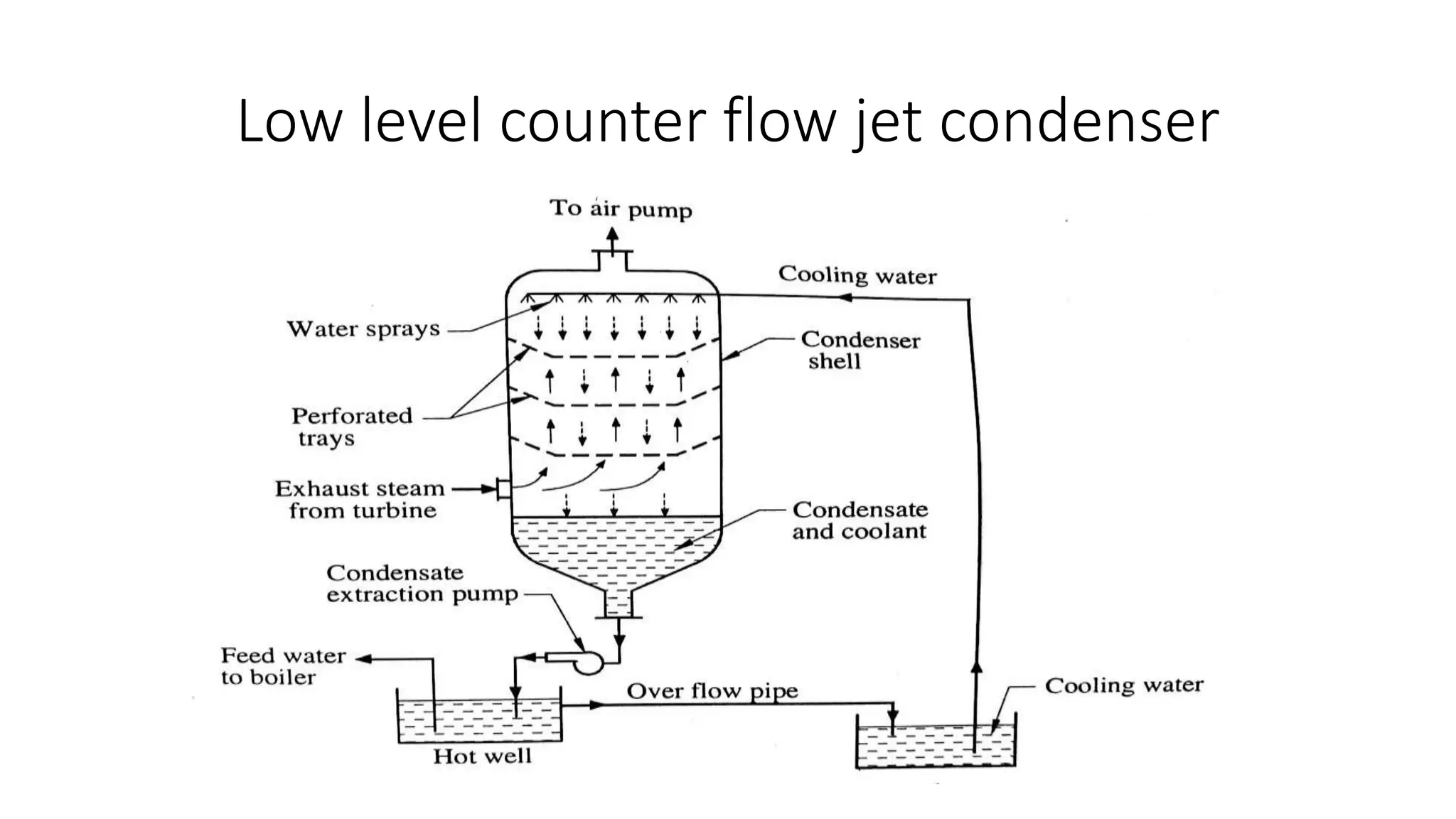
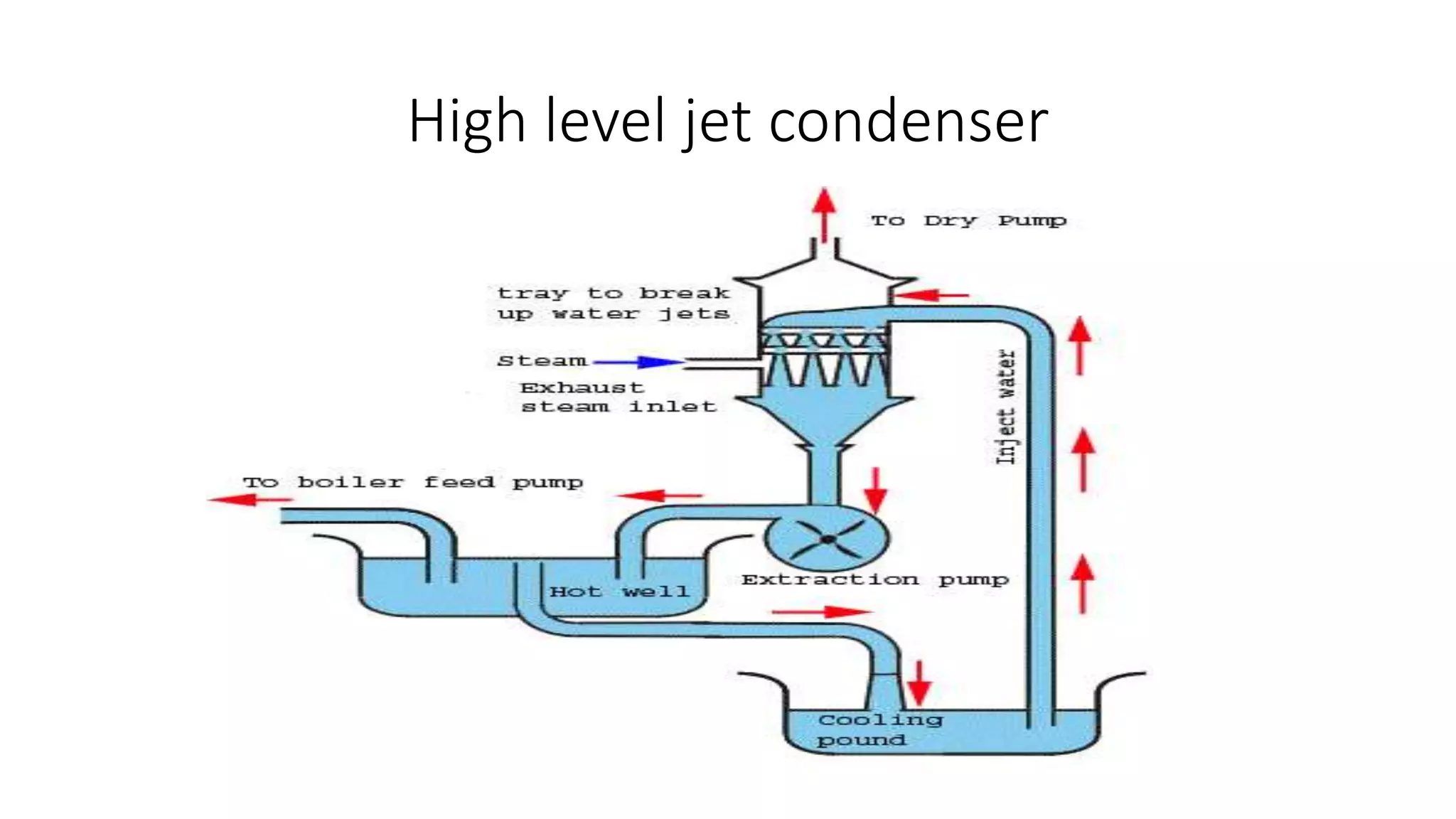
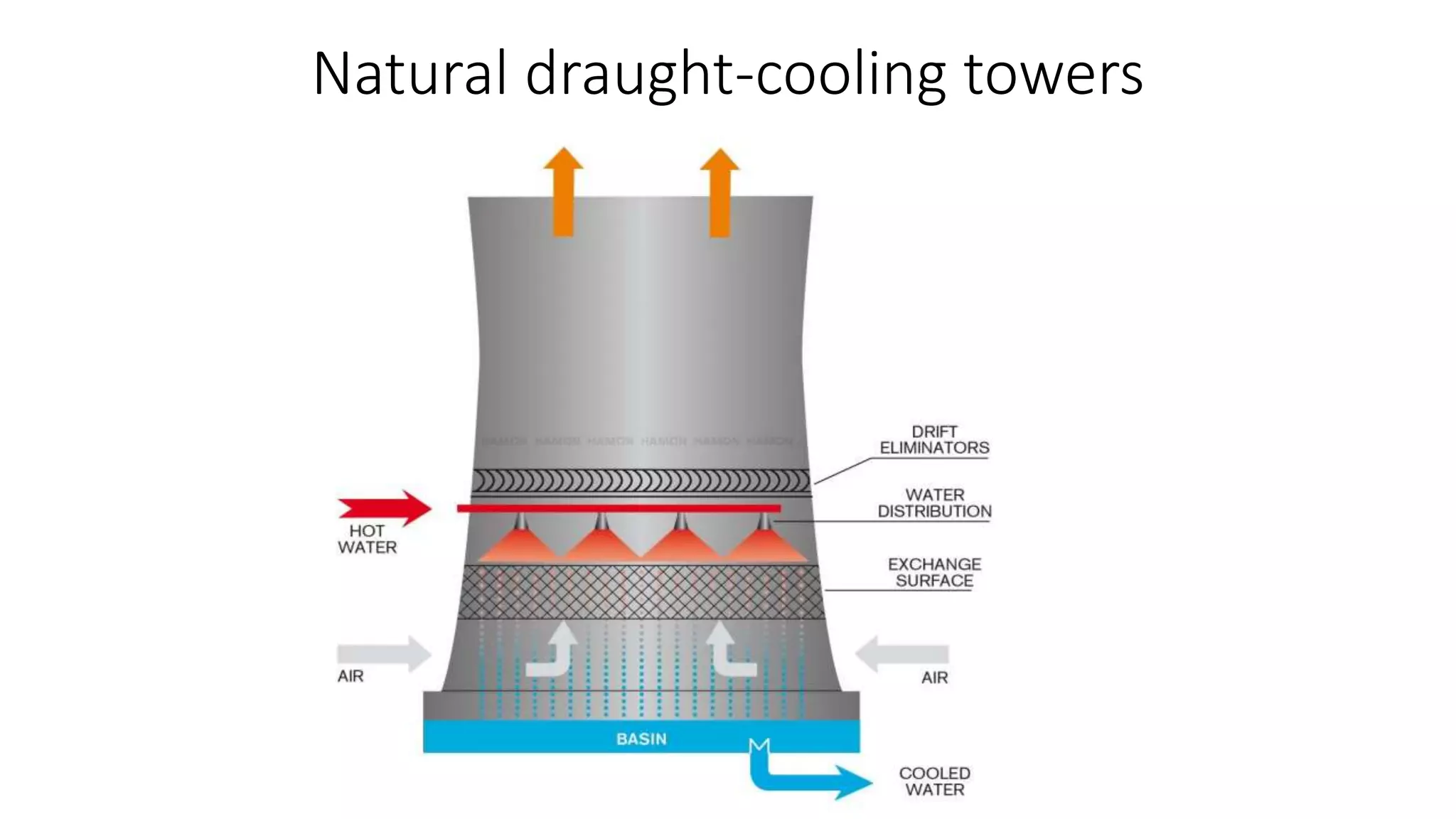
Condensers and cooling towers are used to condense steam from turbines and cool the condensate. There are two main types of condensers - jet condensers, where cooling water and steam are in direct contact, and surface condensers, where they are not. Surface condensers can achieve higher vacuums up to 760 mm Hg and are more suitable for high capacity plants. Leakage of air into condensers reduces vacuum and efficiency. Various methods like air pumps and deaerated feedwater are used to maintain vacuum. Cooling towers and ponds are used to cool condenser water and transfer heat to the atmosphere, with towers being more efficient but with higher costs than ponds.