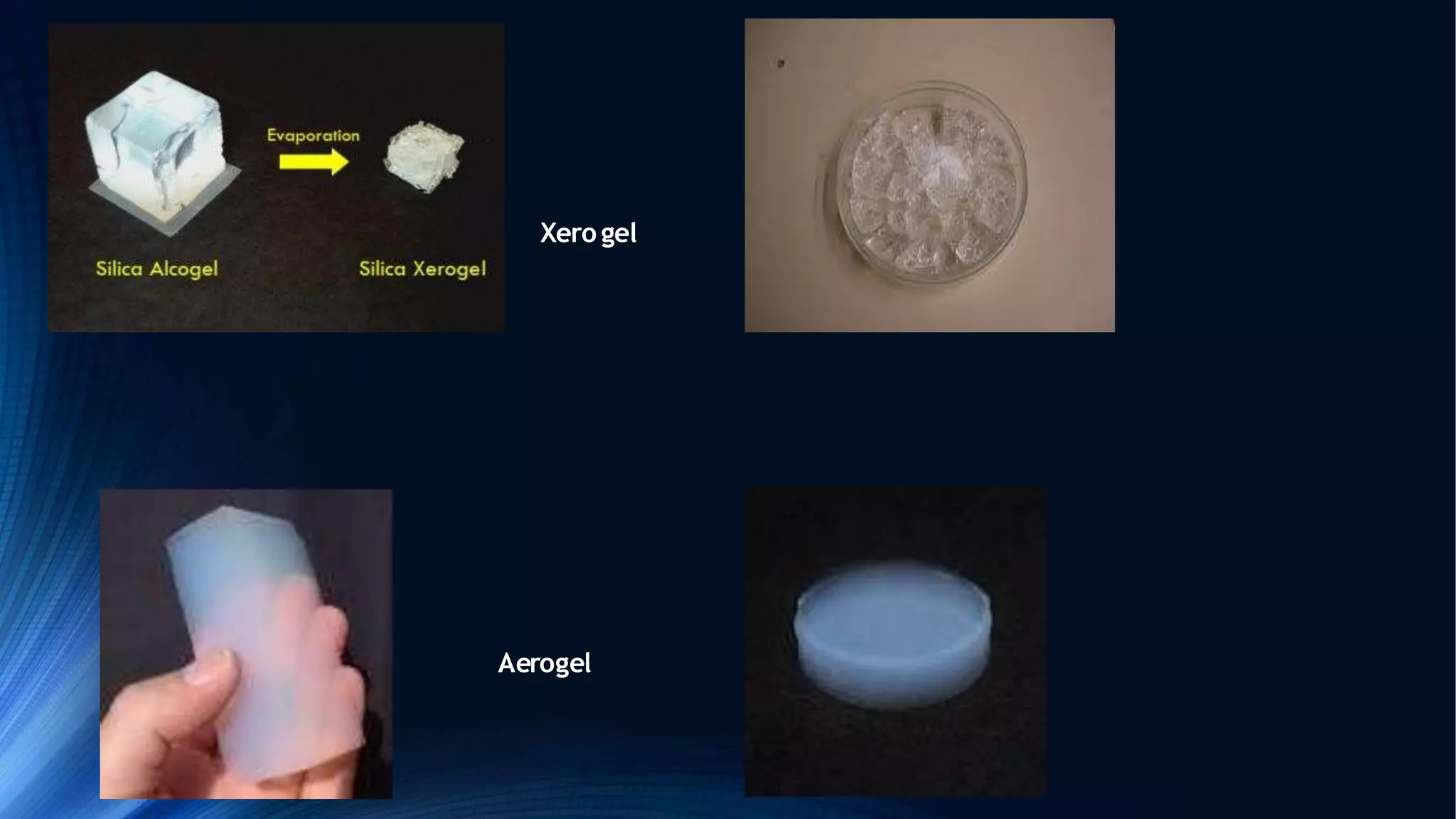
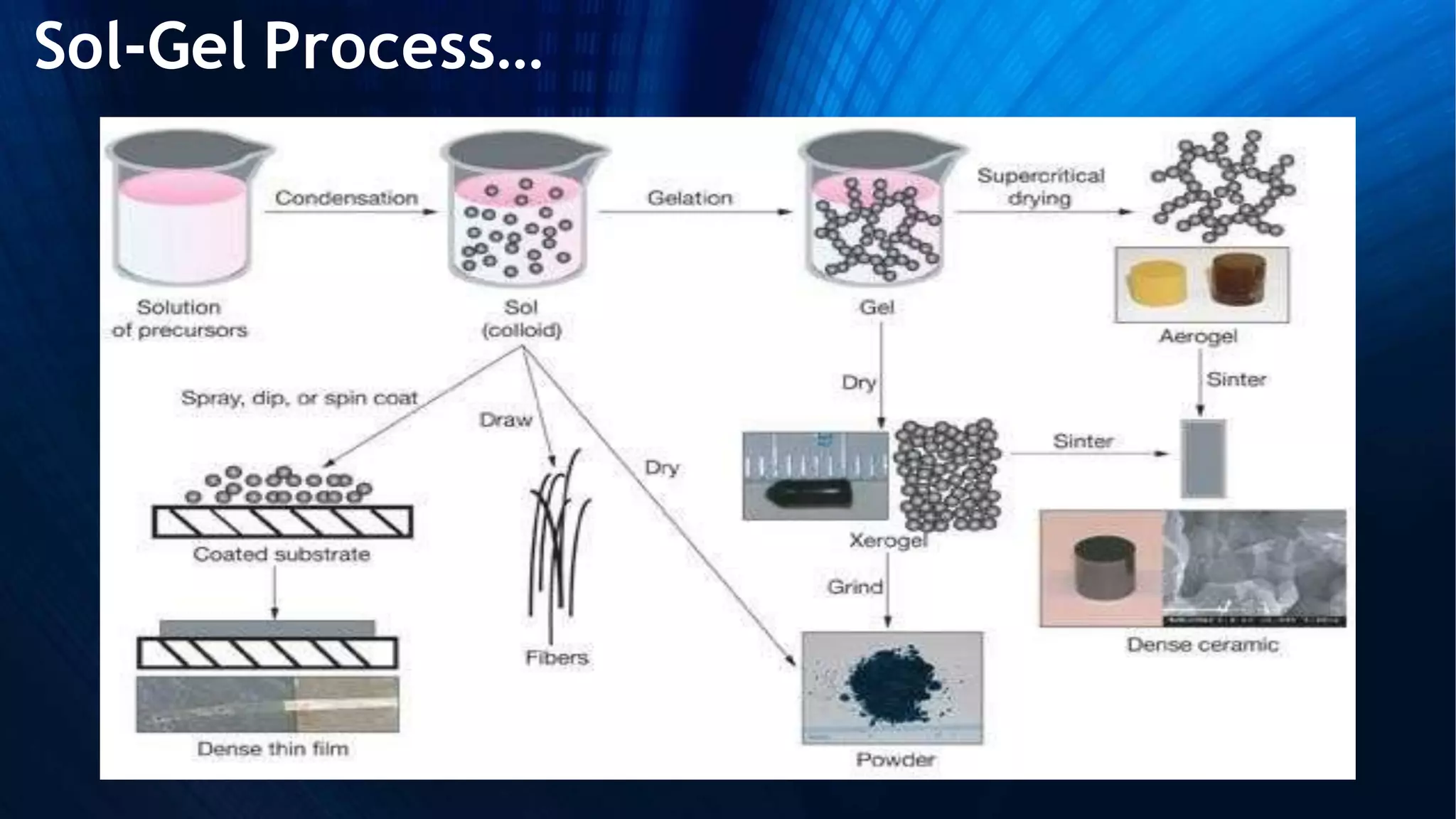
Sol-gel technology is a synthesis method for solid materials using a liquid at low temperatures, allowing for the controlled formation of nanoparticles. The process involves hydrolysis, condensation, gelation, and drying, influenced by factors such as the water to alkoxide ratio and the type of catalyst. Applications range from optical and biomedical uses to electronic and thermal applications, while advantages include the production of high-purity materials and complex shapes, although it has limitations like weak bonding and high permeability.