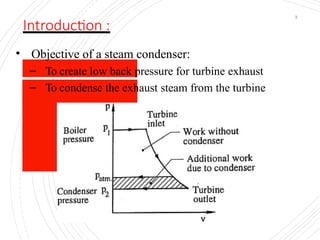
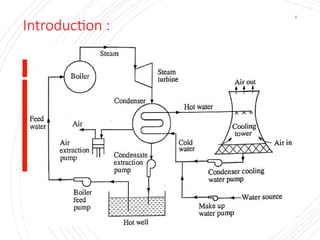
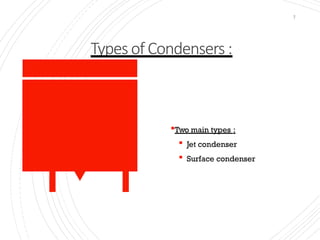
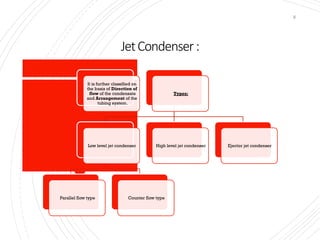
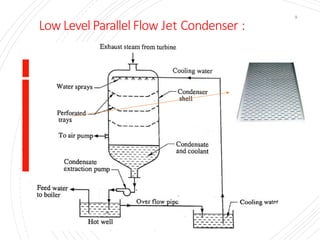
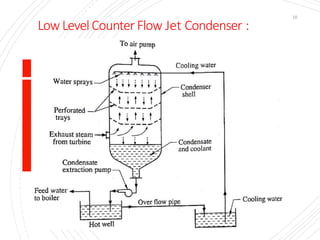
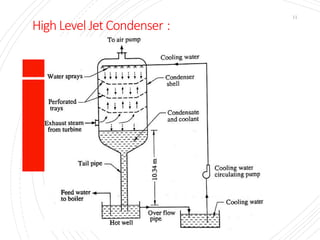
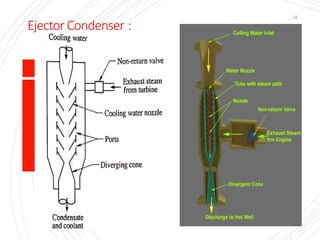
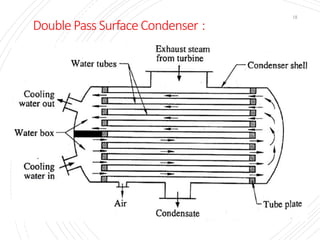
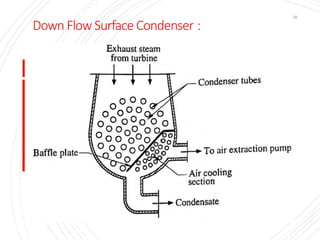
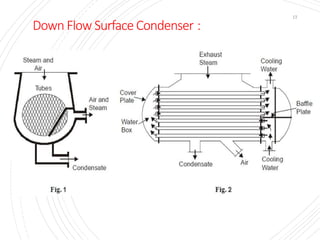
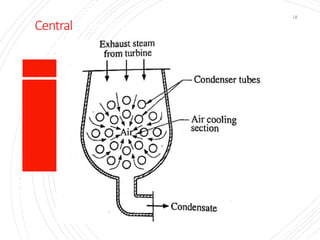
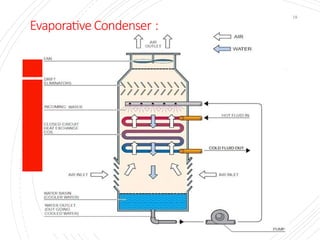
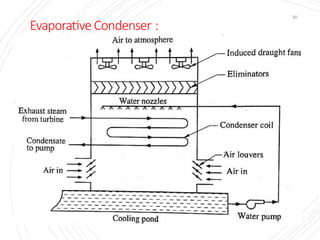
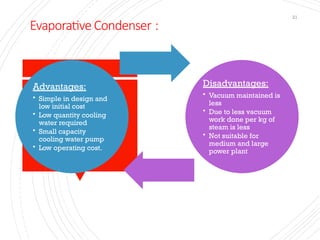
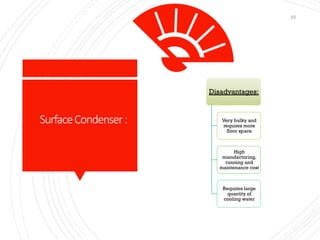
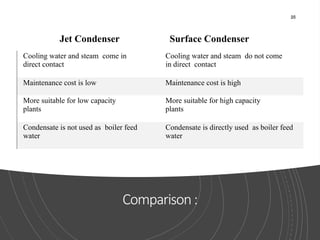
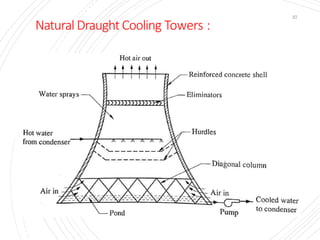
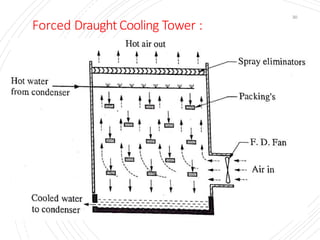
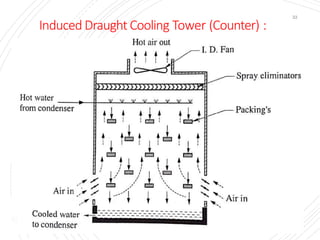
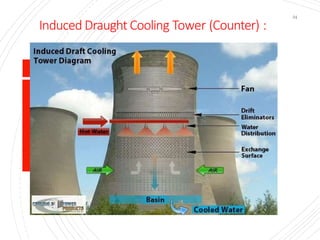
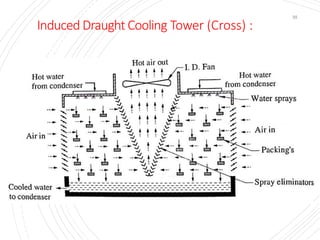
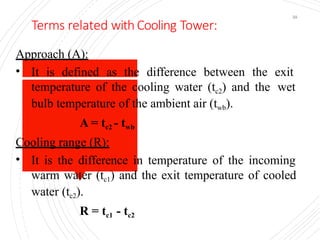
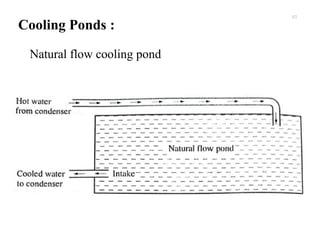
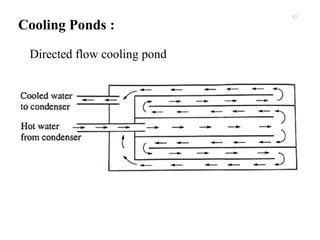
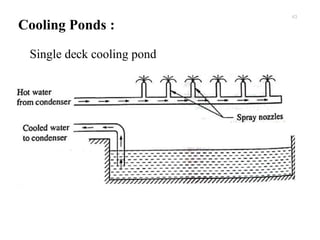
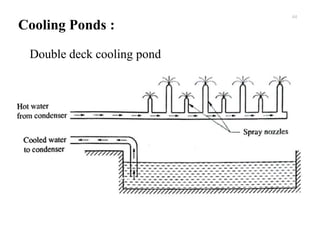
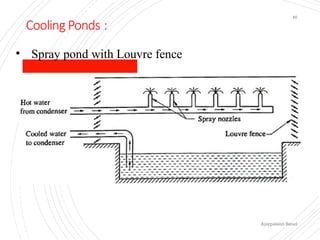
The document provides an overview of condensers and cooling towers, focusing on their types, functions, advantages, and disadvantages. It explains the role of steam condensers in enhancing thermal efficiency and the characteristics of various condenser types, including jet and surface condensers. Additionally, it discusses different cooling tower systems, their operational costs, and efficiencies, as well as the concept of cooling ponds as an alternative cooling method.