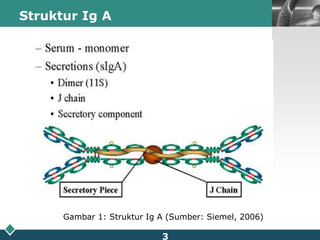
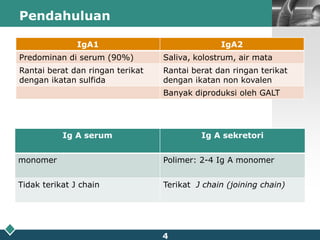
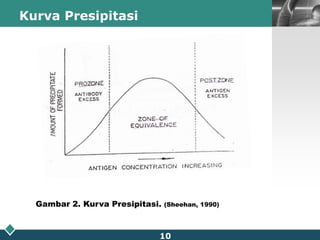
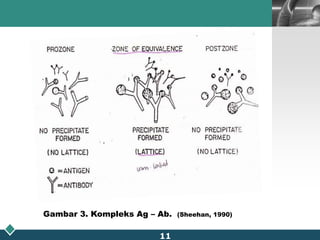
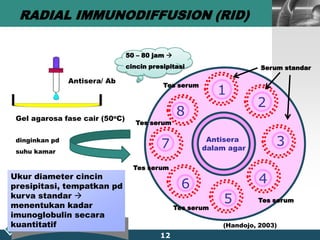
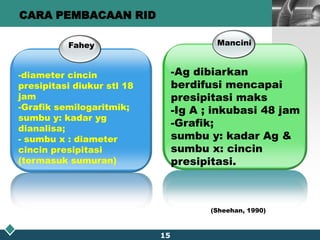
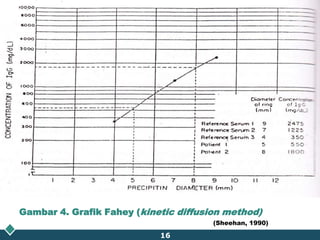
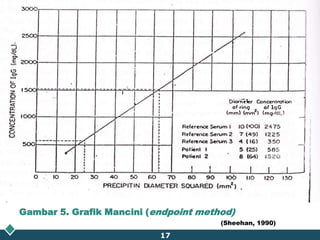
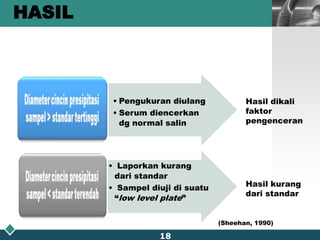
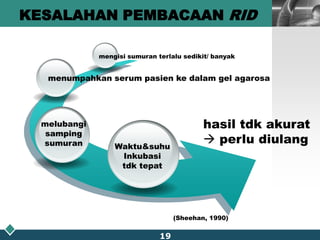
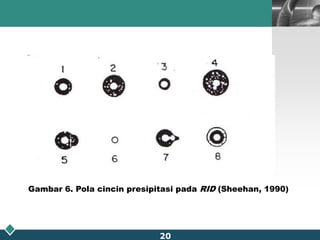
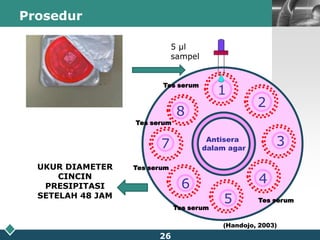
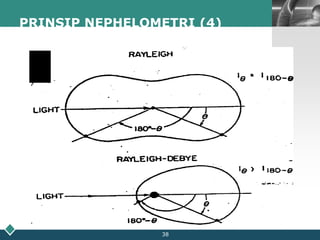
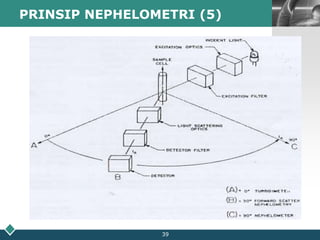
This document summarizes methods for quantitatively determining serum immunoglobulin A (IgA) concentration, including radial immunodiffusion (RID), nephelometry, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). RID involves measuring the diameter of precipitation rings formed between serum IgA and antibody-containing agar. Nephelometry measures light scatter from immune complexes formed between serum IgA and anti-IgA antiserum. ELISA uses a capture antibody to bind serum IgA and a labeled secondary antibody for detection. ELISA provides the best sensitivity while nephelometry is most commonly used in clinical labs due to its rapid automation capabilities. Normal IgA levels, deficiencies, and causes of high values are also