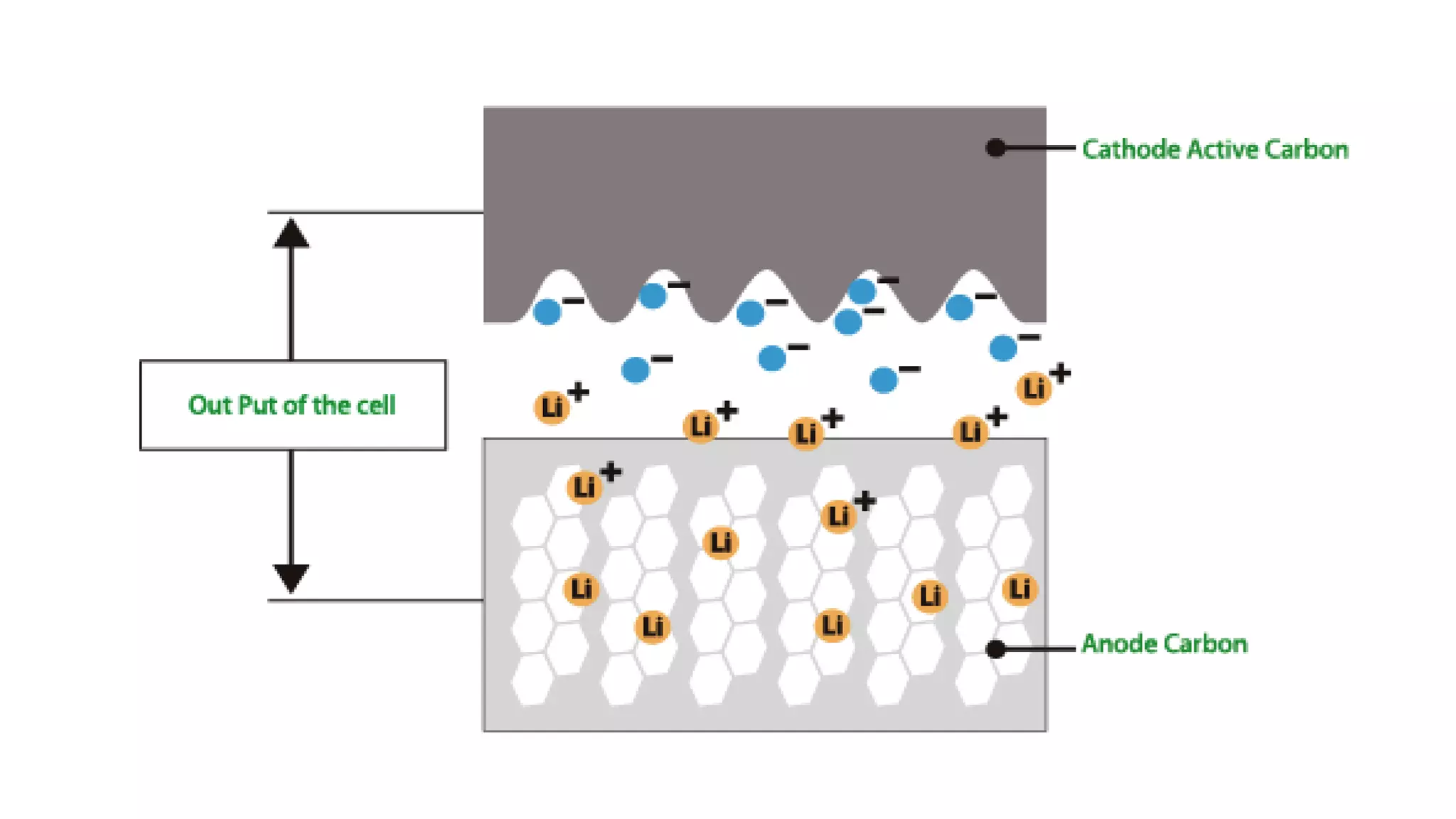
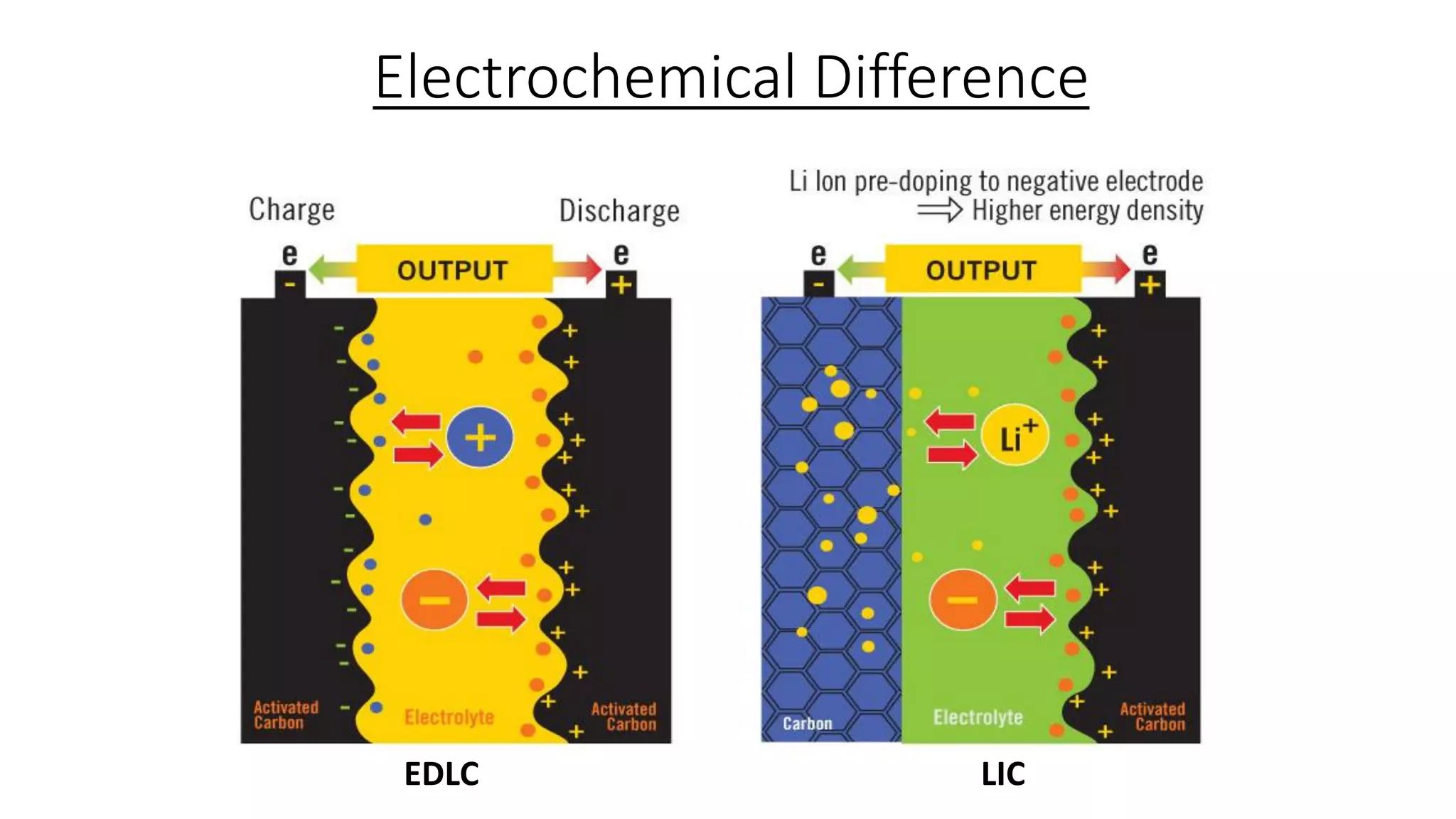
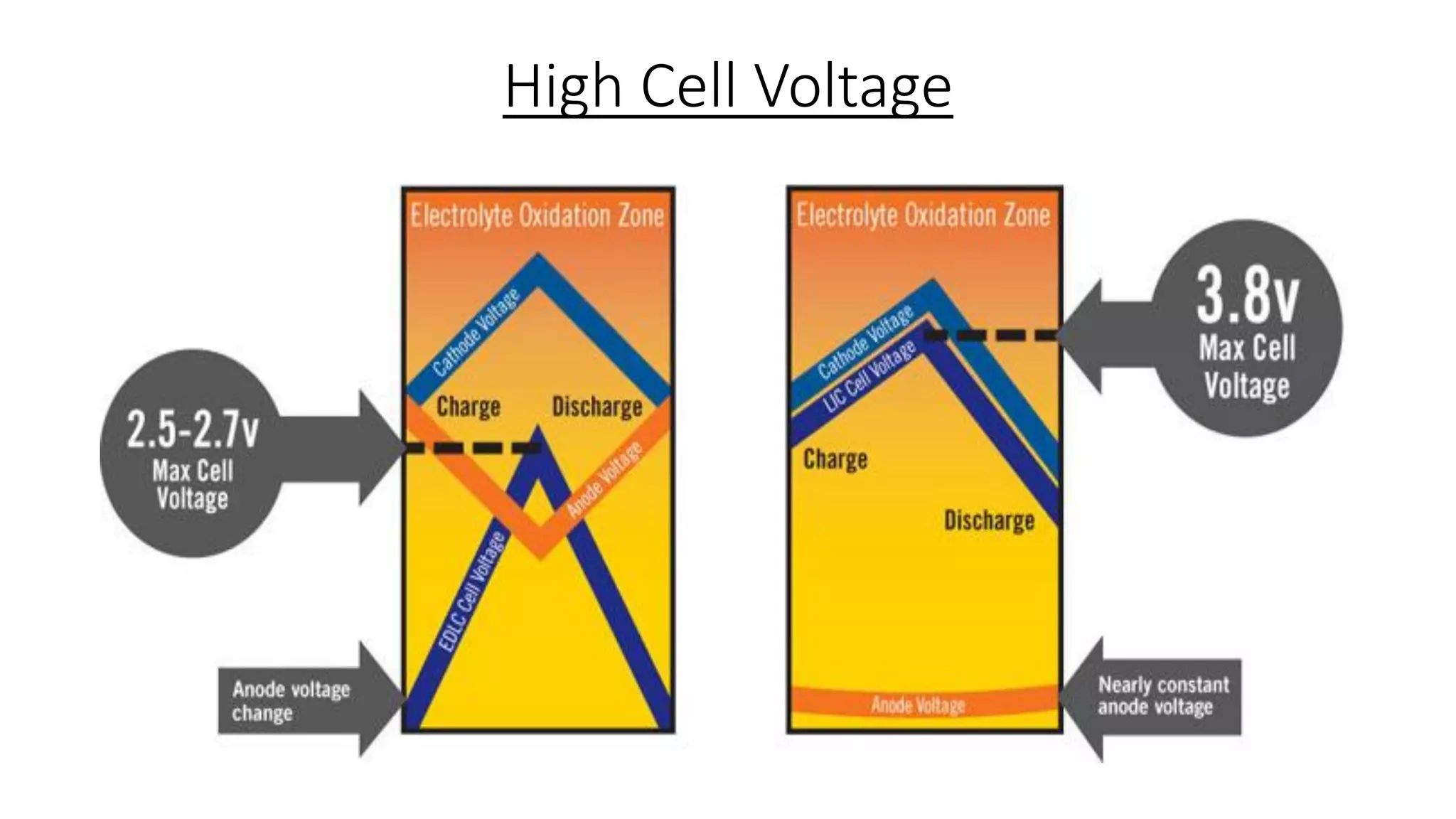
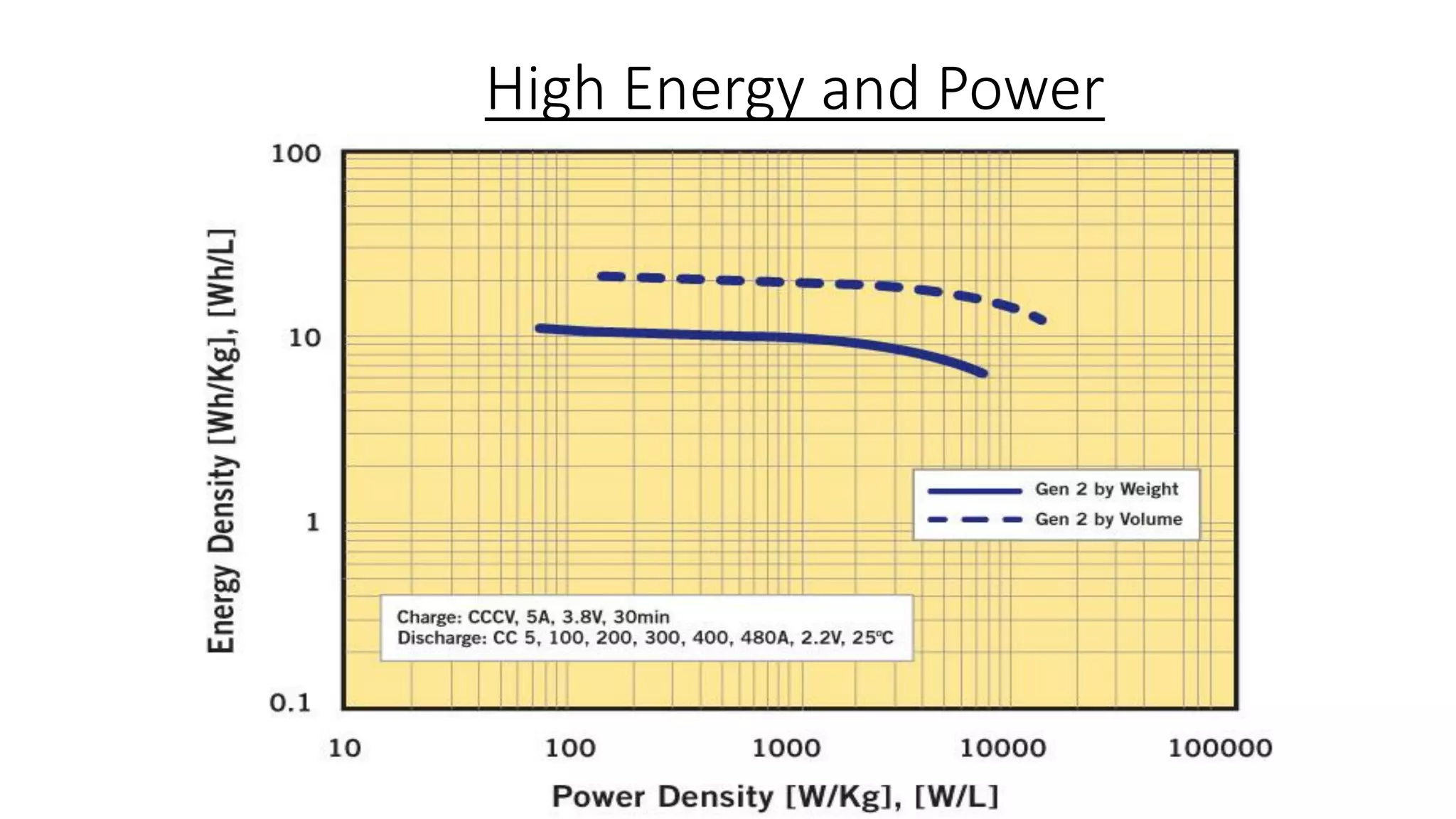
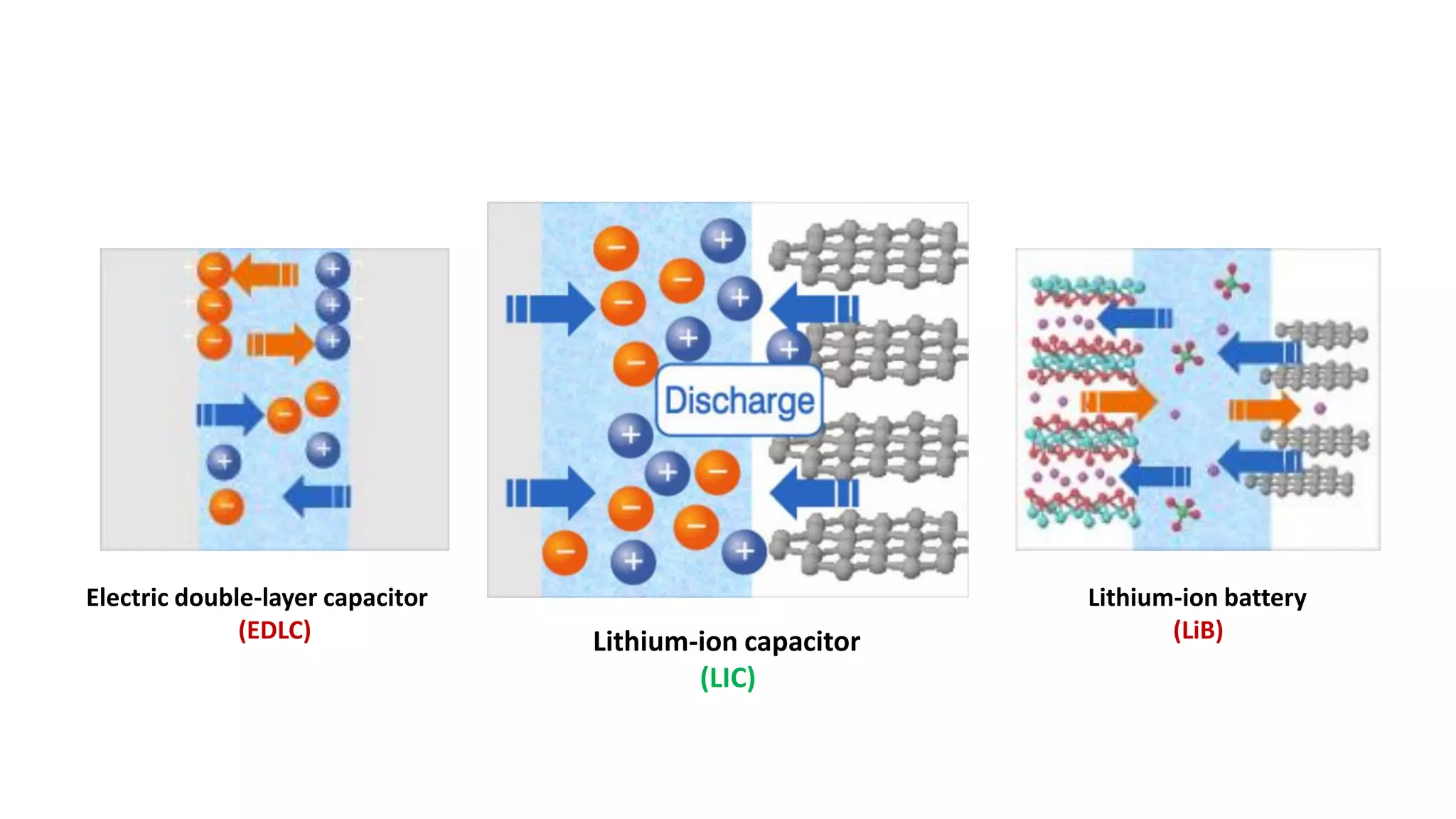
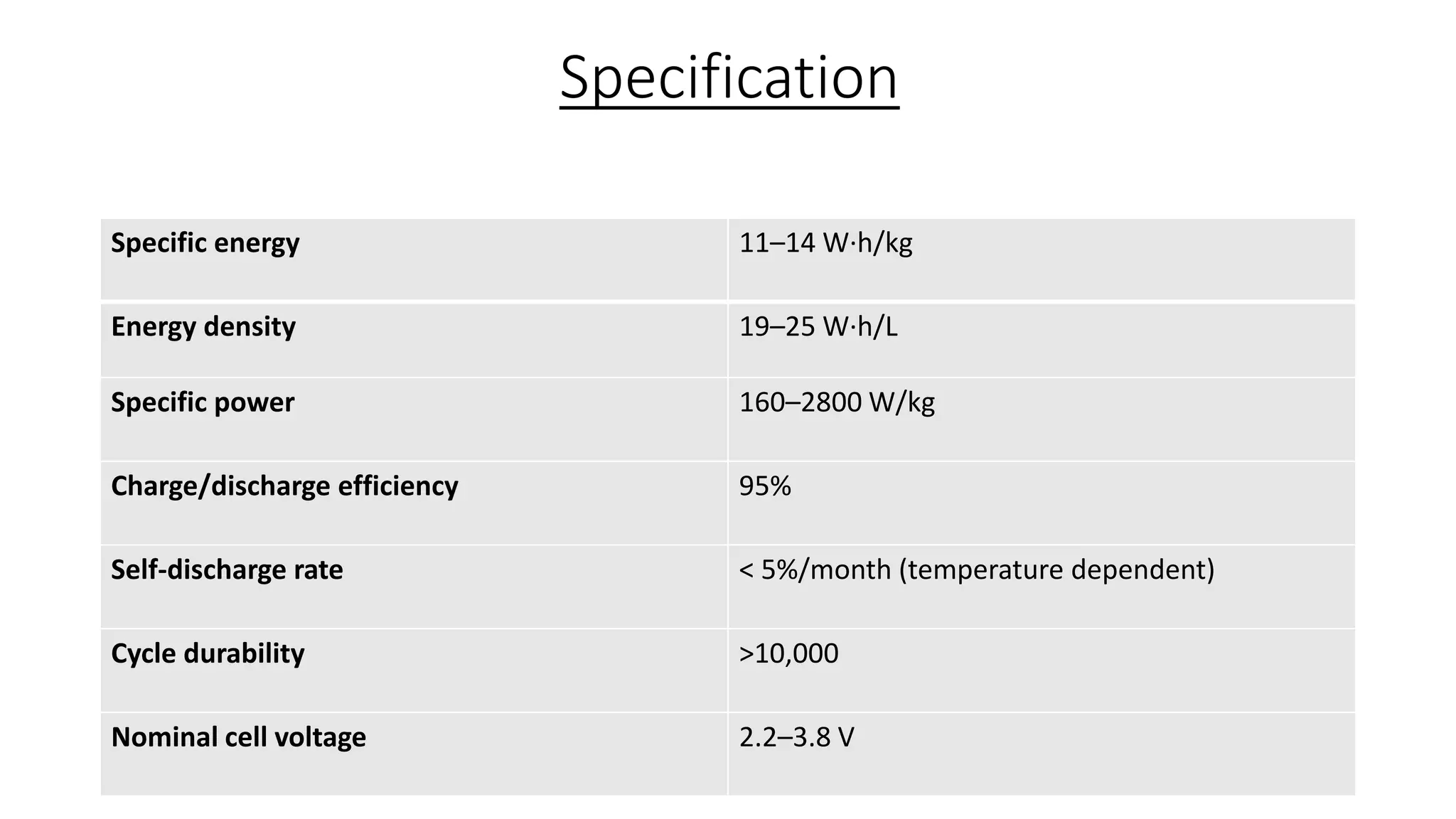
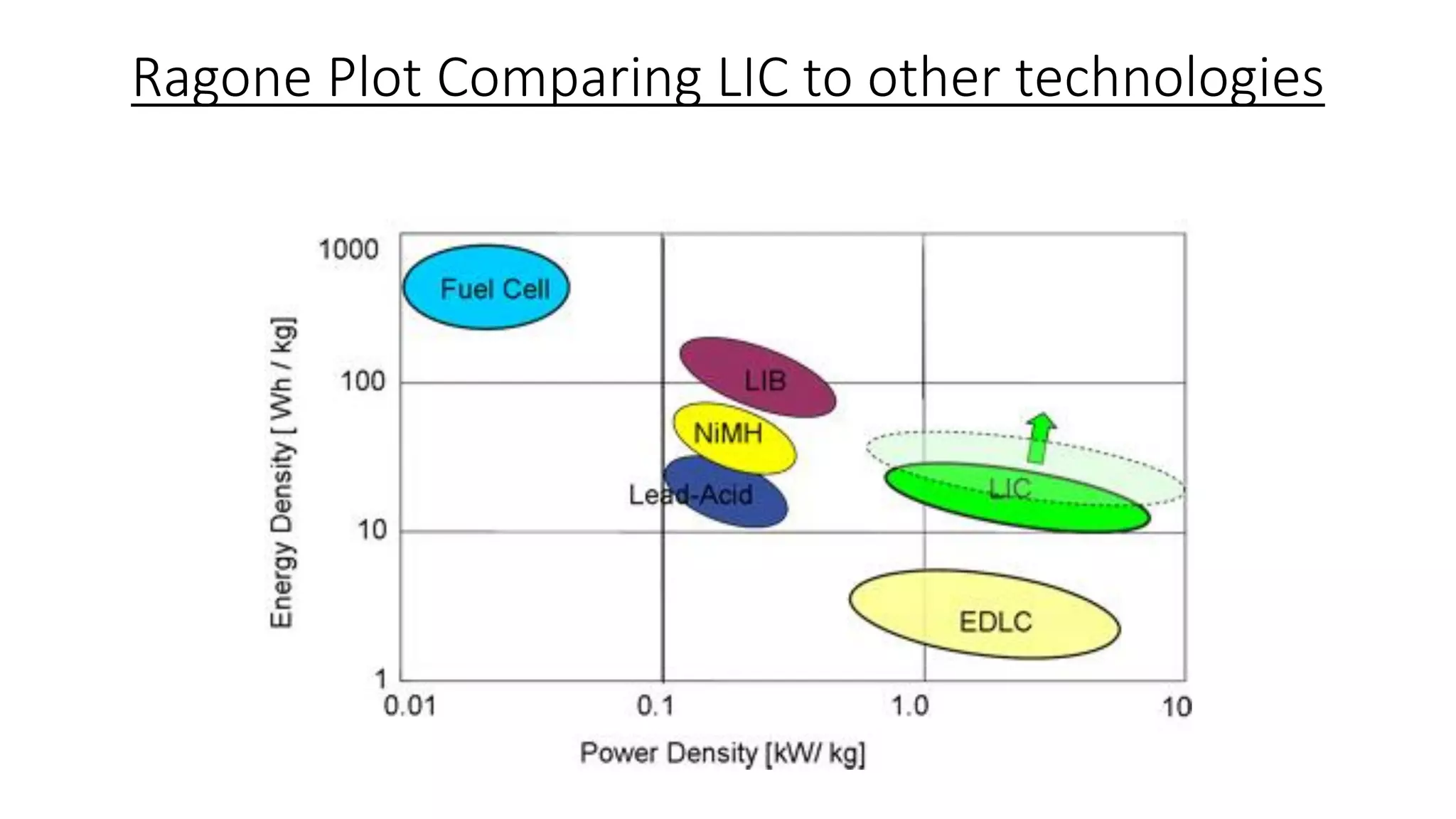
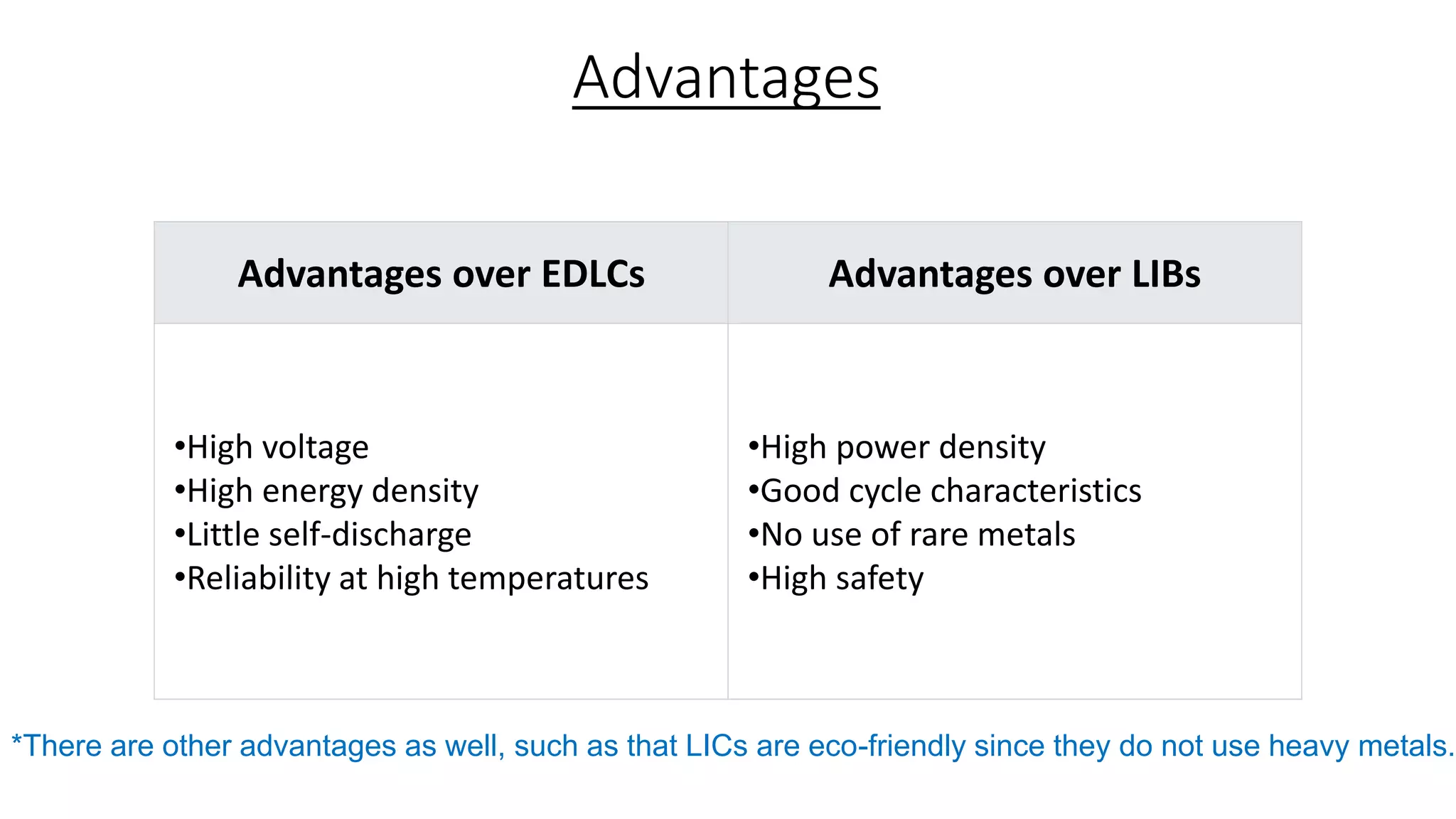
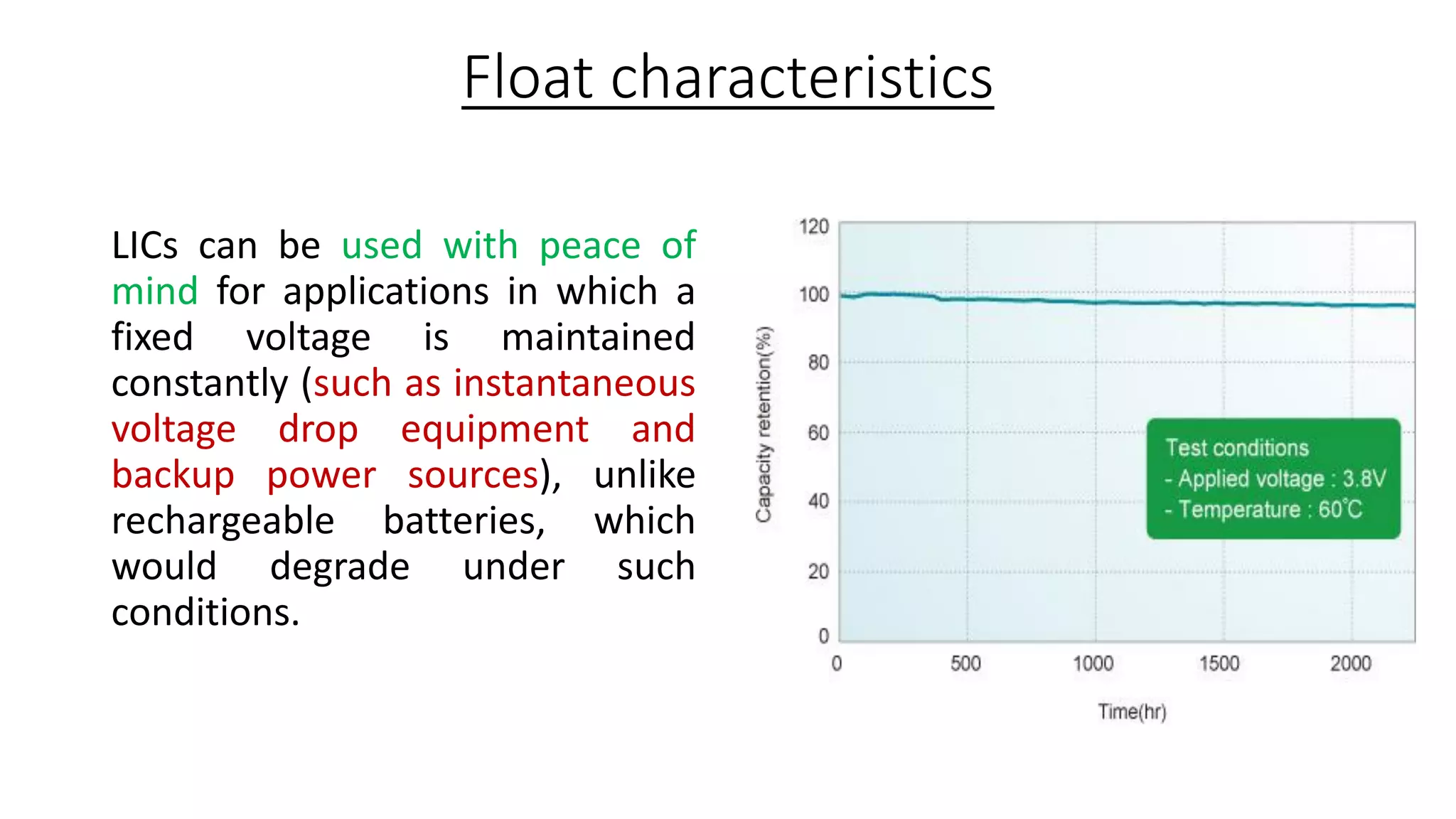
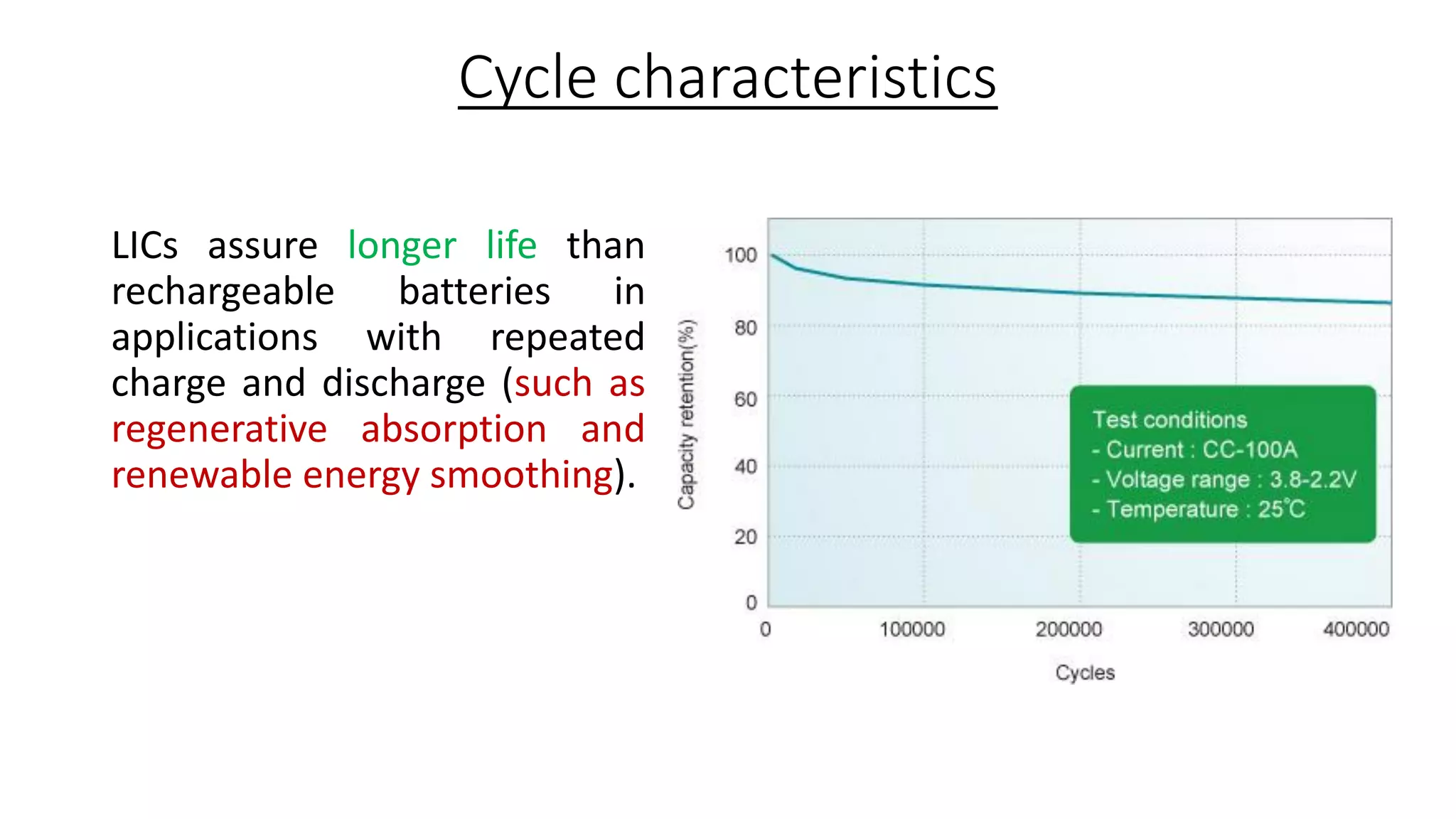
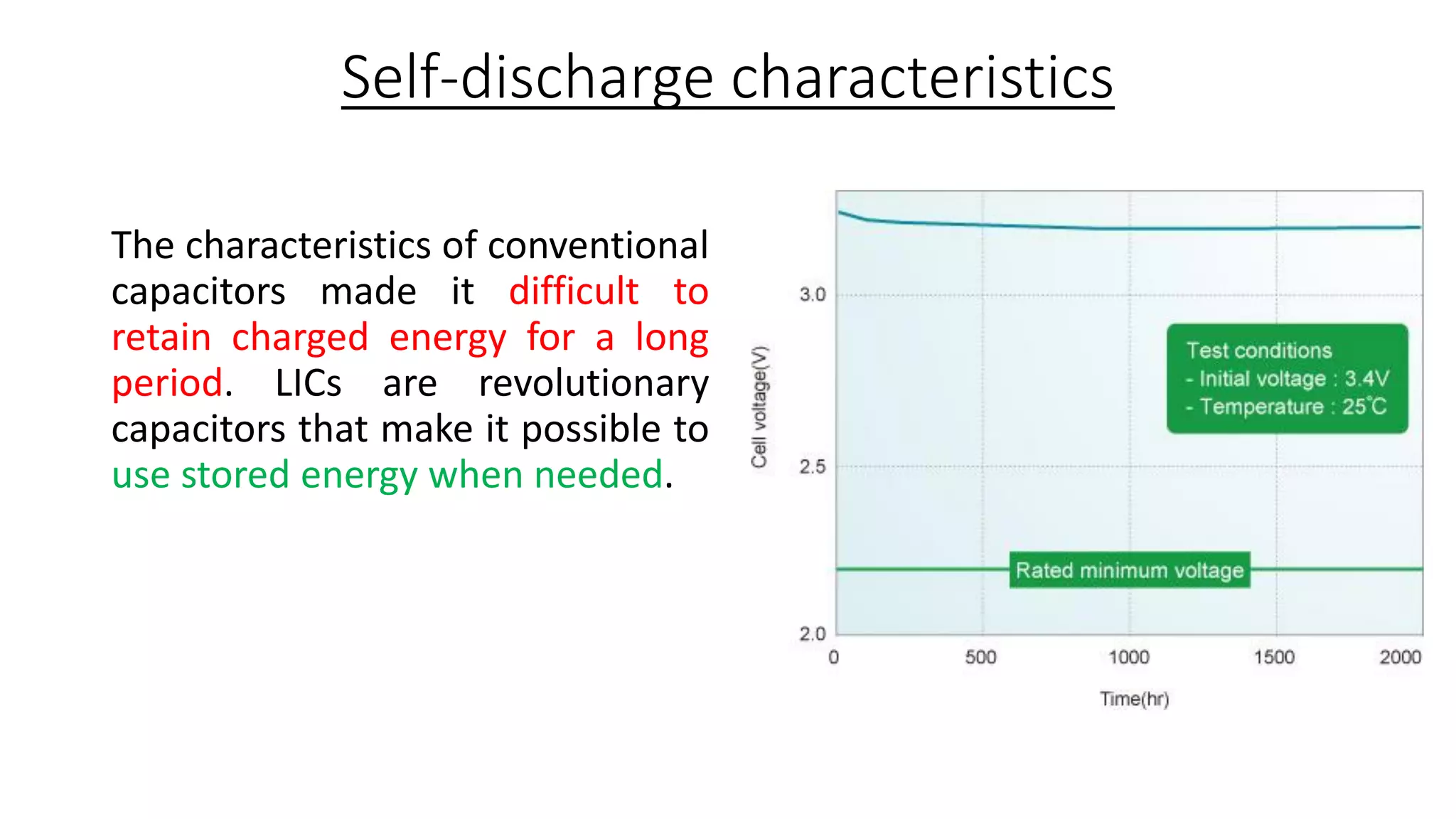
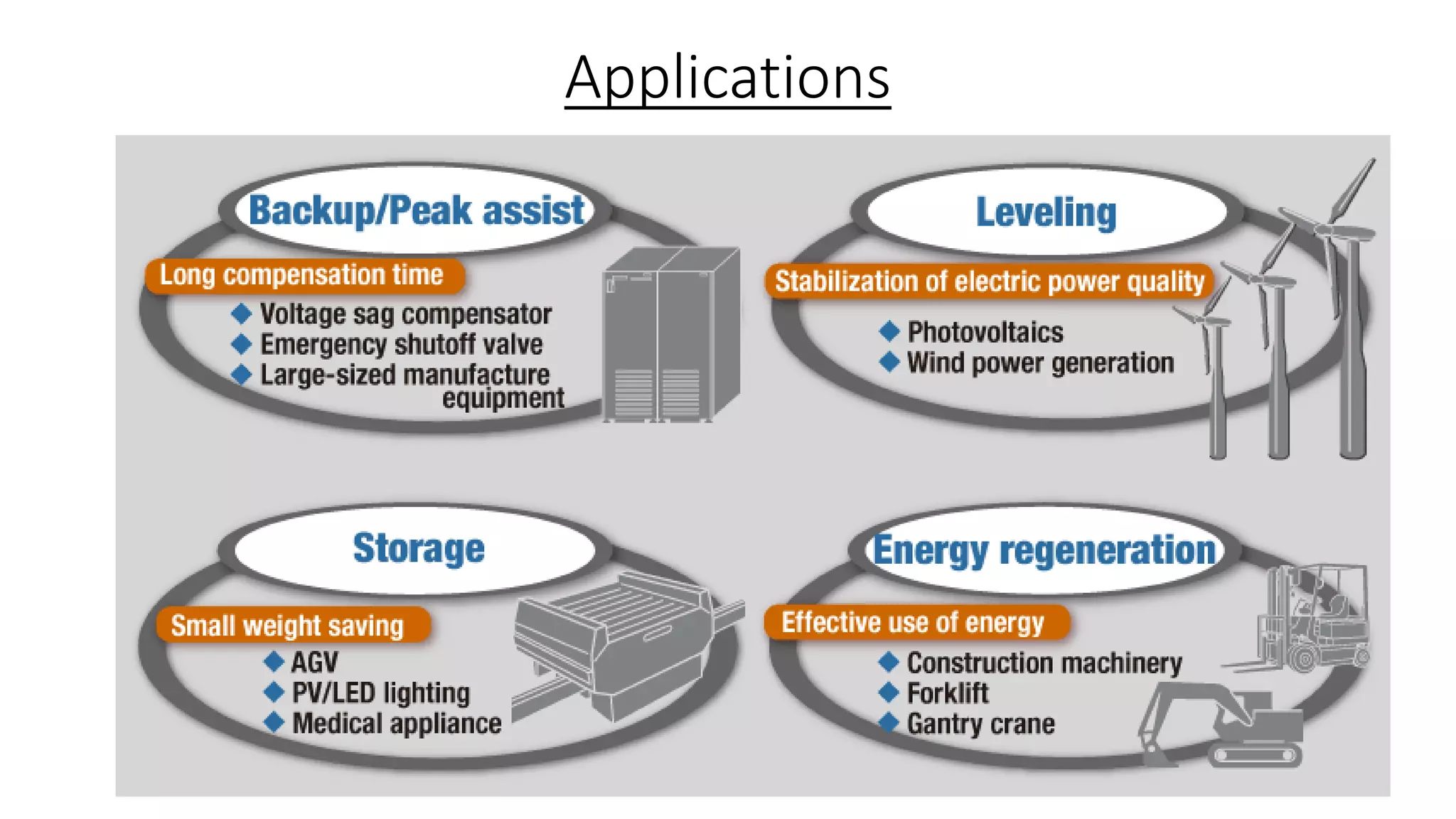
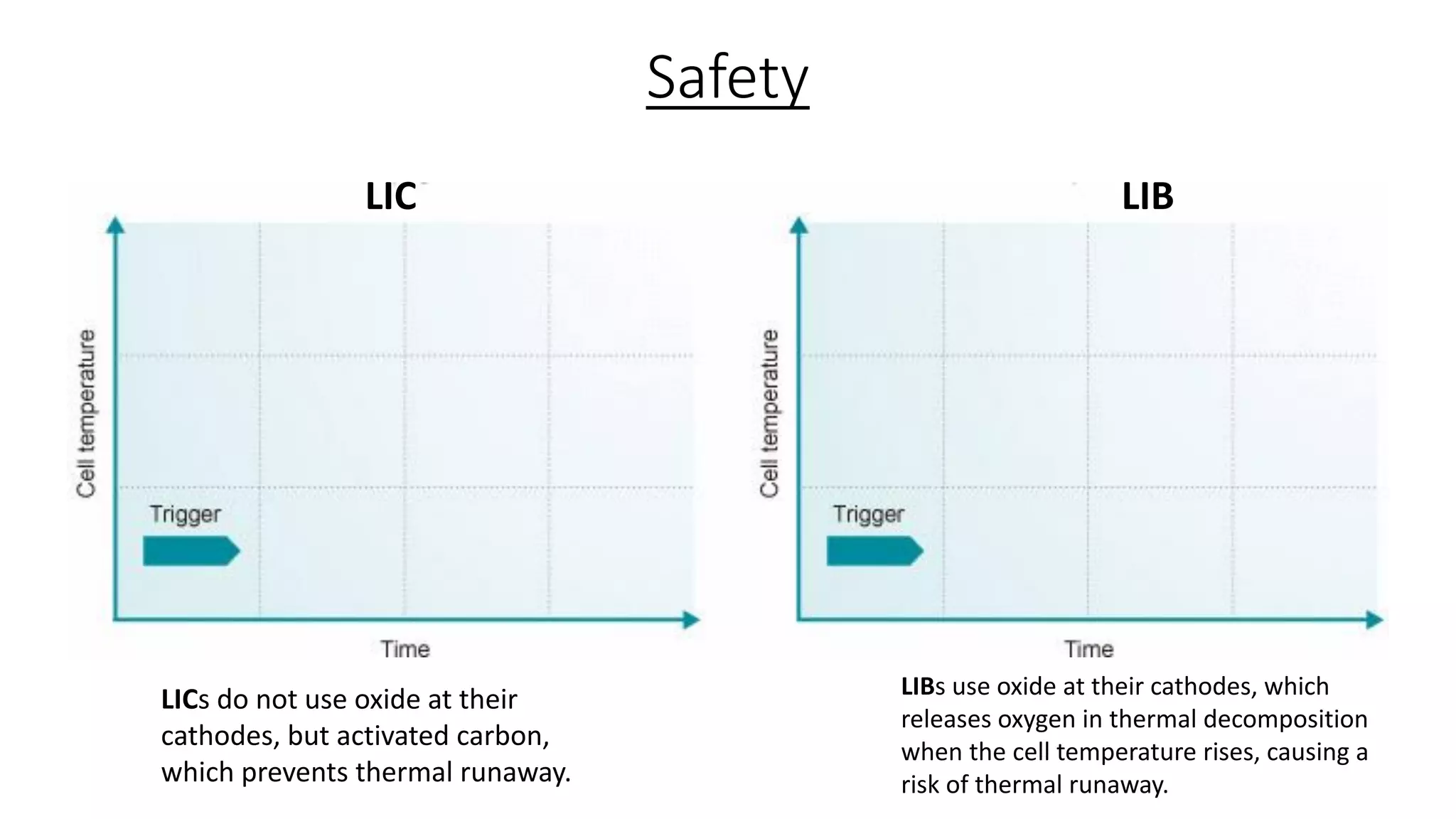
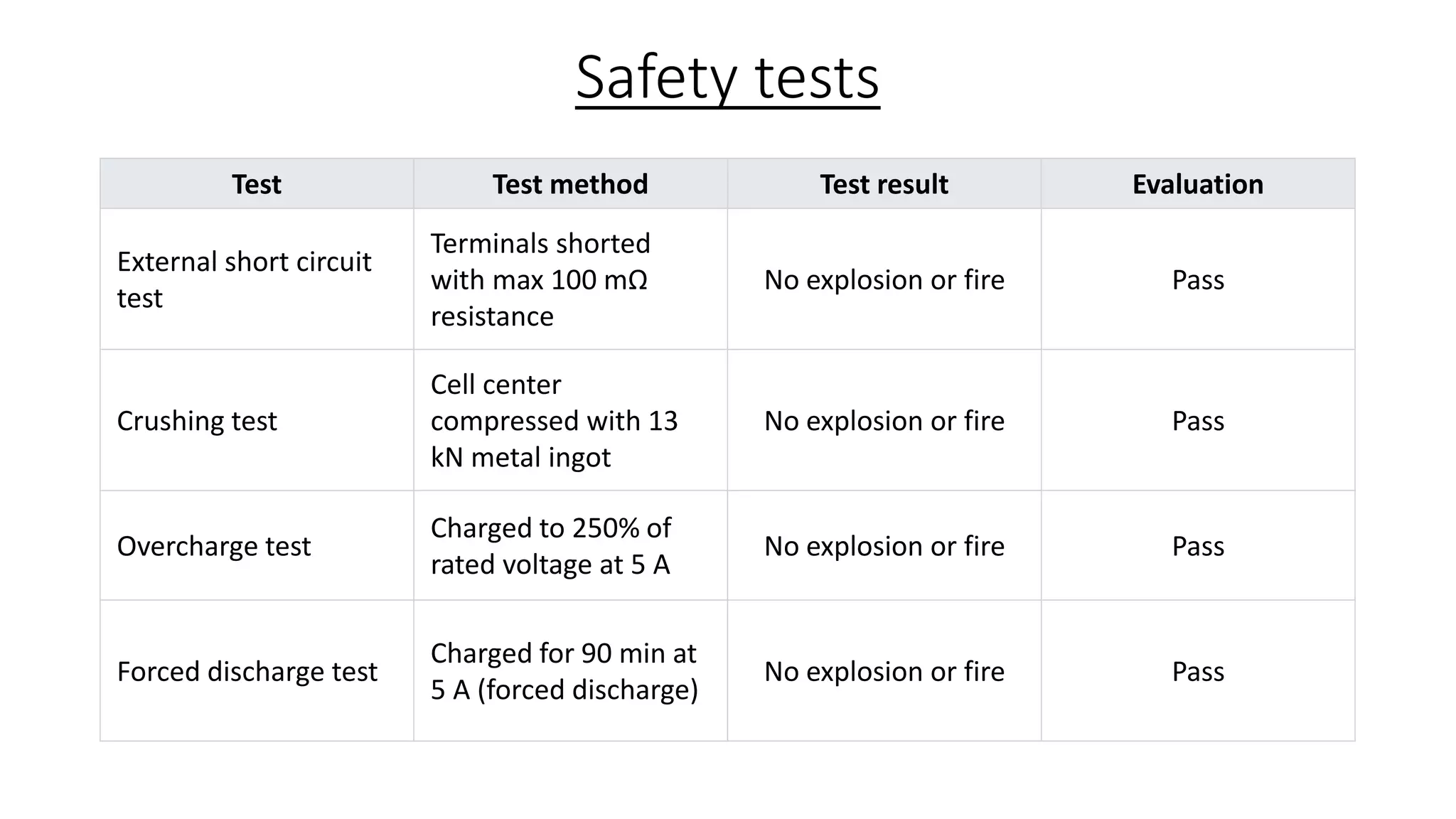
Lithium-ion capacitors (LICs) combine the charge storage principles of electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs) and lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), resulting in a high energy density, high power density, and a reliable performance across a wide temperature range. They exhibit several advantages over traditional EDLCs and LIBs, including high voltage, low self-discharge, and improved safety due to the absence of oxide materials at their cathodes. With applications in areas requiring stable voltage and repeated charging cycles, LICs present a safer and more efficient alternative in energy storage technology.