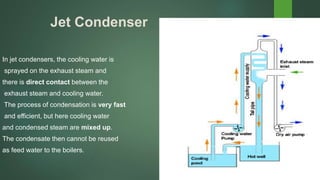
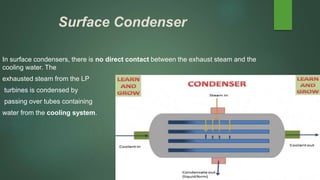
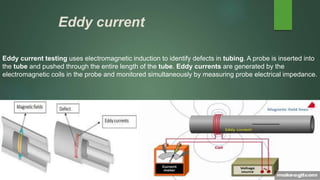
The document provides an overview of steam condensers used in power plants, detailing their types, functions, materials, and importance in maximizing efficiency and reusing water. It distinguishes between jet and surface condensers, discusses vacuum maintenance, air ingress issues, and leak testing methods. Additionally, it addresses fouling concerns and cleaning techniques to prevent operational inefficiencies.