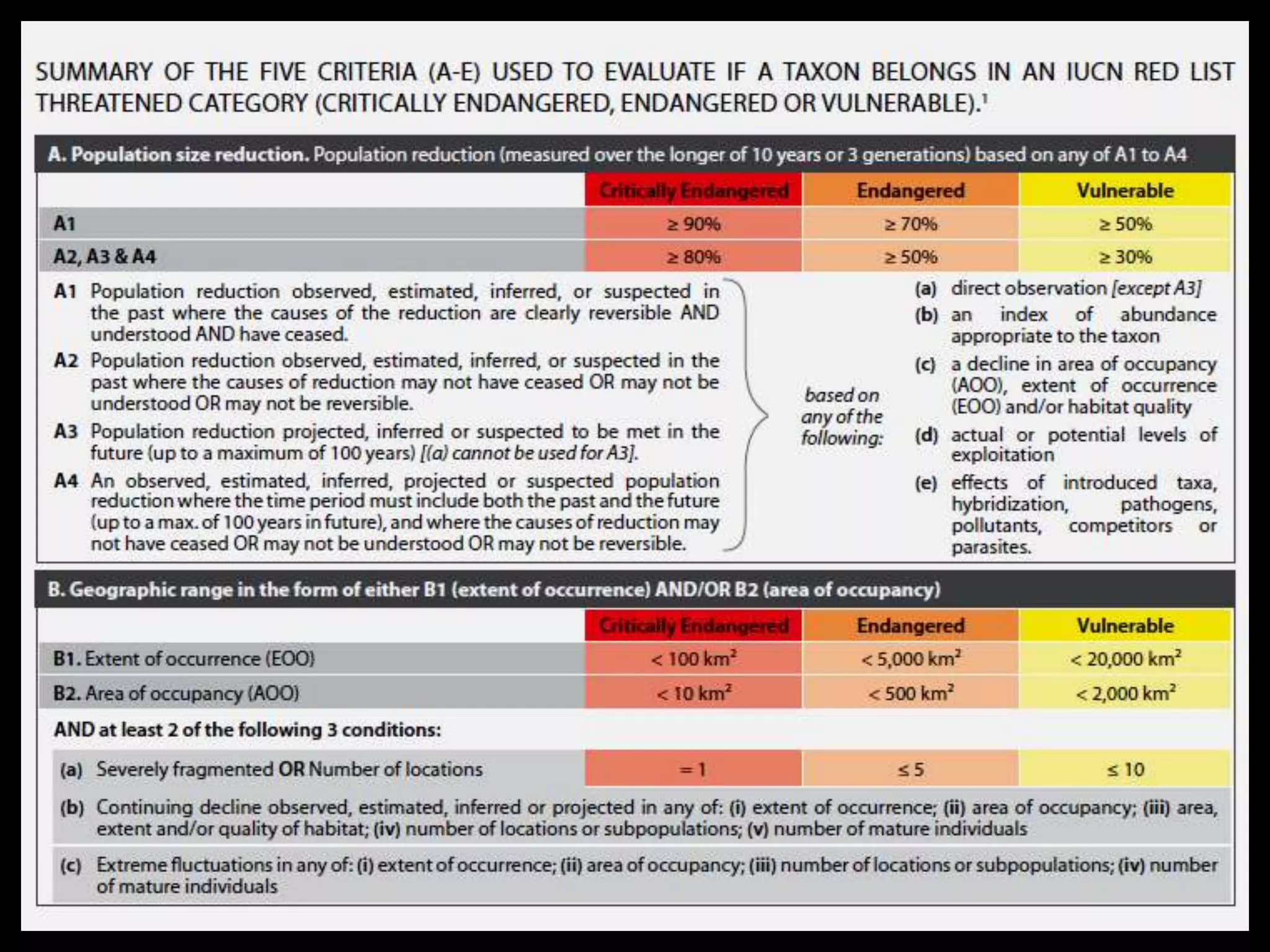
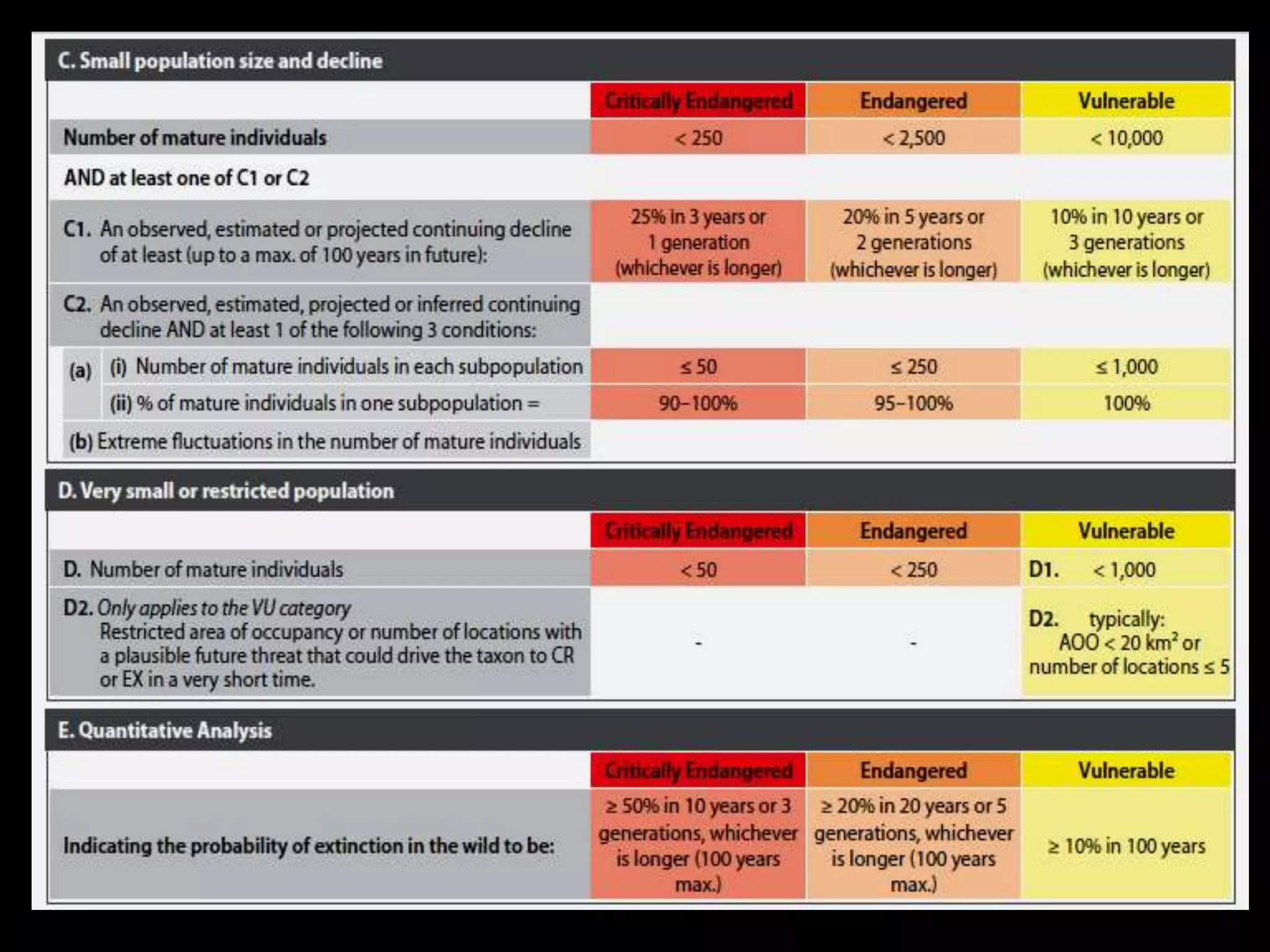
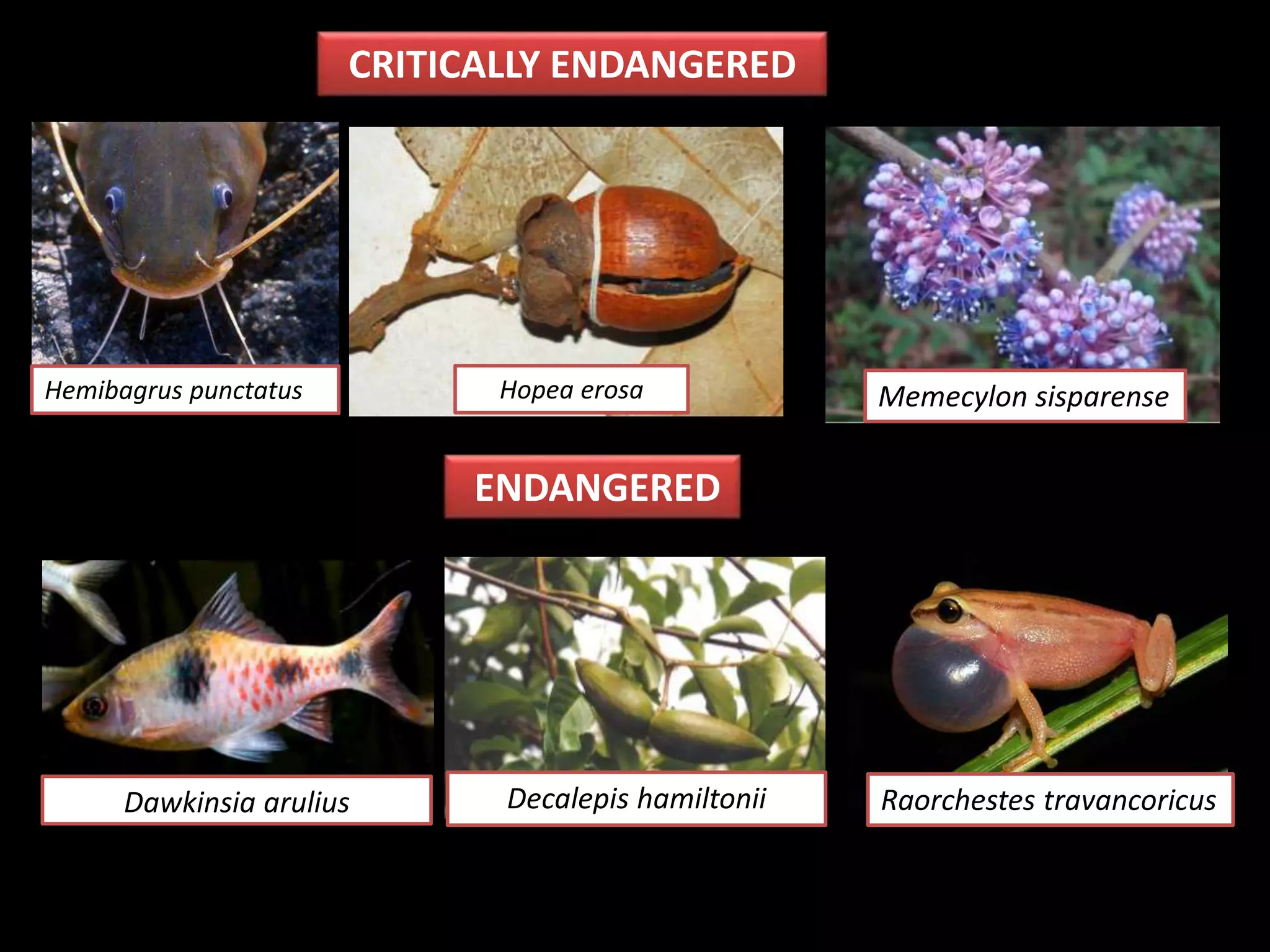
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) focuses on nature conservation and the sustainable use of natural resources, known for its Red List that assesses global species conservation status. Established in 1948, IUCN collaborates with numerous states and organizations, operating from its headquarters in Switzerland, while its India office, opened in 2007, emphasizes India's biodiversity. The Red List categorizes species based on their likelihood of extinction, promoting conservation efforts worldwide.