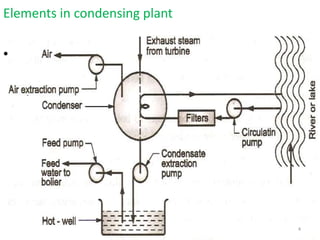
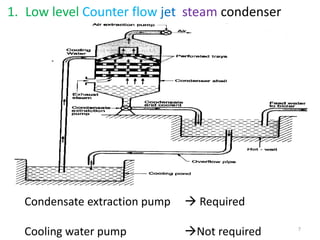
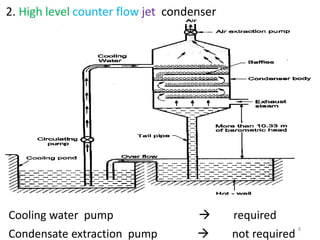
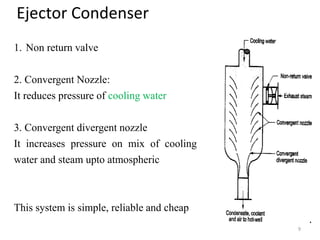
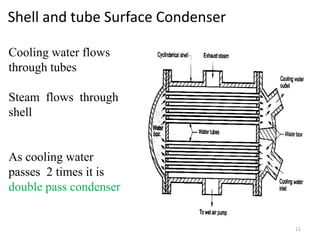
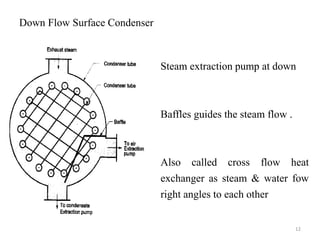
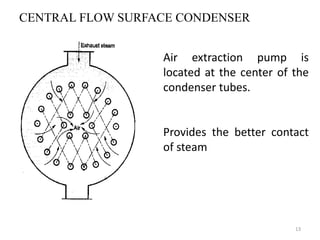
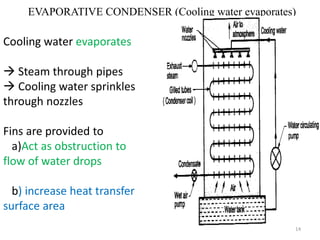
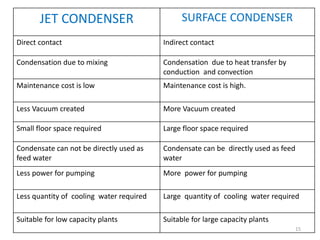
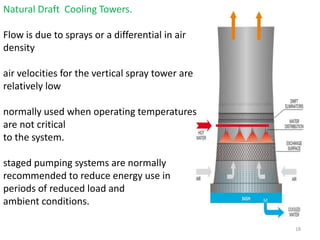
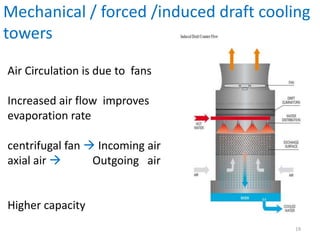
This document discusses different types of condensers and cooling towers used in power plants. It describes steam condensers, which condense steam using water as the cooling media. Surface condensers are also discussed, which use indirect contact between steam and cooling water through tubes. Jet condensers use direct contact between steam and cooling water. The document also covers different types of cooling towers, including natural draft towers which use density differences to circulate air, and mechanical draft towers which use fans to increase air flow and improve evaporation.