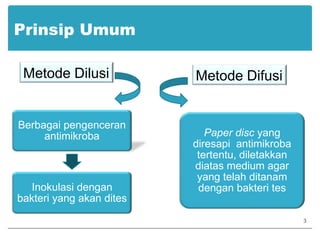
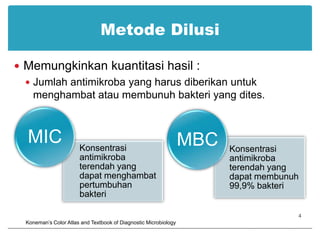
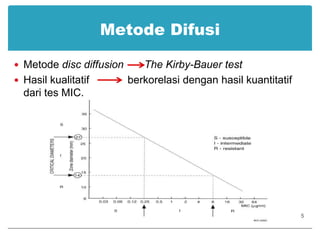
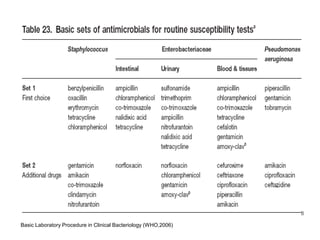
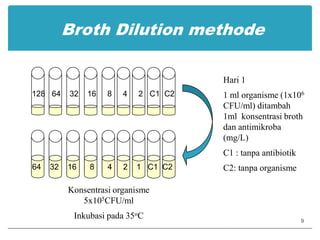
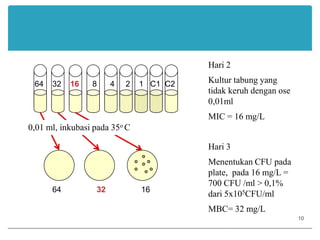
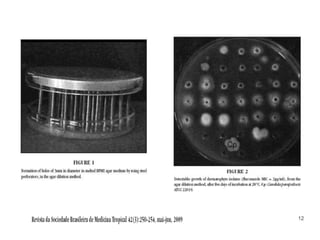
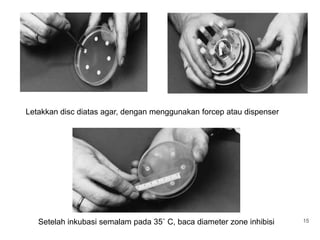
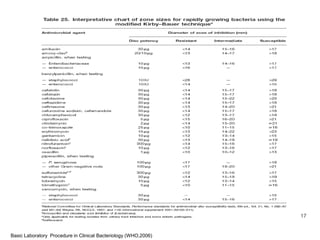
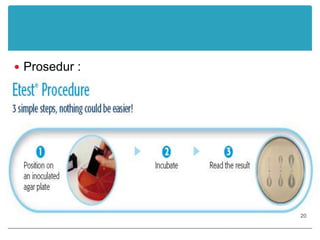
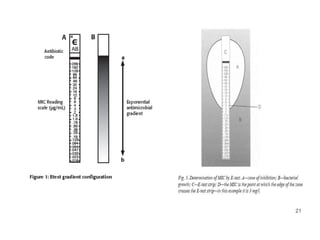
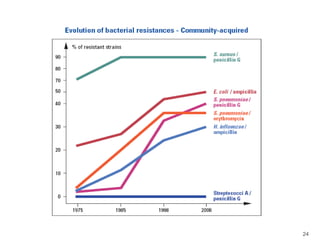
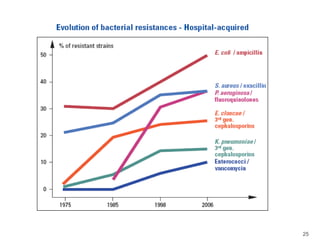
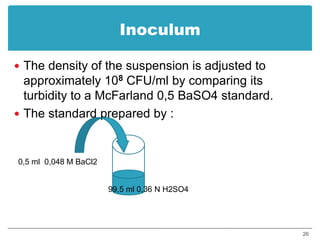
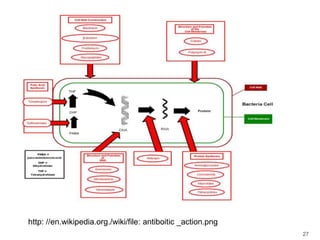
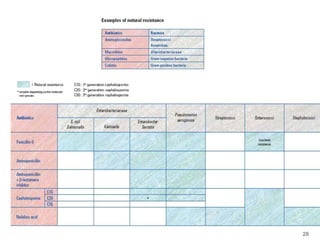
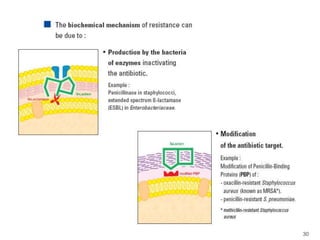
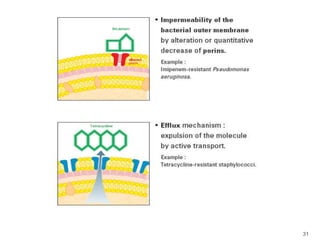
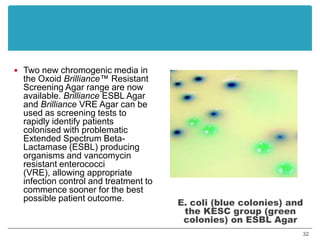
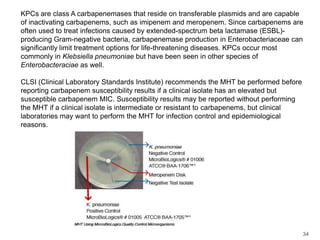
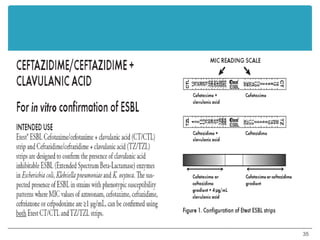
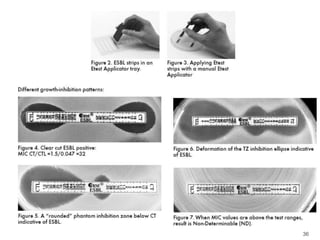
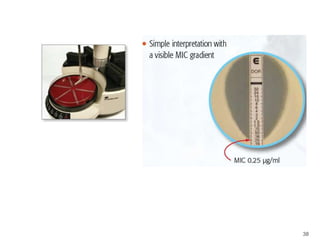
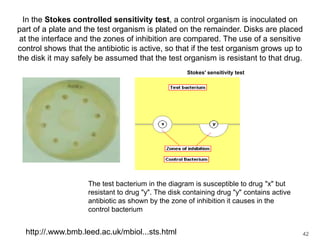
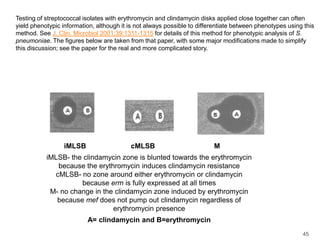
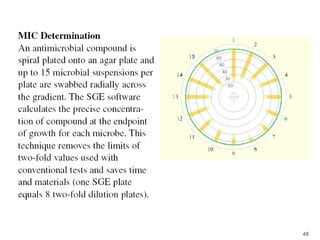
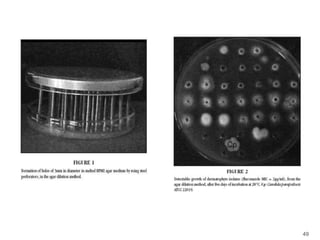
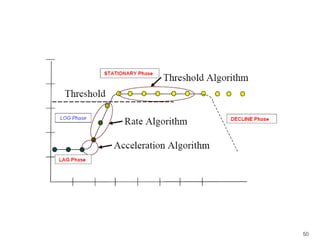
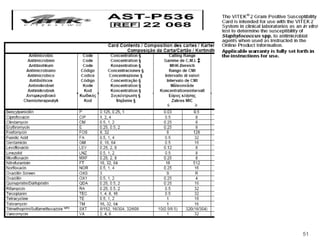
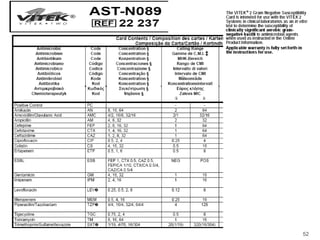
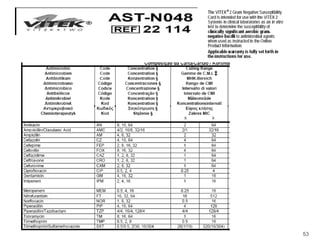
This document provides information about various antimicrobial susceptibility testing methods, including broth dilution, agar dilution, disc diffusion (Kirby-Bauer), and Etest. It discusses preparing bacterial inoculums, selecting antimicrobials, reading results, and factors that can influence zone sizes. Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) and minimum bactericidal concentrations (MBCs) are determined. Chromogenic media can be used to rapidly identify organisms producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamases or vancomycin-resistant enterococci.