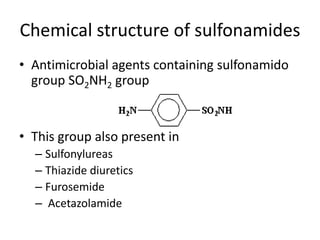
Sulfonamides are antimicrobial agents containing a sulfonamide group. Domagk discovered their efficacy in 1938 by inhibiting the growth of streptococci with prontosil. Sulfonamides work by competing with para-aminobenzoic acid to inhibit dihydrofolic acid synthesis. They are classified based on duration of action and are used to treat various bacterial, protozoal, and chlamydial infections. Common adverse effects include gastrointestinal issues, hematological toxicity, hypersensitivity, and renal toxicity. Trimethoprim is a diaminopyrimidine that also inhibits dihydrofolic acid synthesis and has synergistic effects when combined with sulfonamides in co-tri