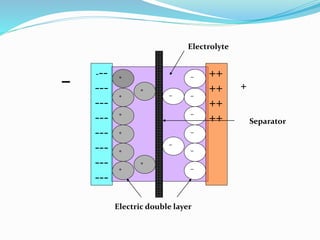
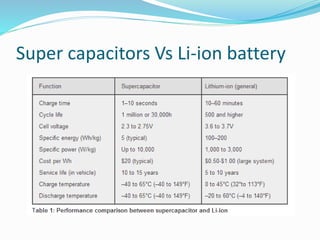
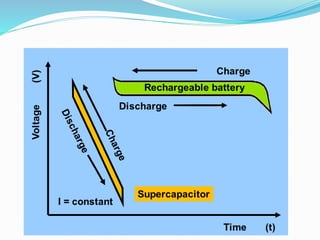
The document discusses the significance of energy storage in transitioning from non-renewable to renewable energy sources, emphasizing the need for improved storage devices. It outlines various types of energy storage technologies including chemical, electrochemical, and thermal methods, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of supercapacitors and lithium-ion batteries. Furthermore, it details the applications, efficiency, and limitations of these storage methods in providing reliable energy supply.