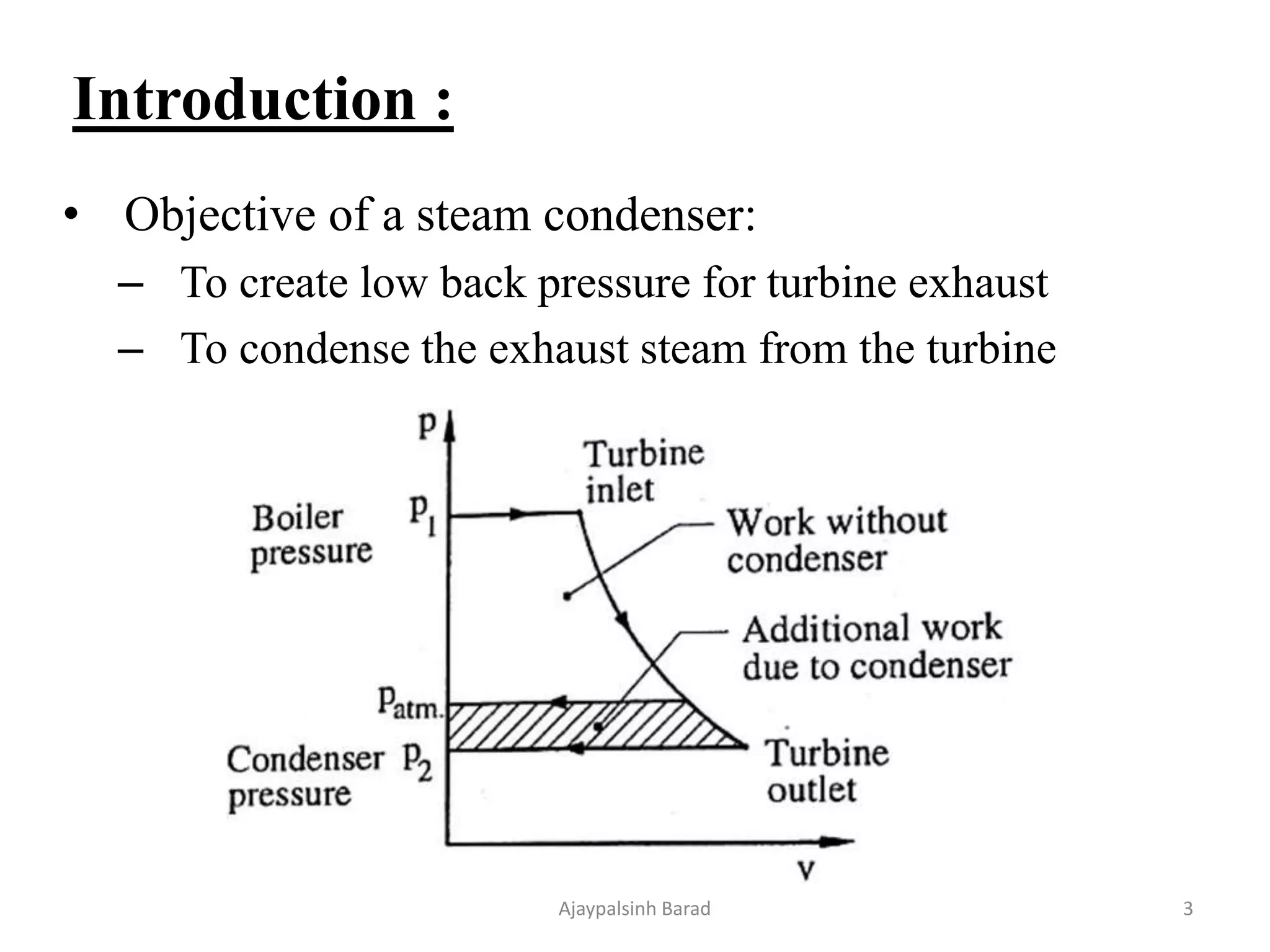
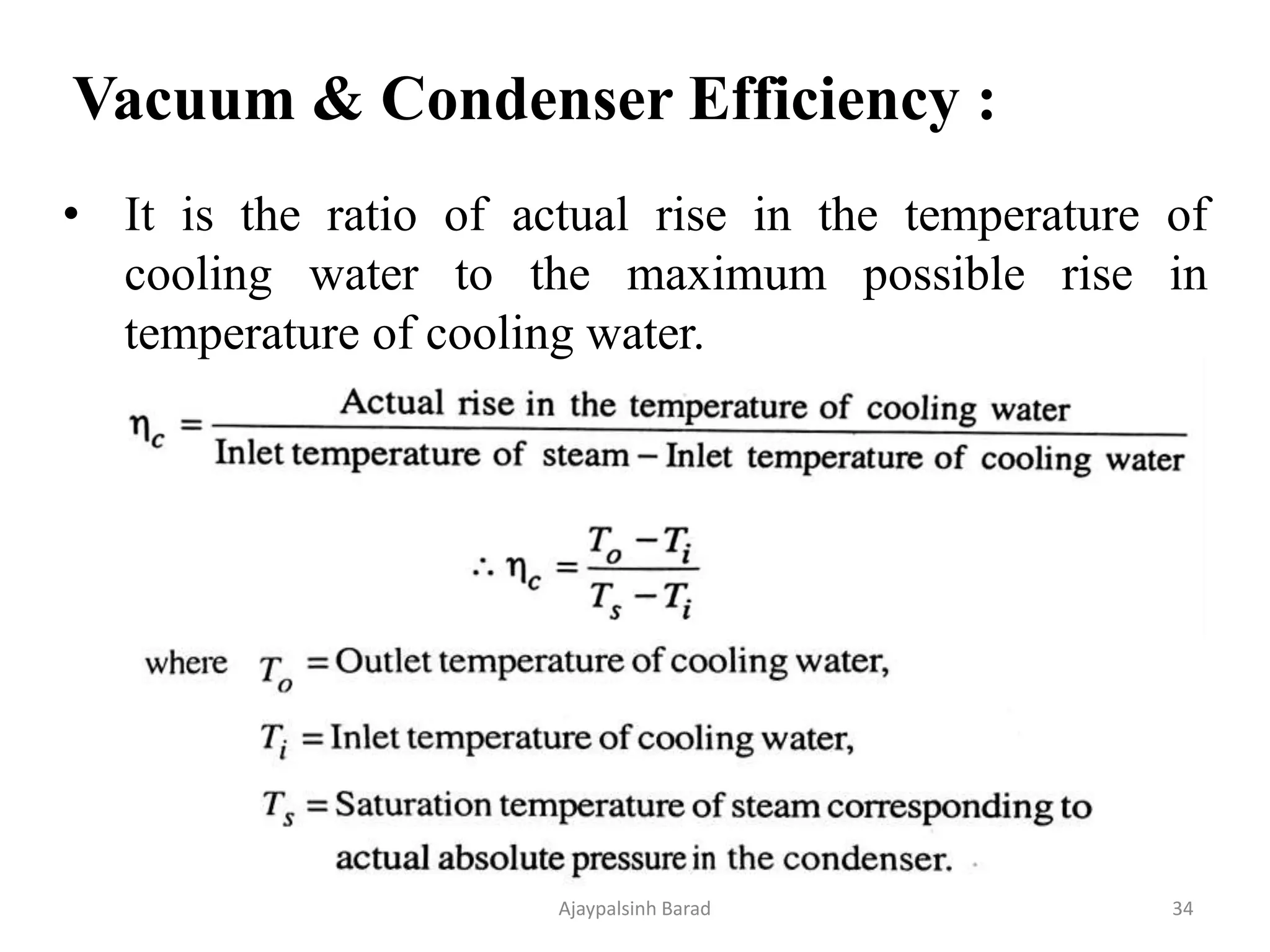
The document outlines various aspects of condensers and cooling towers in power plant engineering, including types of condensers (jet and surface), their advantages and disadvantages, and the necessity of cooling ponds and towers for effective heat management. It also discusses the impact of air leakage on condenser efficiency, methods to maintain vacuum, and the differences between open and closed cooling systems. Lastly, it compares different cooling tower designs and the respective cooling ponds, emphasizing efficiency, costs, and operational considerations.