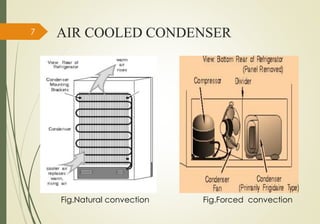
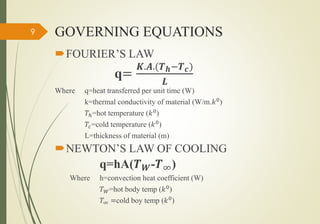
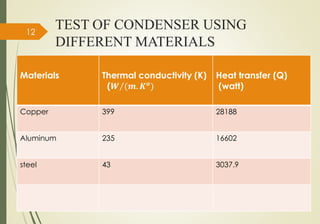
This study examines different types of condensers used in refrigerants. It discusses air cooled and water cooled condensers. Air cooled condensers can use natural or forced convection, while water cooled condensers include tube-in-tube, shell-and-coil, and shell-and-tube designs. The study tests different materials for condensers, finding that copper has the highest thermal conductivity and best heat transfer, followed by aluminum and steel. The objective is to select the best material for a condenser by considering factors like thermal conductivity and heat transfer performance.