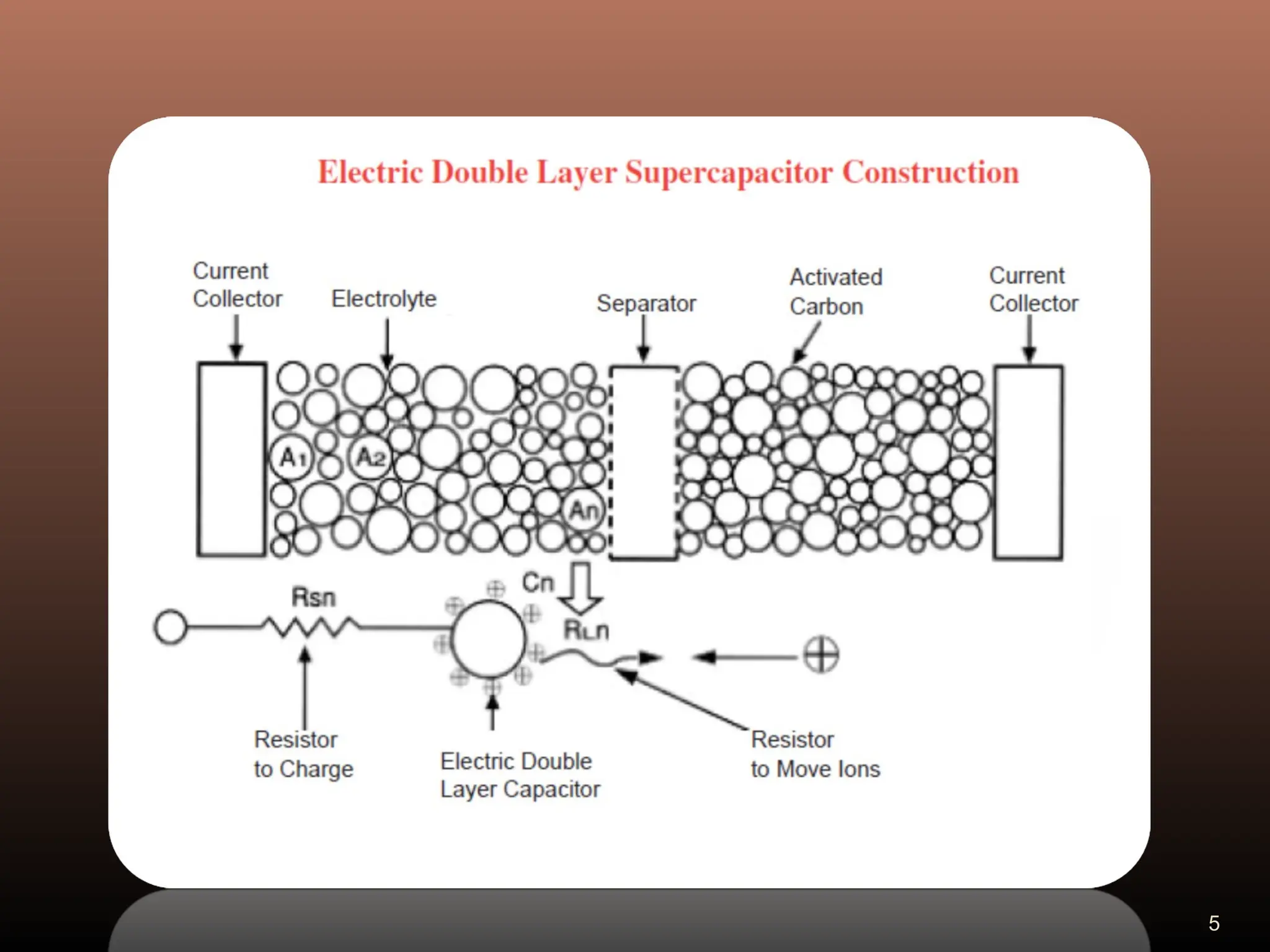
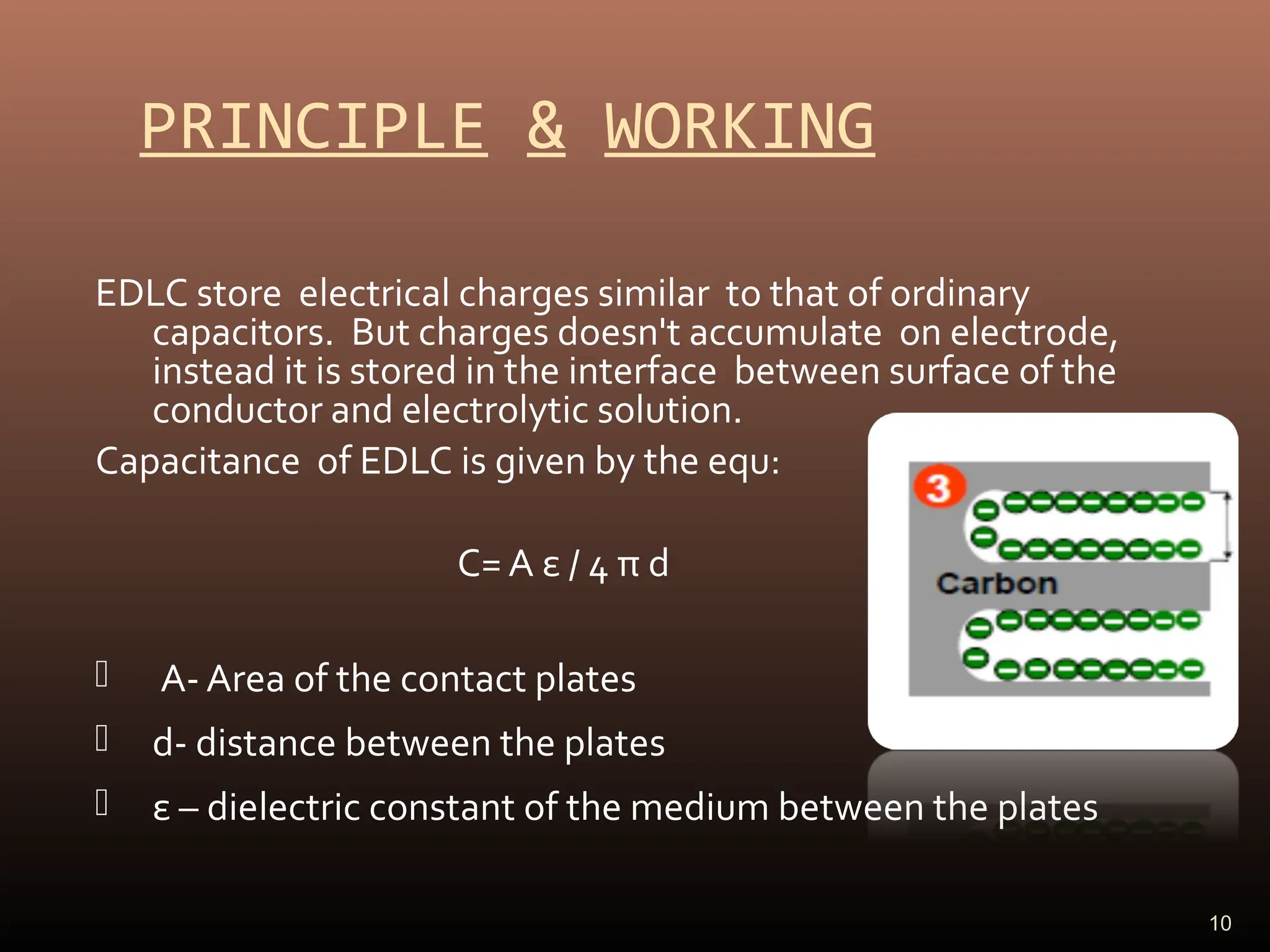
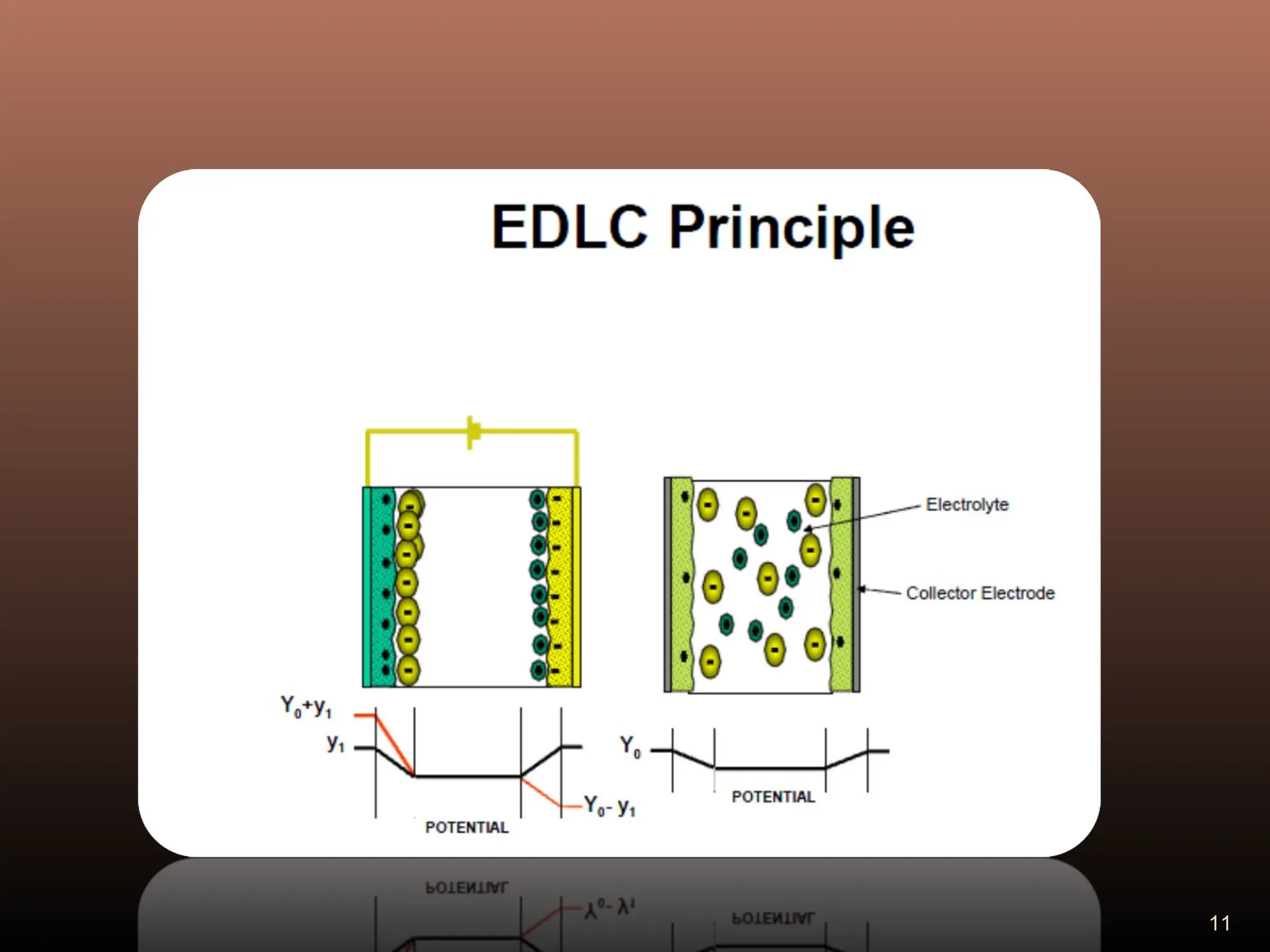
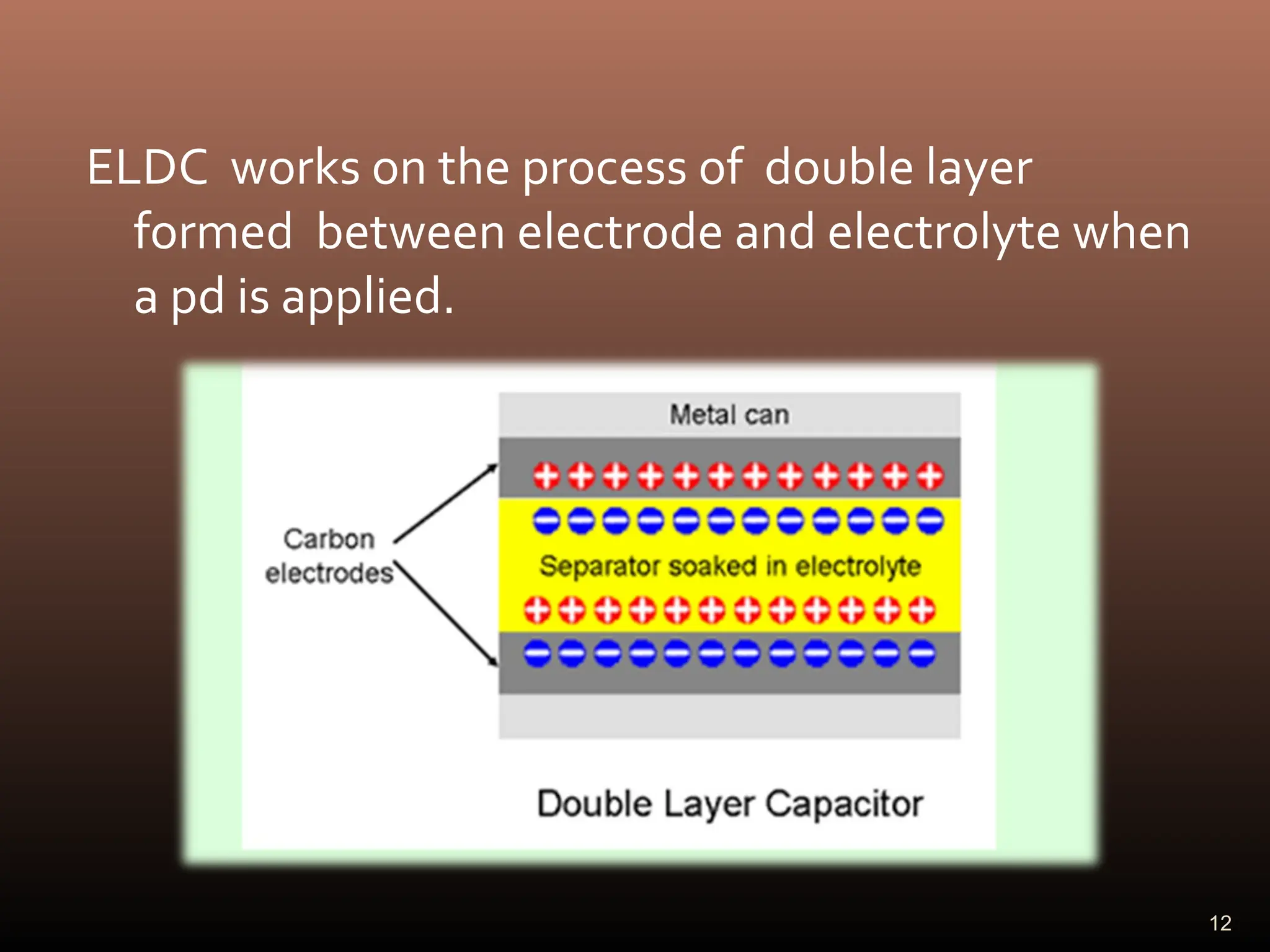
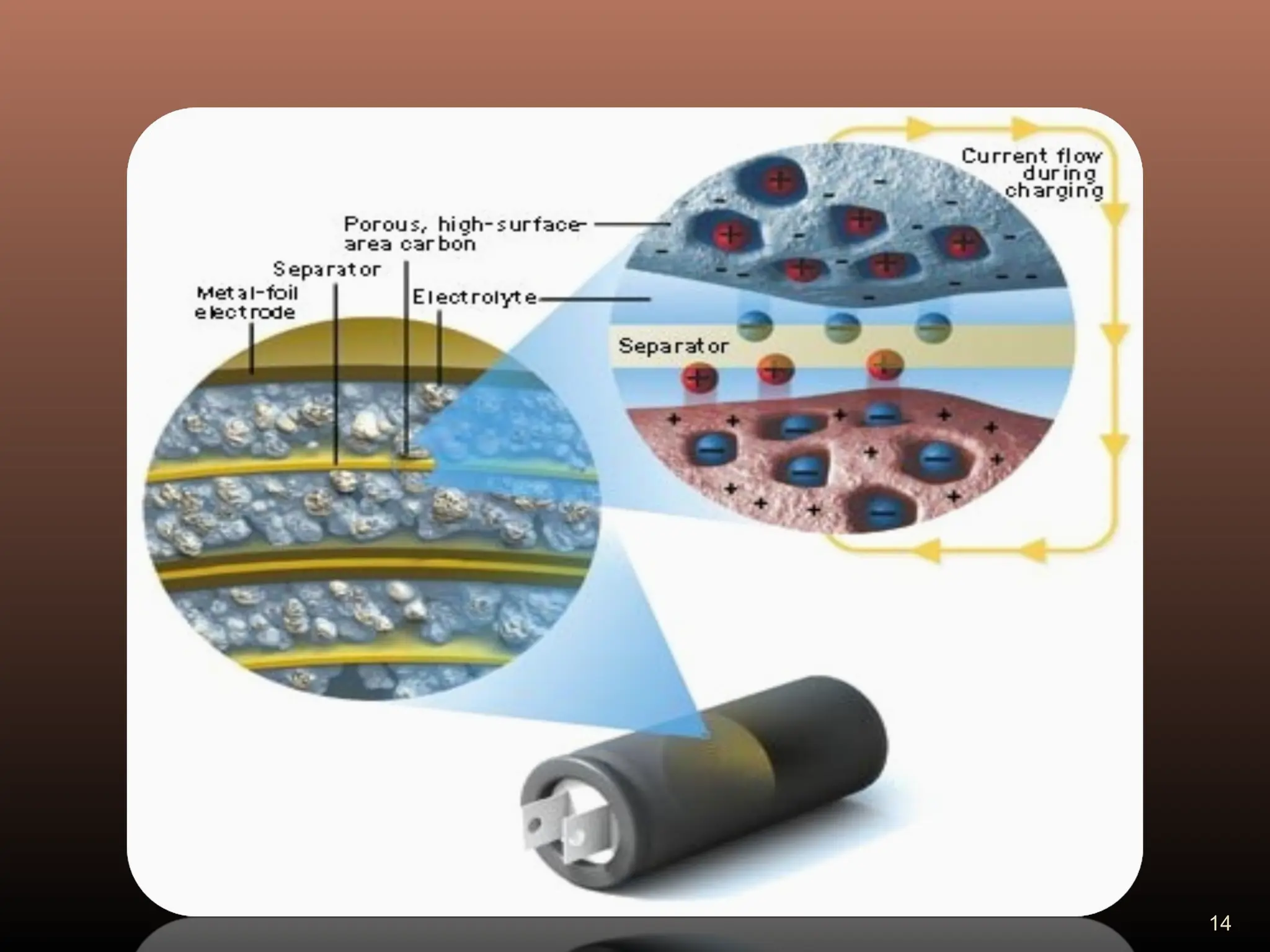
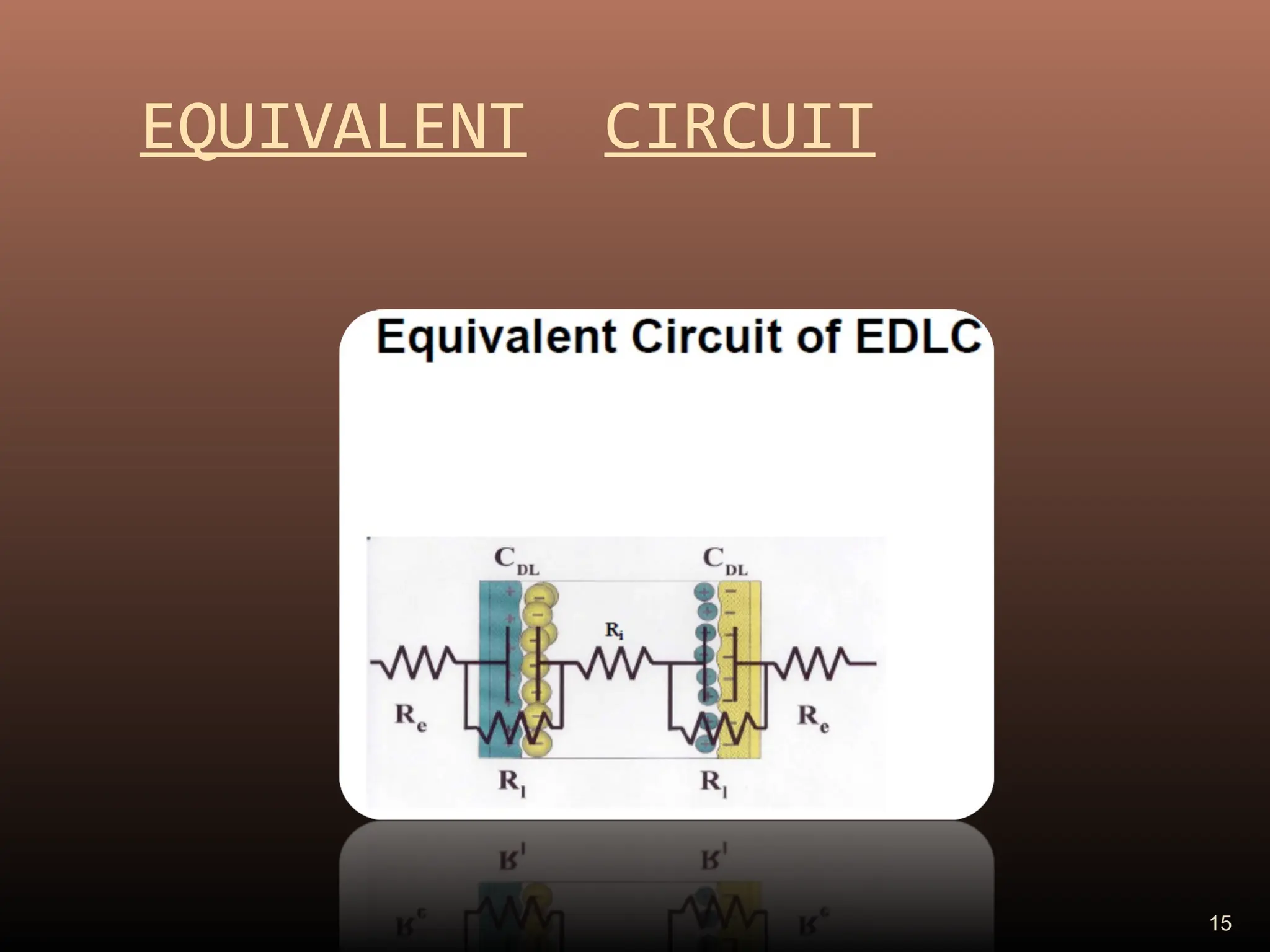
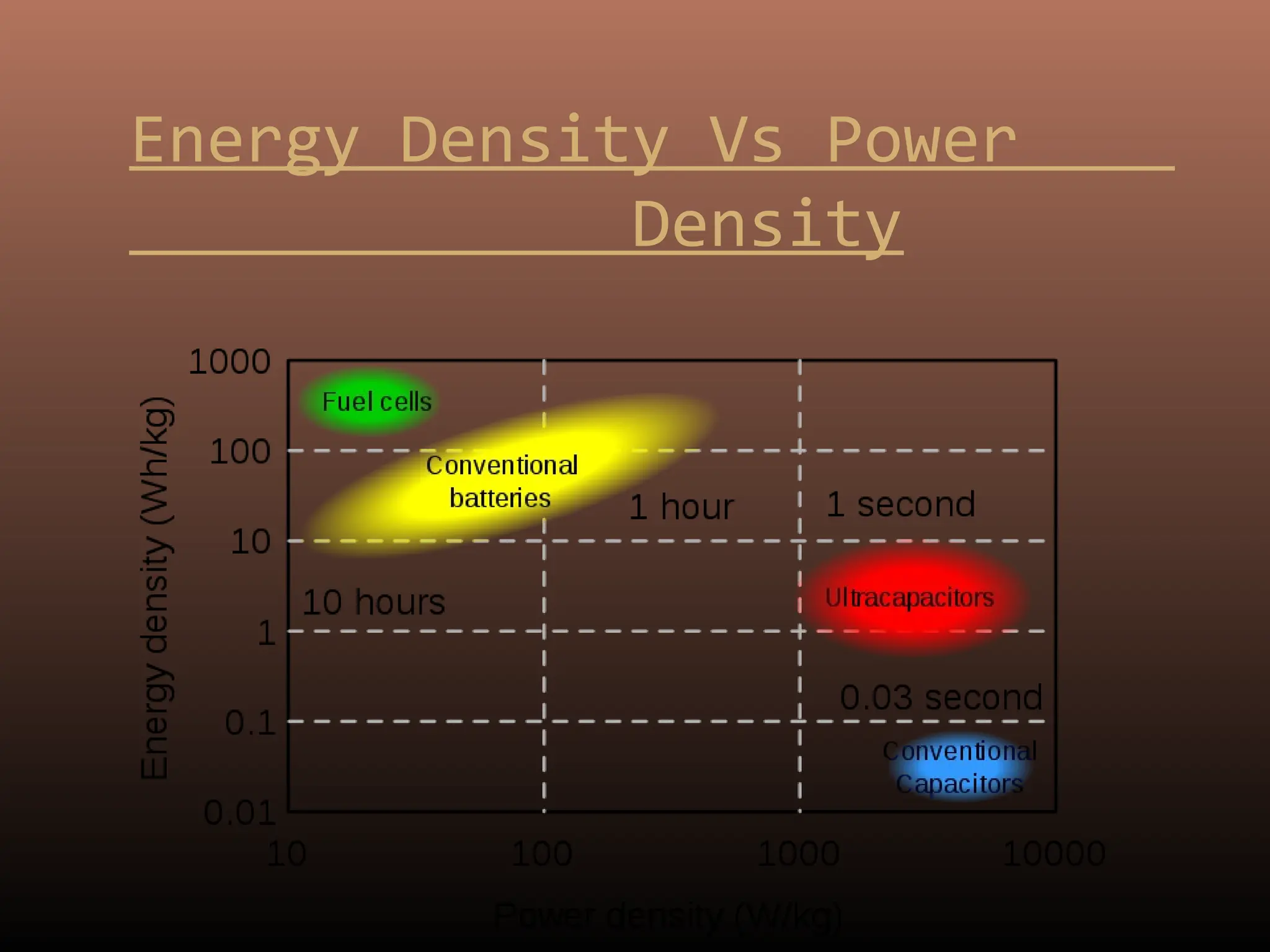
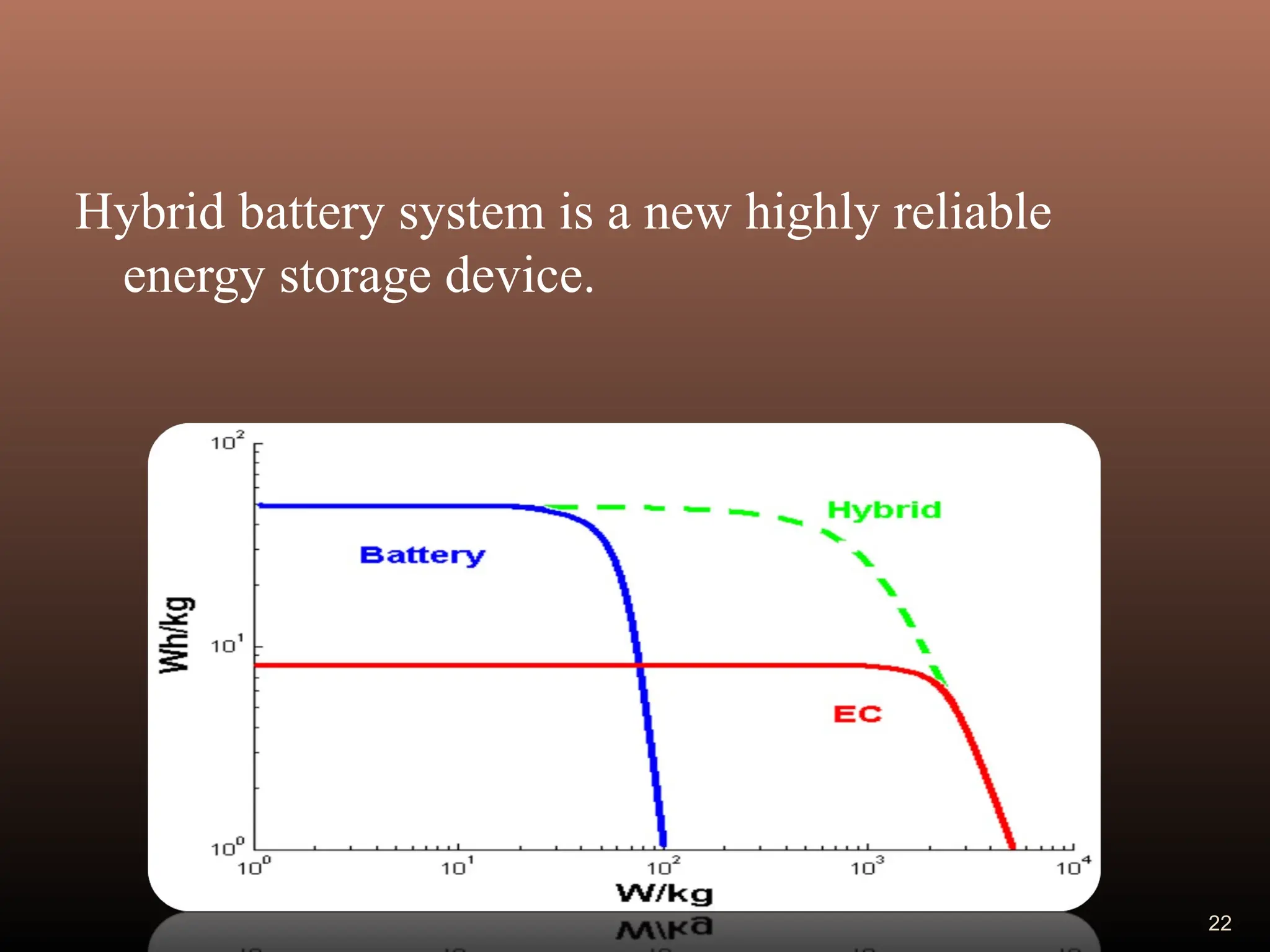
Electric double layer capacitors (EDLCs), also known as supercapacitors or ultracapacitors, store energy through static charges in an electric double layer at the interface between electrode and electrolyte surfaces. They resemble conventional capacitors but have much higher energy density. EDLCs use activated charcoal or carbon nanotubes as electrodes to provide a large surface area for charge storage, and ions in the electrolyte form separated layers of charge on either side of the electrode surfaces when a voltage is applied. While having advantages like rapid charging/discharging and long lifecycles, EDLCs also have lower energy density than batteries. They find applications requiring high power delivery like hybrid vehicles and consumer electronics.