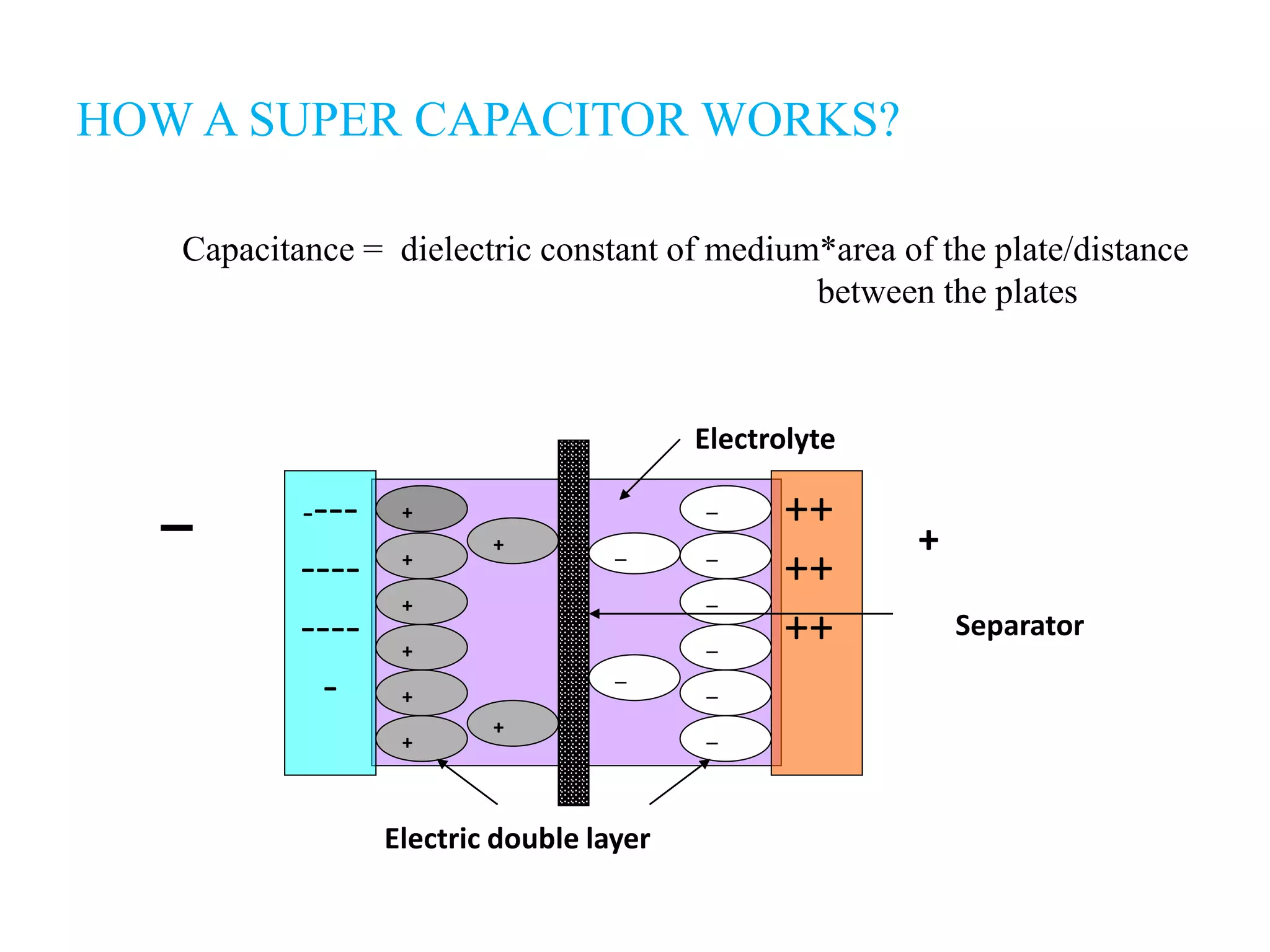
Super capacitors, also known as ultracapacitors, are energy storage devices that can store and release energy faster than batteries. They store energy electrostatically through a process called electric double-layer capacitance. While super capacitors have lower energy density than batteries, they can provide burst of power and undergo hundreds of thousands of charge/discharge cycles. Applications of super capacitors include use in electric buses for rapid charging at stops, diesel engine startups, and as power sources for devices requiring brief high power.