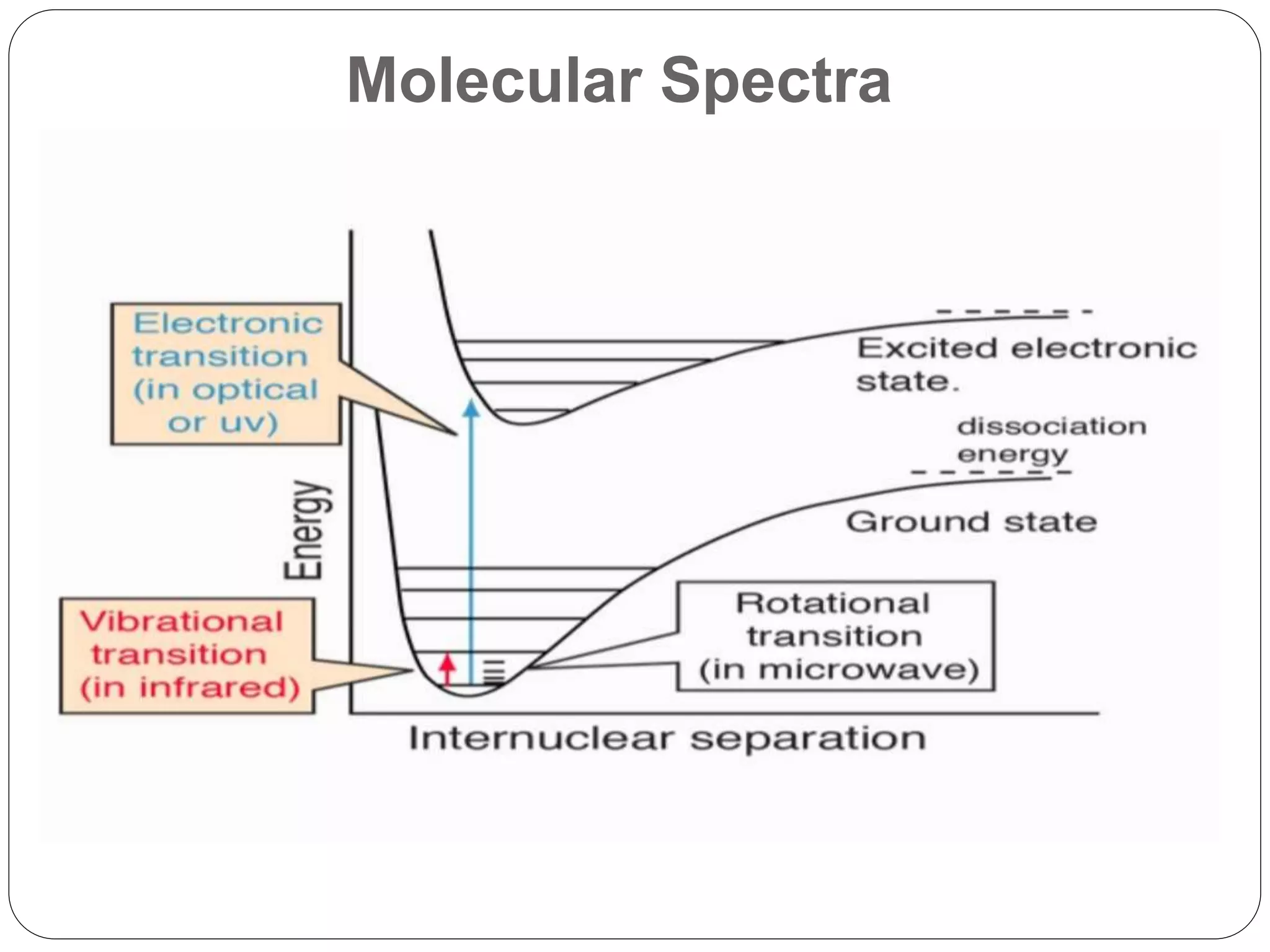
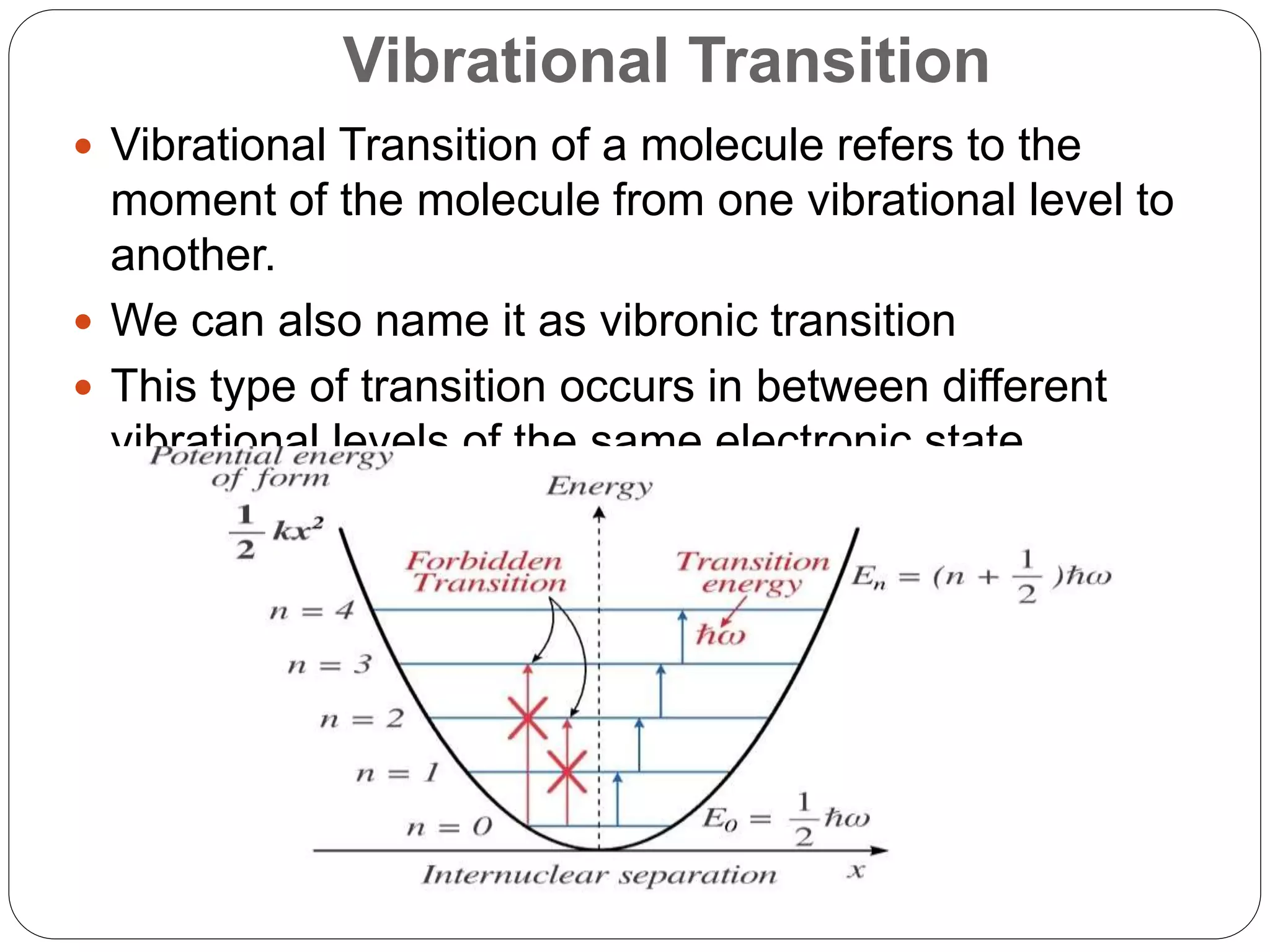
The document summarizes the Franck-Condon principle, which states that during an electronic transition between two states of a molecule, the transition occurs so rapidly that the positions of the nuclei remain almost unchanged. It describes the different types of molecular energy levels and vibrational transitions. It also provides three cases that illustrate how the Franck-Condon principle determines the relative intensities of vibrational transitions between electronic states based on differences in the equilibrium internuclear distances of the states.