This document discusses various classes of antimicrobial drugs, including their mechanisms of action, spectra of activity, and mechanisms of resistance. It focuses on penicillin, cephalosporins, quinolones, and aminoglycosides. The key points are:
1) Penicillin and cephalosporins inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis via competitive inhibition of transpeptidase. Resistance can arise via beta-lactamase production or alterations to penicillin binding proteins.
2) Quinolones inhibit DNA gyrase, blocking DNA replication in bacteria. They are well-absorbed and mainly eliminated by the kidneys.
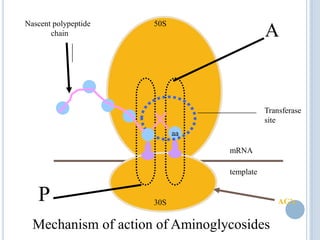
3) Aminoglycosides bind to bacterial ribosomes,