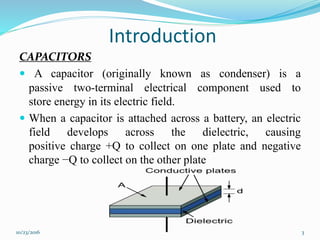
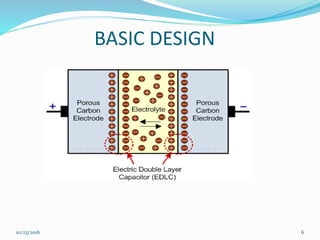
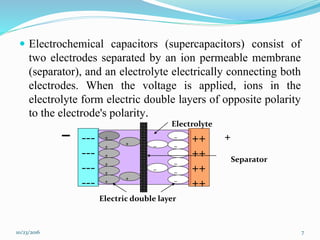
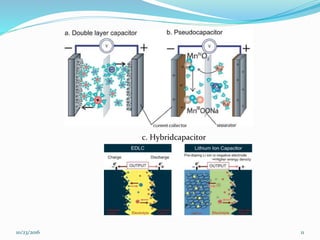
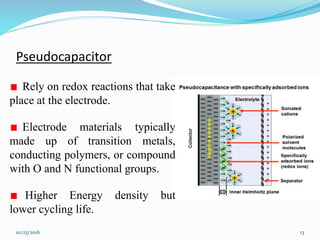
This document discusses supercapacitors, also known as electric double layer capacitors or ultracapacitors. It defines supercapacitors as electrochemical capacitors that can store much higher energy than common capacitors. The document outlines the basic design of supercapacitors, including their electrodes, electrolyte, and separator. It describes the three main types - electrochemical double layer capacitors, pseudocapacitors, and hybrid capacitors - and their charge storage mechanisms. Applications, advantages over batteries, and disadvantages of supercapacitors are also summarized.