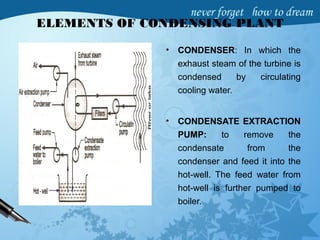
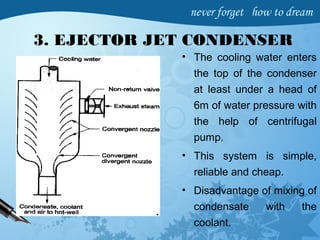
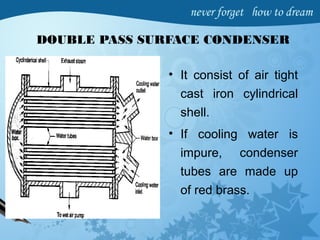
Steam condensers condense exhaust steam from turbines or engines using cooling water. They increase efficiency by reducing steam pressure below atmospheric pressure. There are two main types - jet condensers where steam directly contacts cooling water, and surface condensers where steam condenses on the outer surface of tubes through which cooling water flows. Surface condensers produce higher vacuums and reuse condensate as boiler feedwater. Both require air pumps to remove non-condensable gases from the condenser to maintain vacuum, and circulating pumps to supply cooling water. Proper condenser operation recovers latent heat and increases power plant output and efficiency.