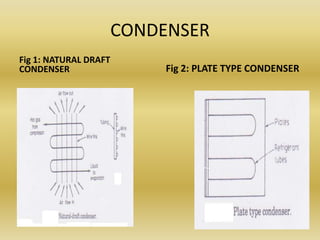
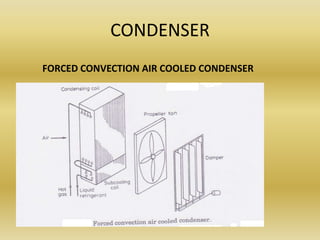
The condenser transfers heat from the refrigerant vapor to the air or water. It removes heat from the refrigerant vapor leaving the compressor, causing the refrigerant to condense from a vapor to a liquid. This liquid refrigerant can then provide cooling in the evaporator. Common types of condensers include air-cooled condensers, which use natural convection or forced convection of air across finned tubes to remove heat, and water-cooled condensers.