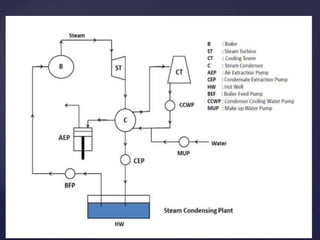
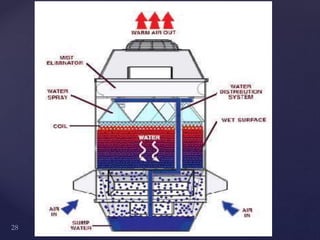
1. A steam condenser converts low pressure exhaust steam from a turbine into water using cooling water circulated from a cooling tower.
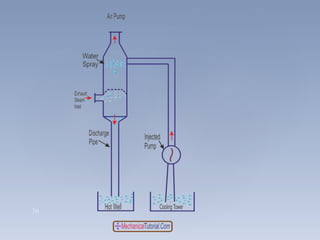
2. The key components of a steam condensing plant include the condenser vessel, pumps to extract condensate and air, a hot well, boiler feed pump, cooling tower, and cooling water pump.
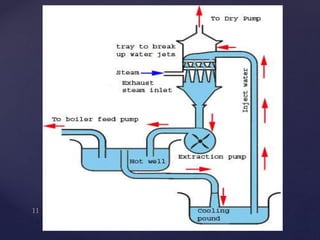
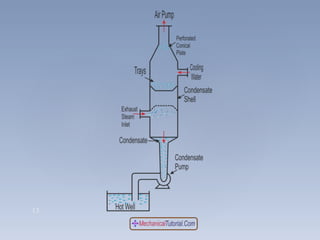
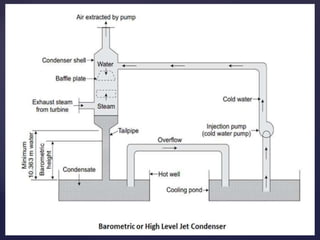
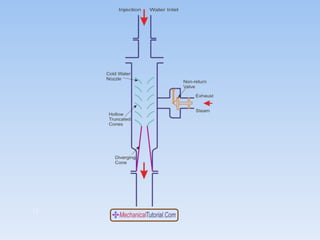
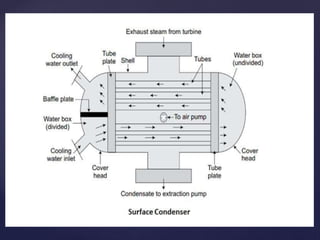
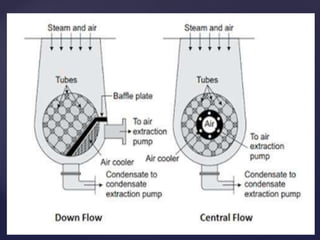
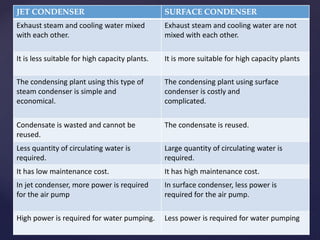
3. There are two main types of steam condensers - jet condensers where steam and cooling water mix, and surface condensers where they do not mix. Surface condensers are more suitable for high capacity plants.