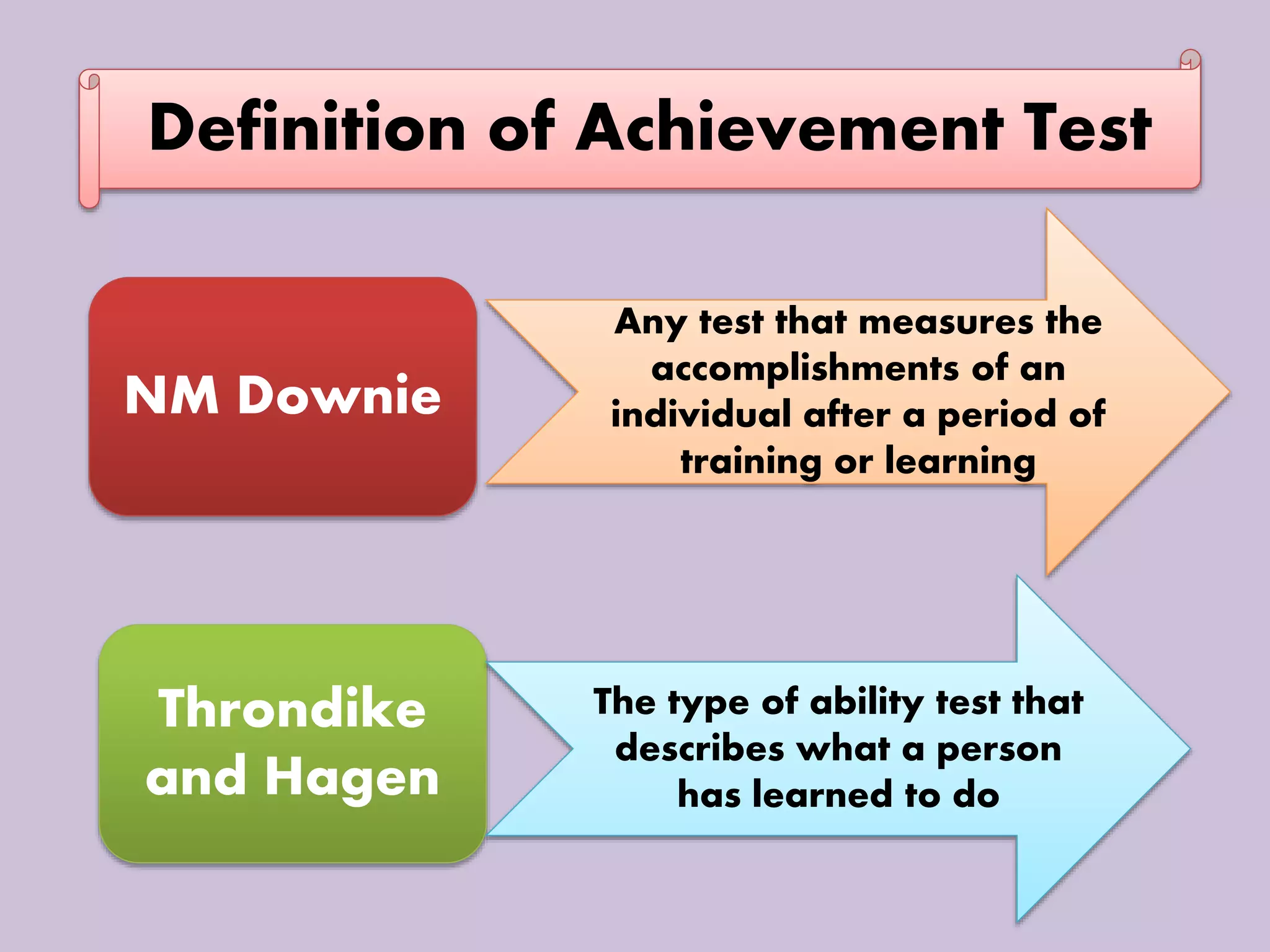
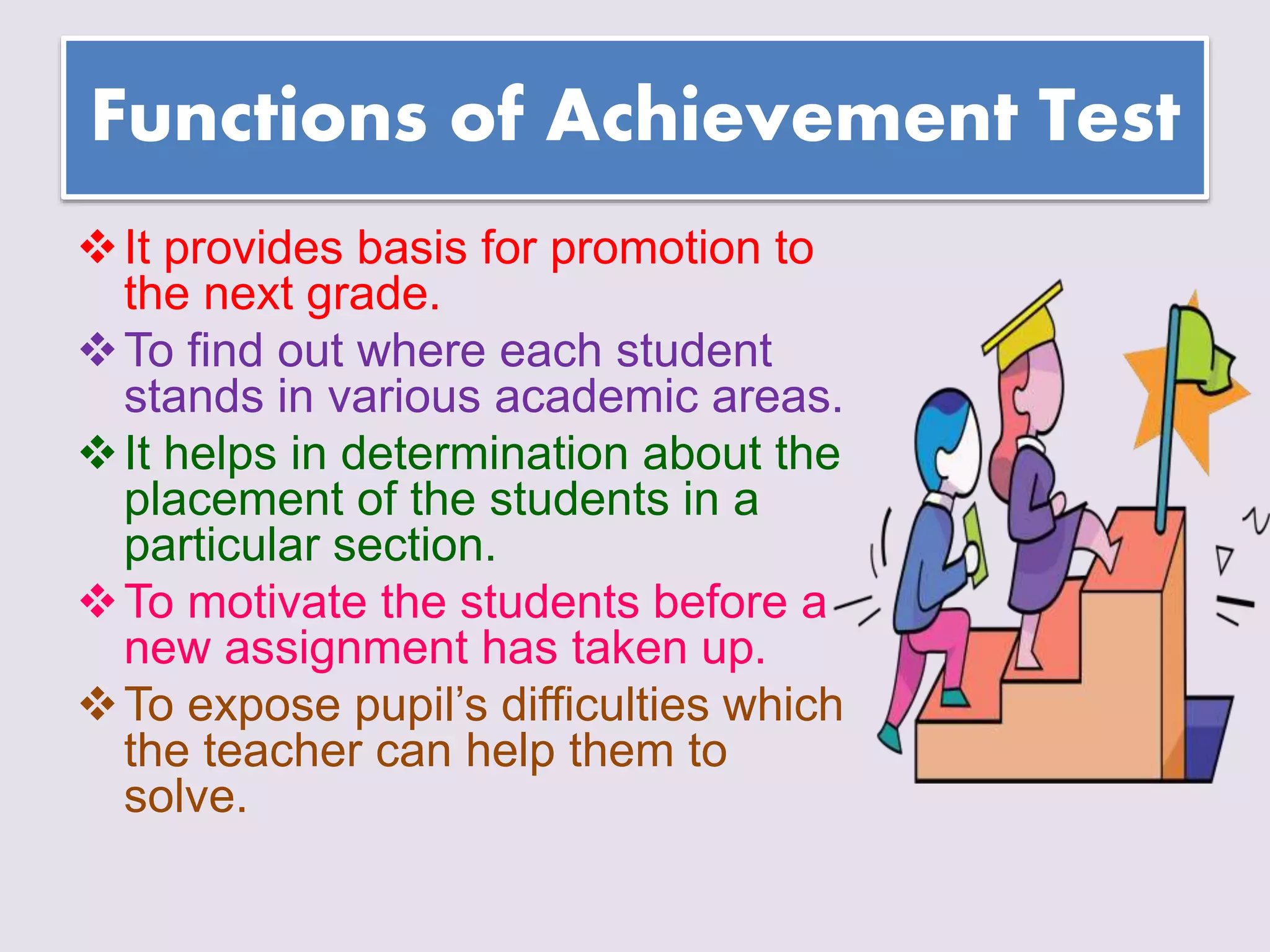
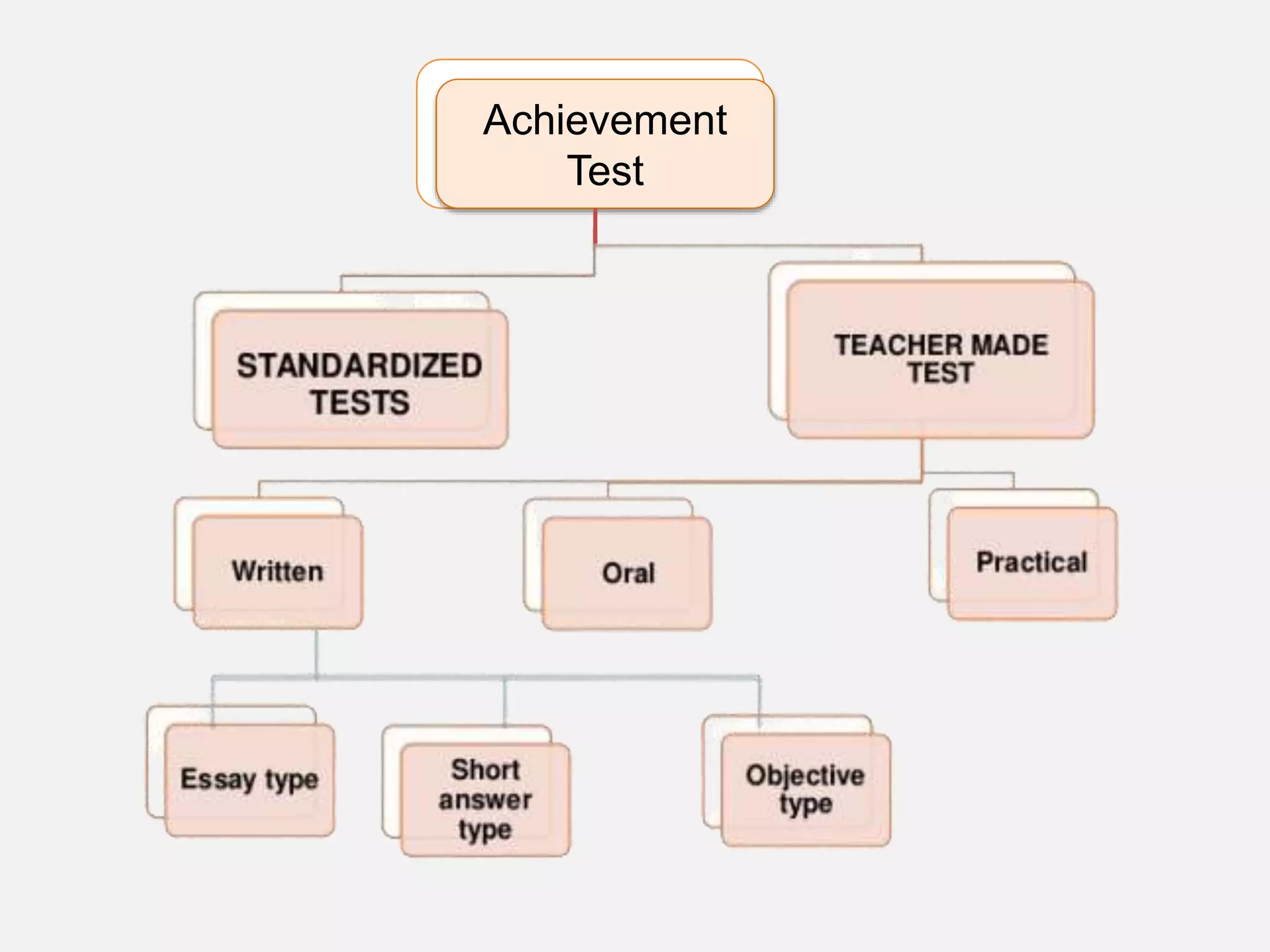
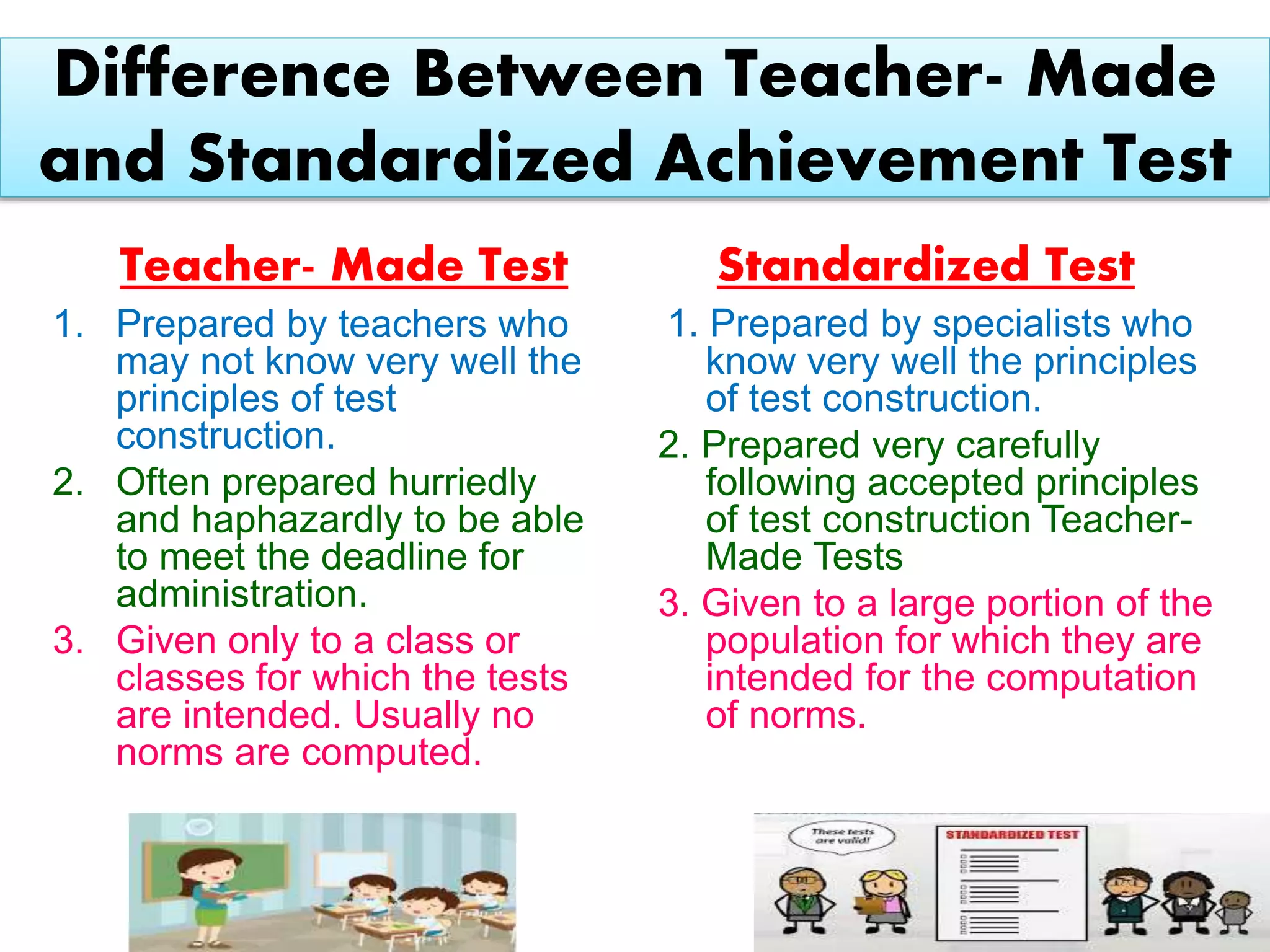
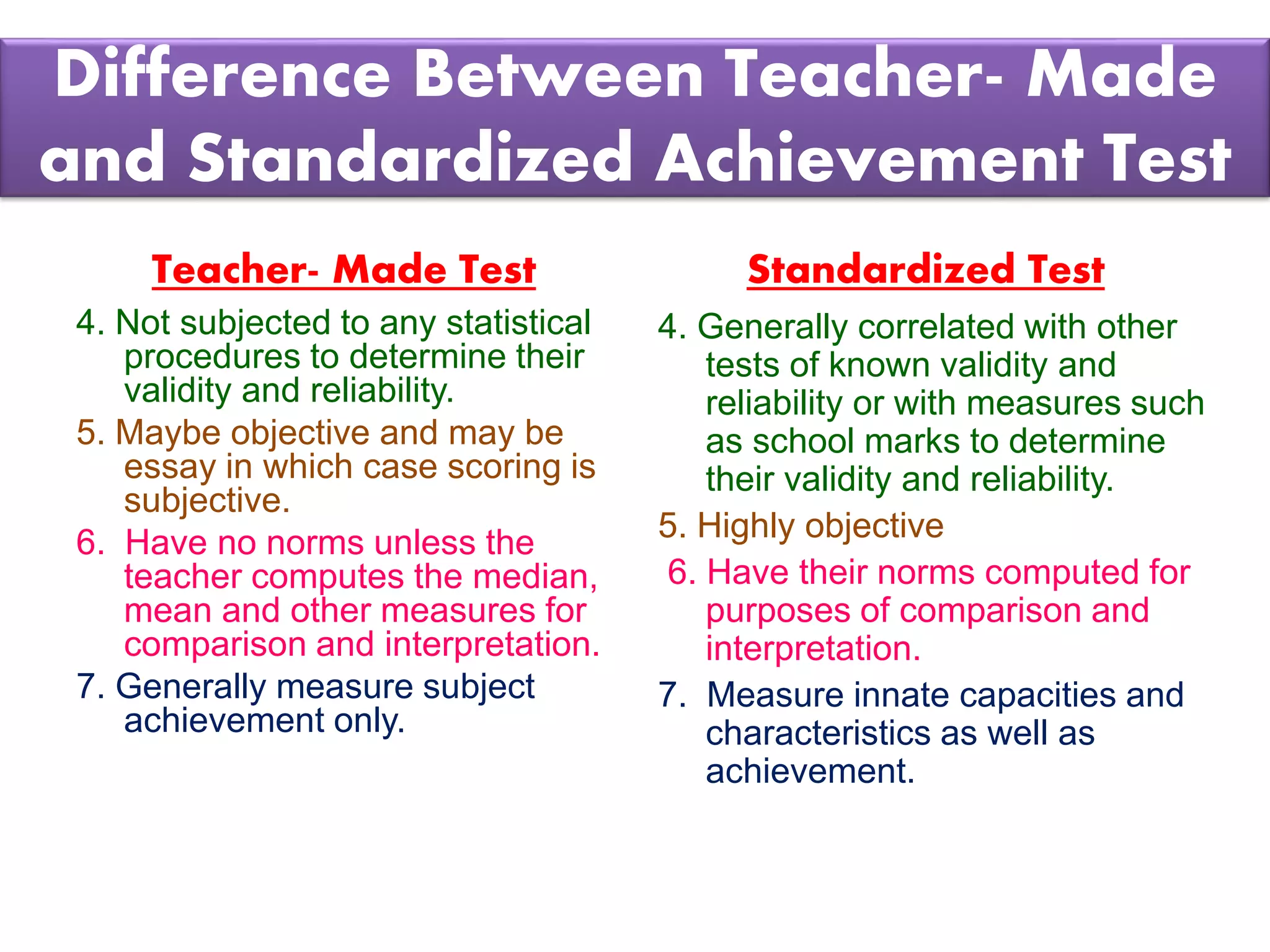
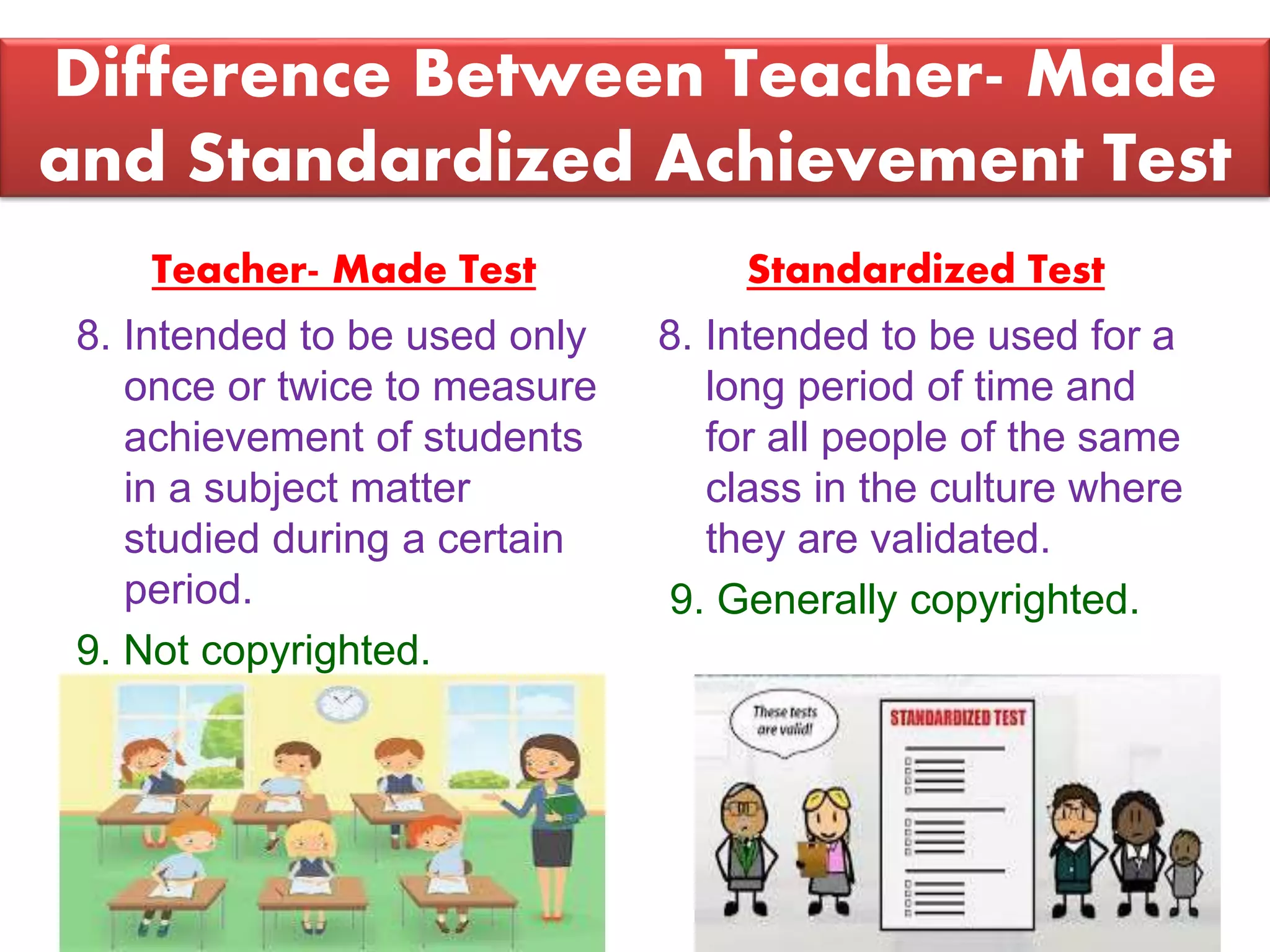
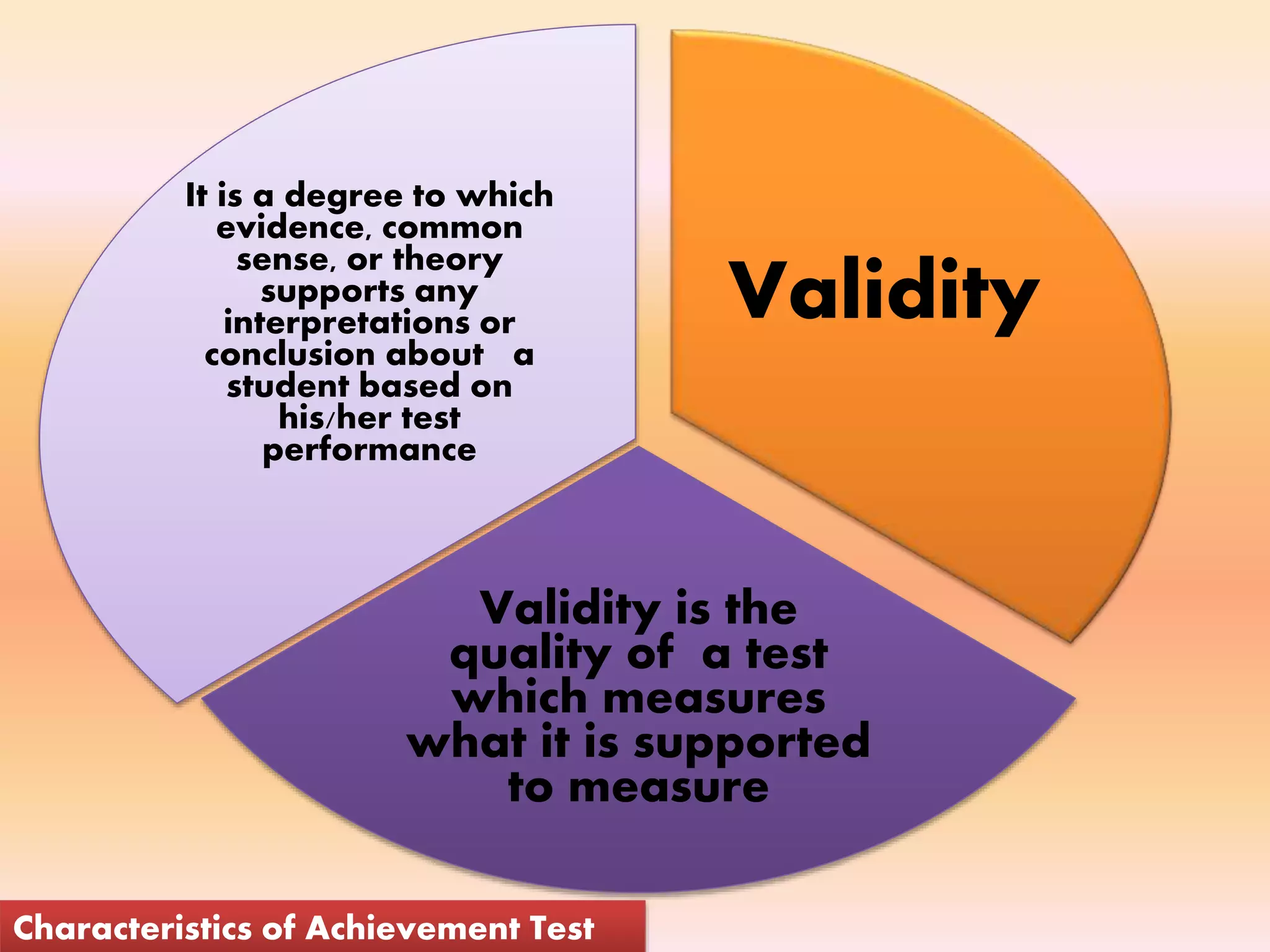
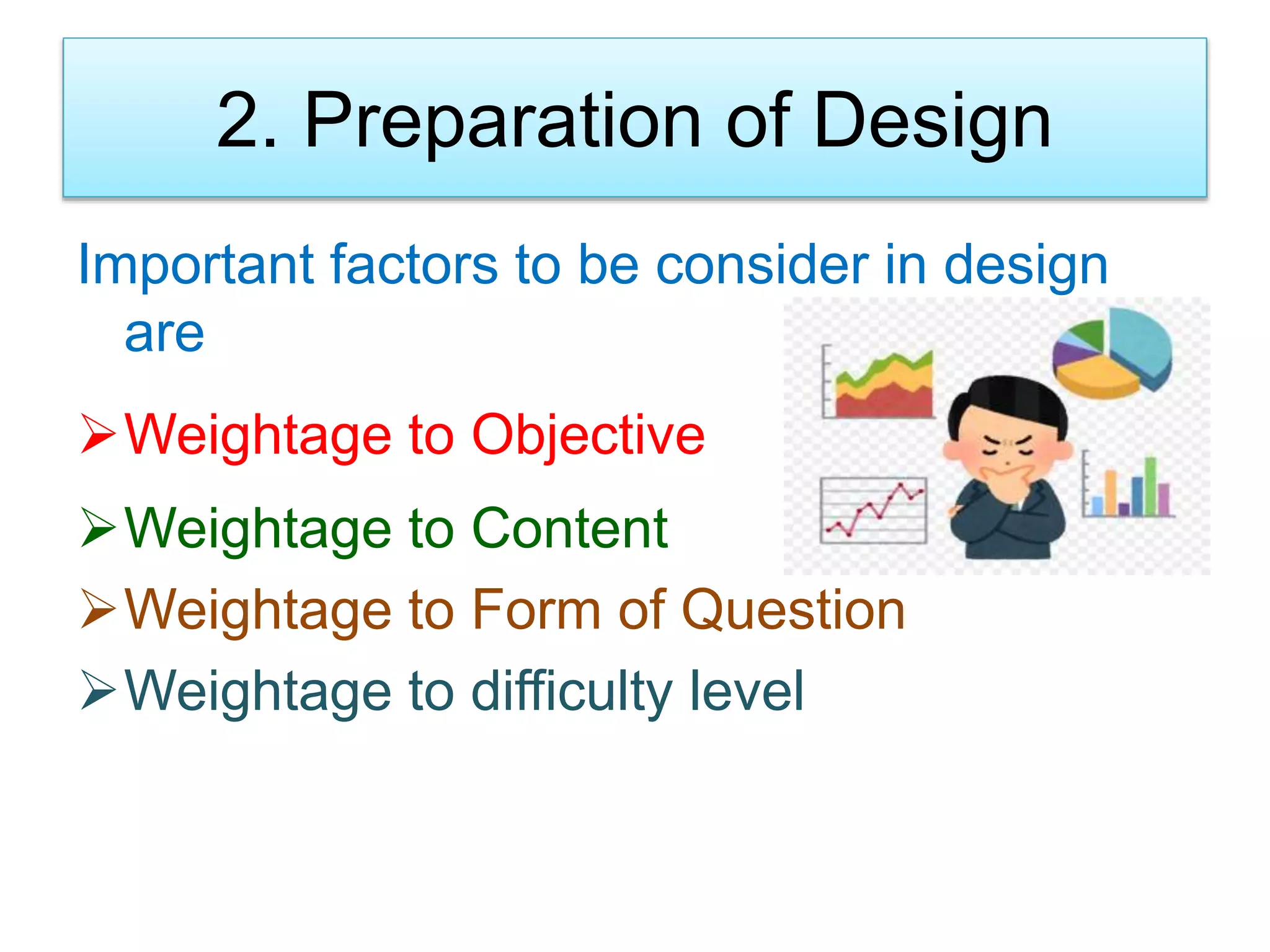
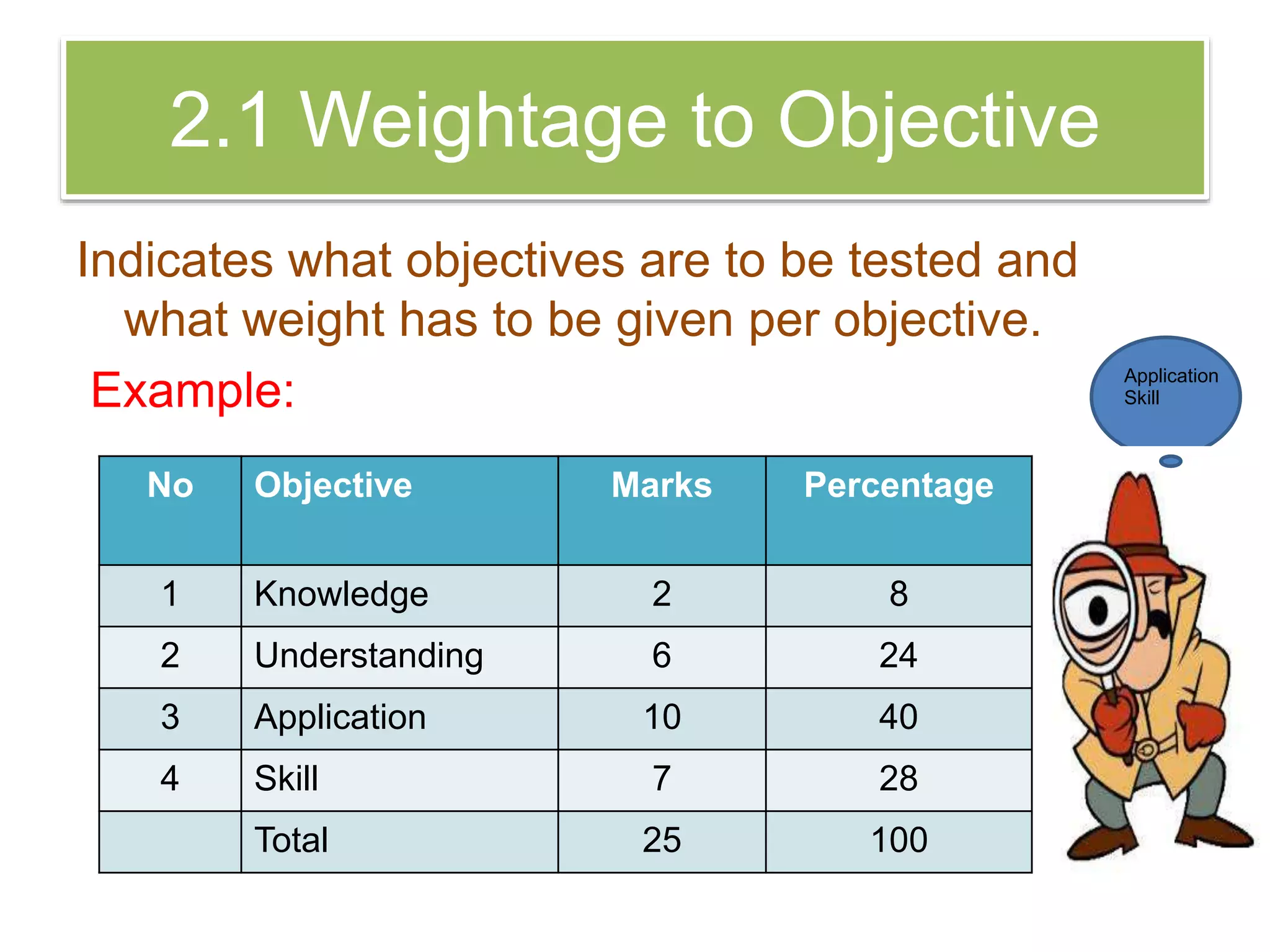
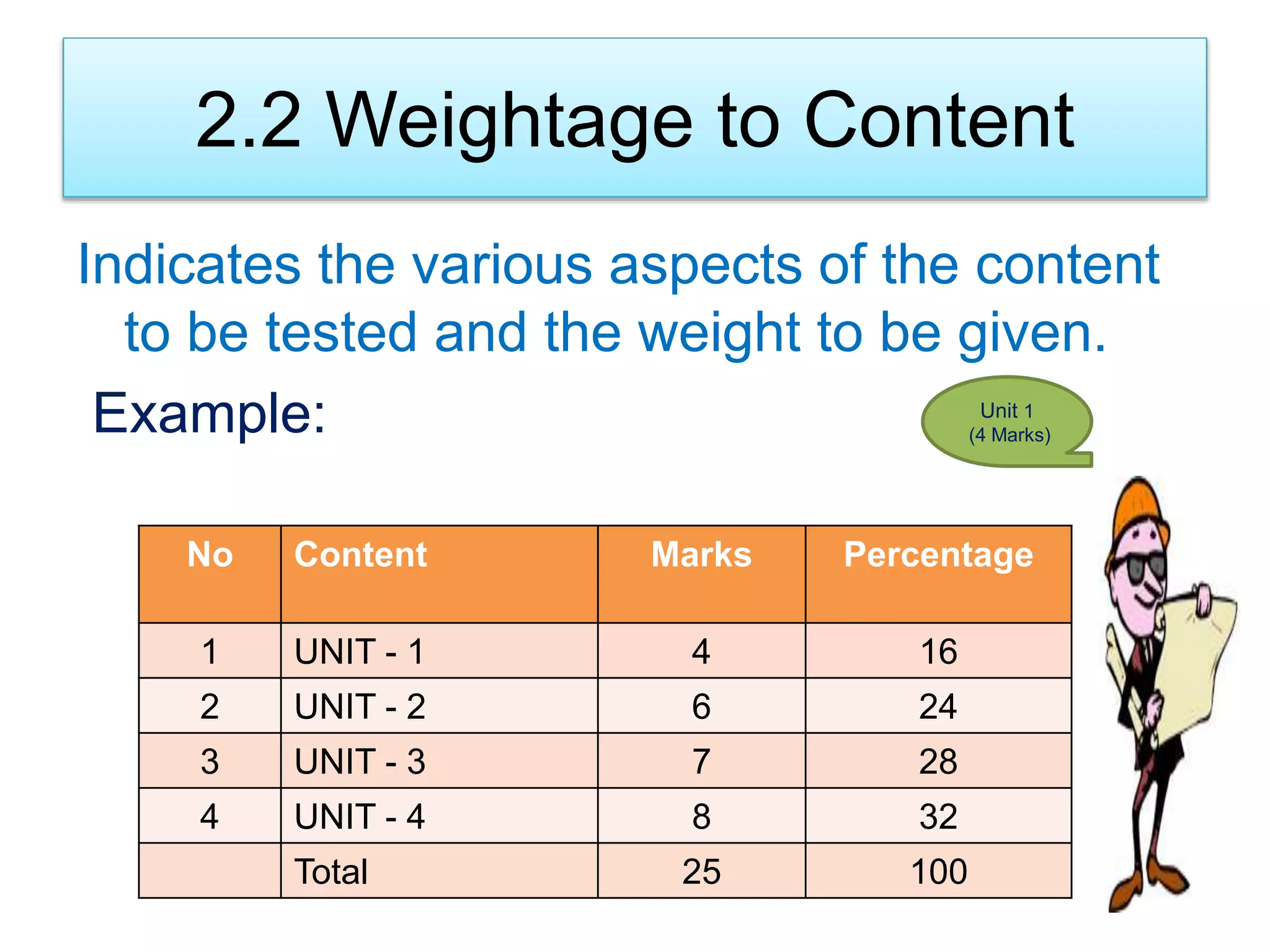
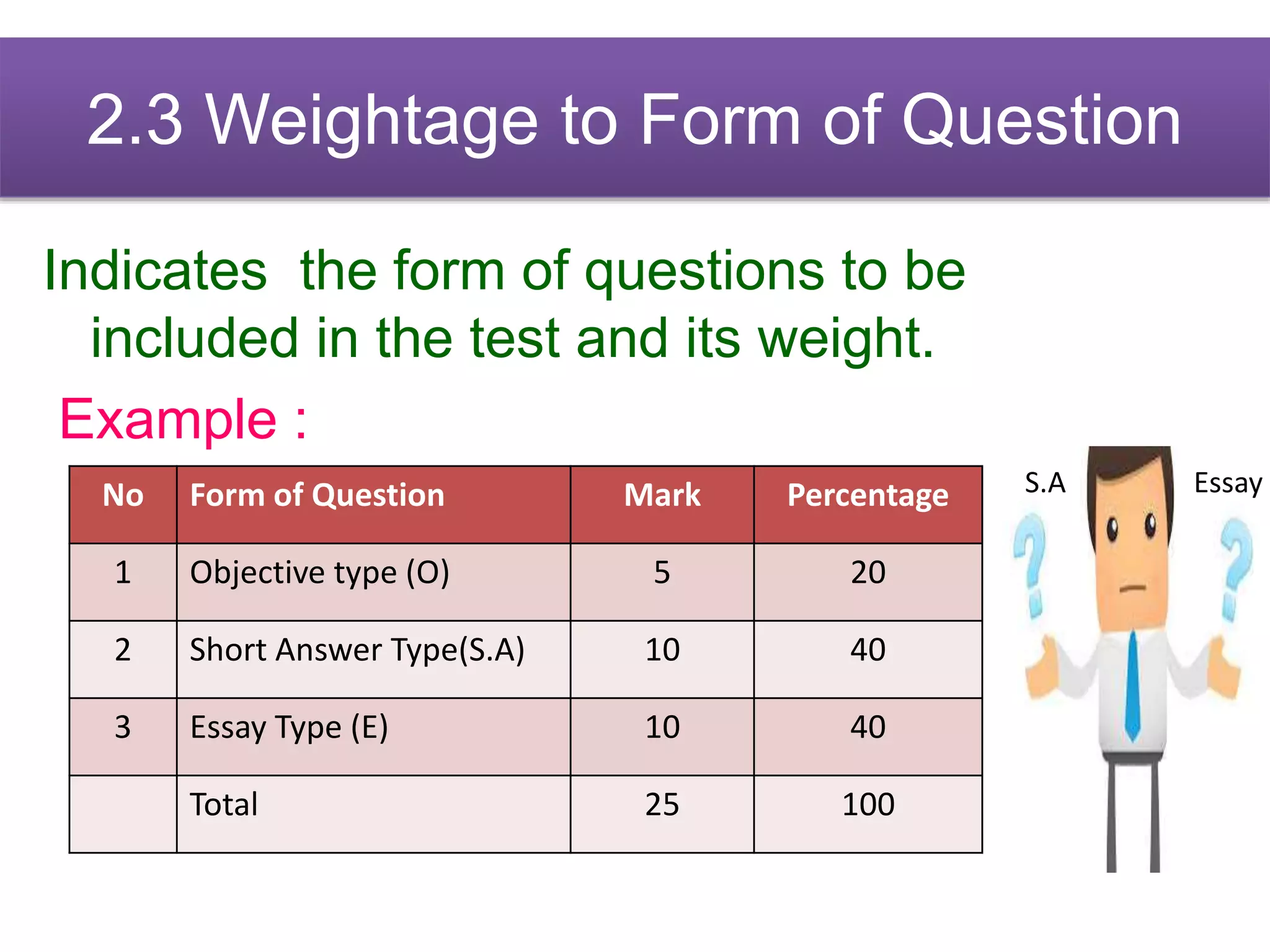
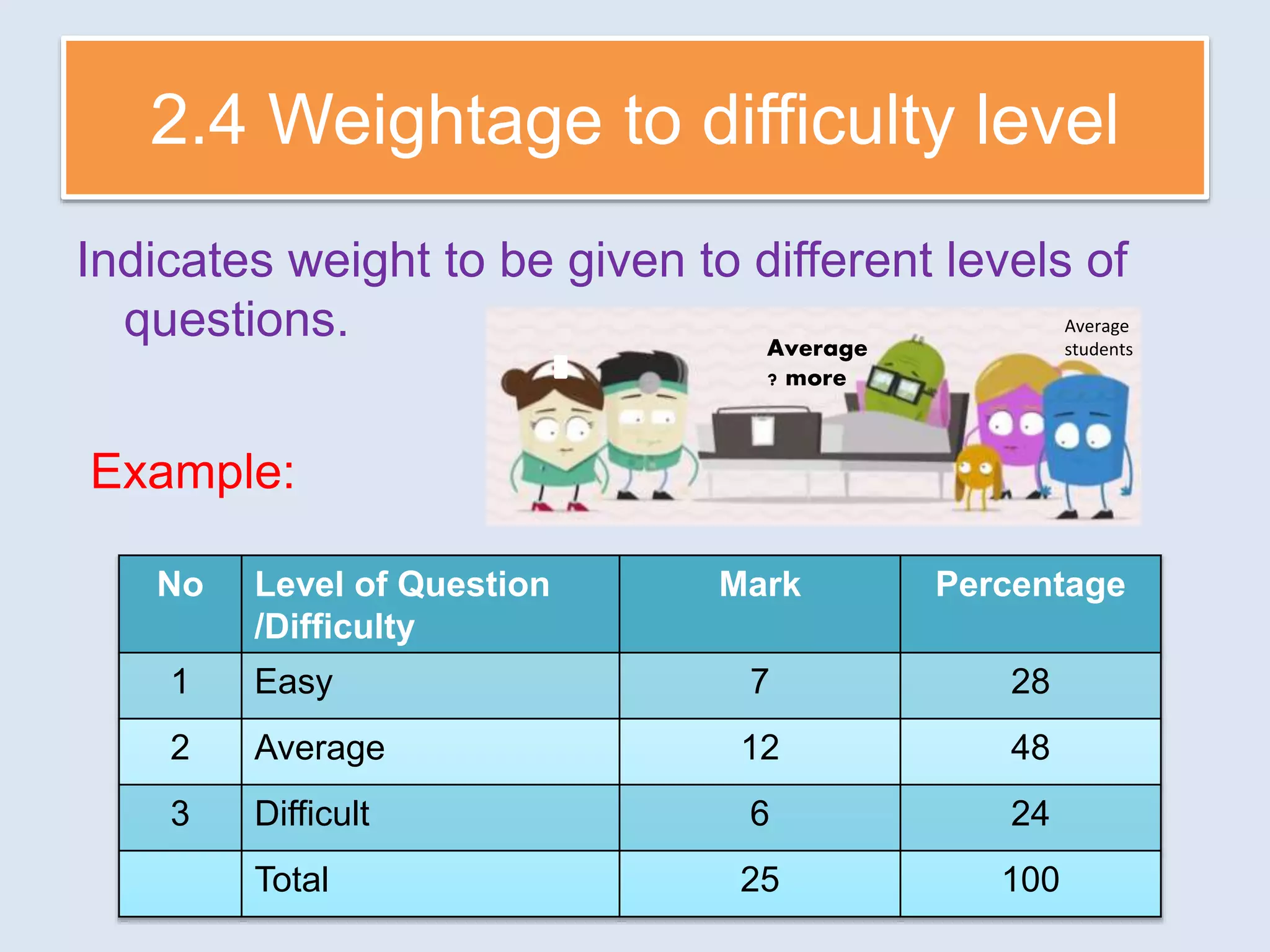
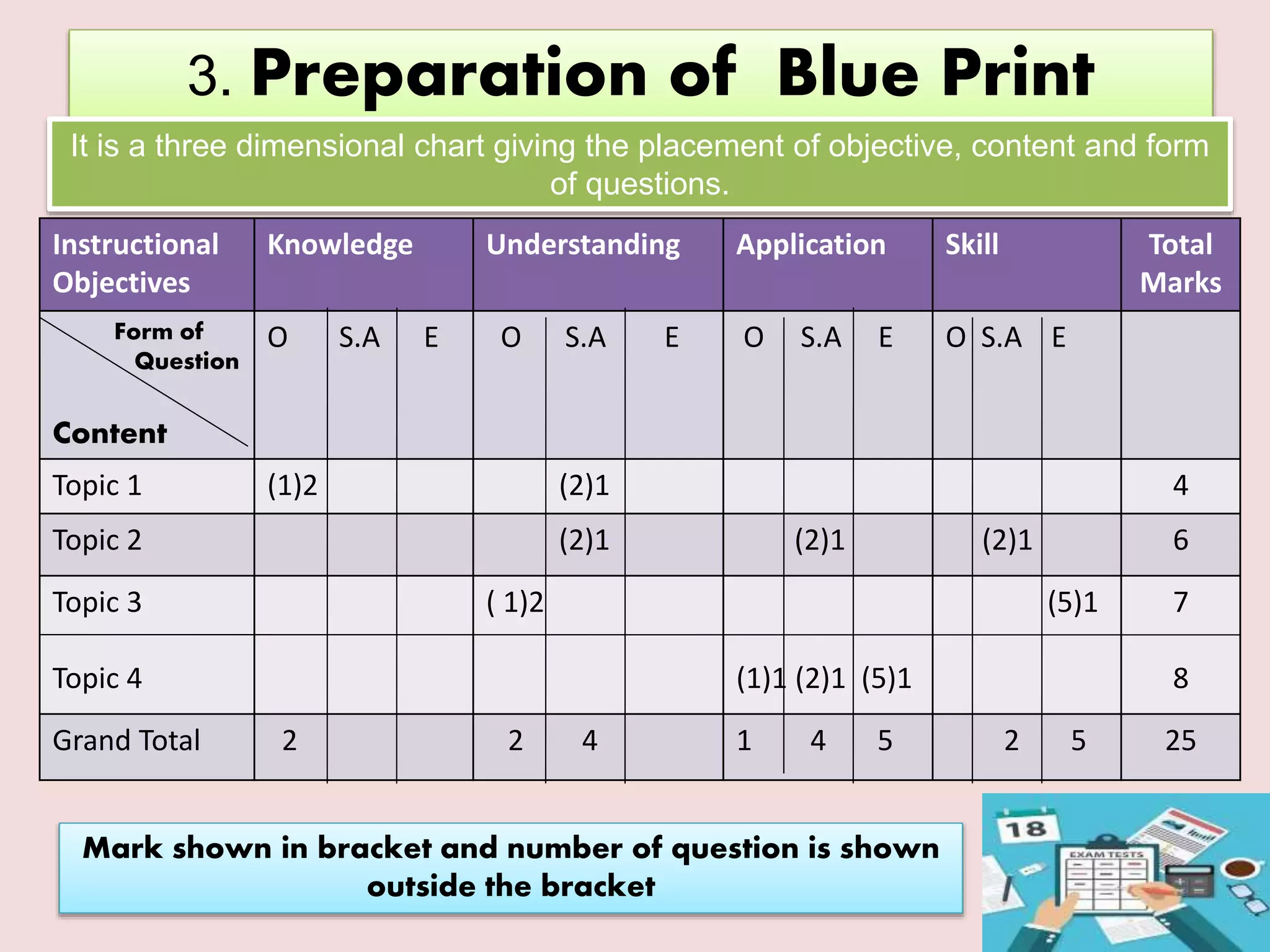
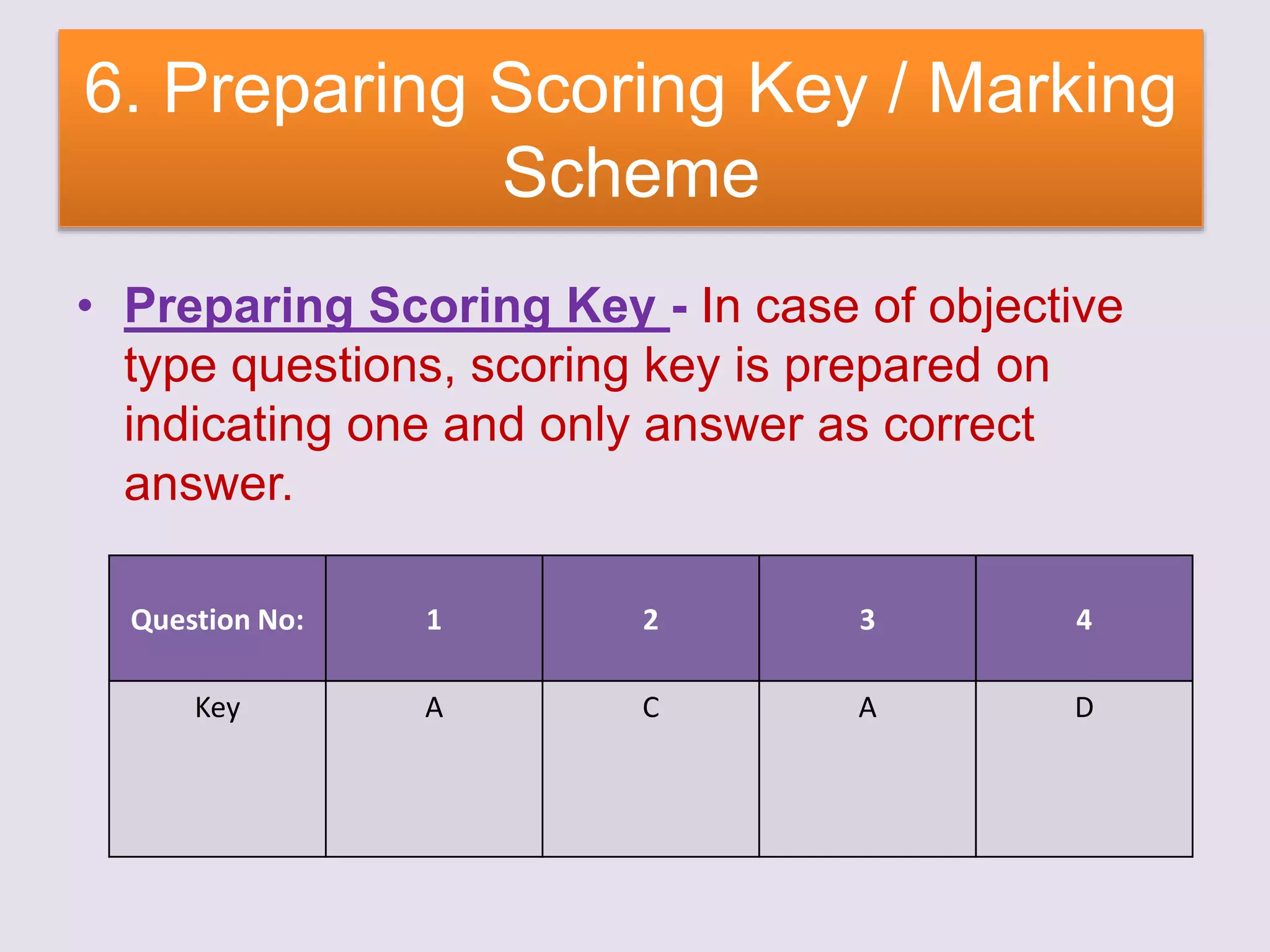
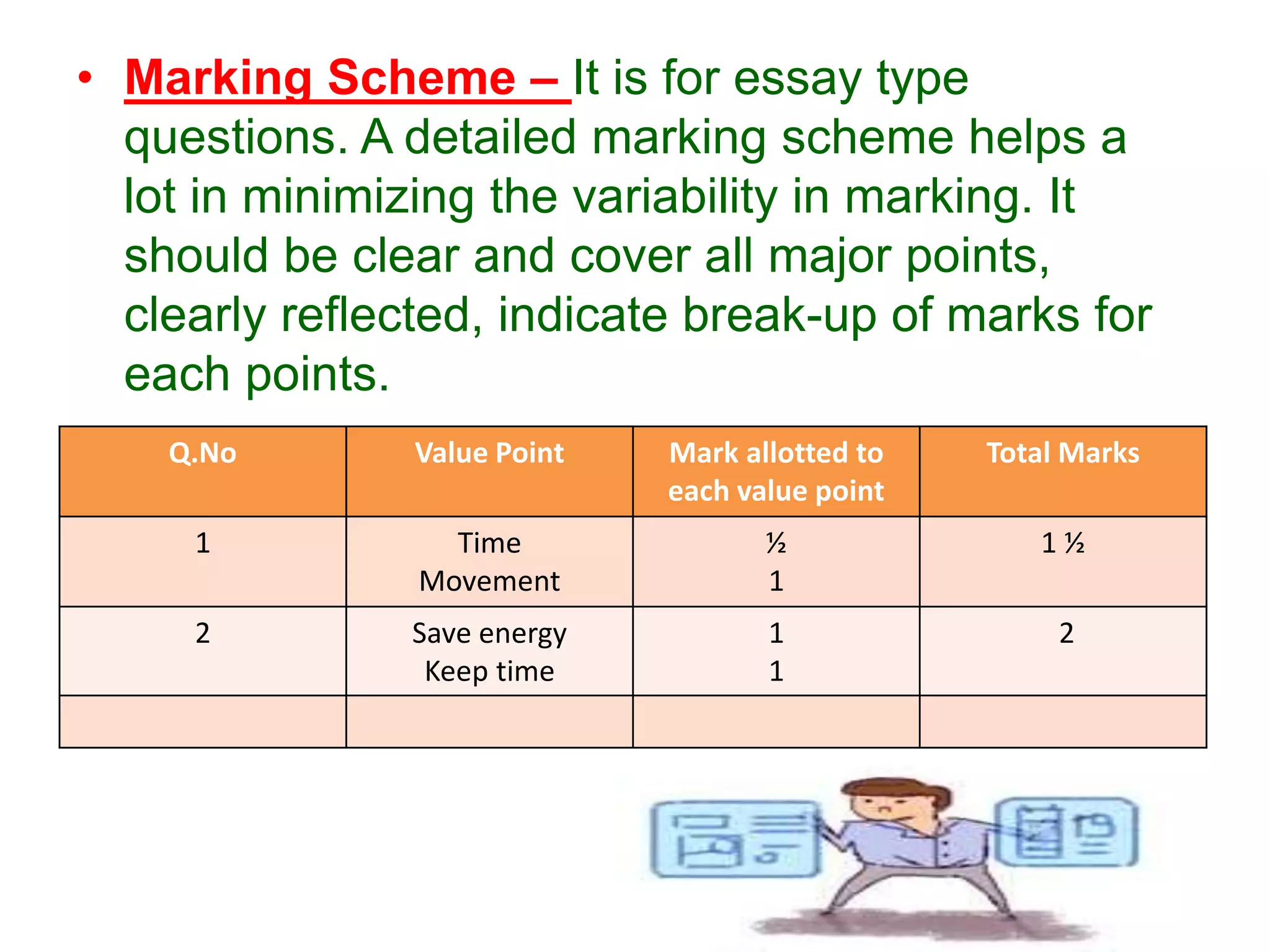
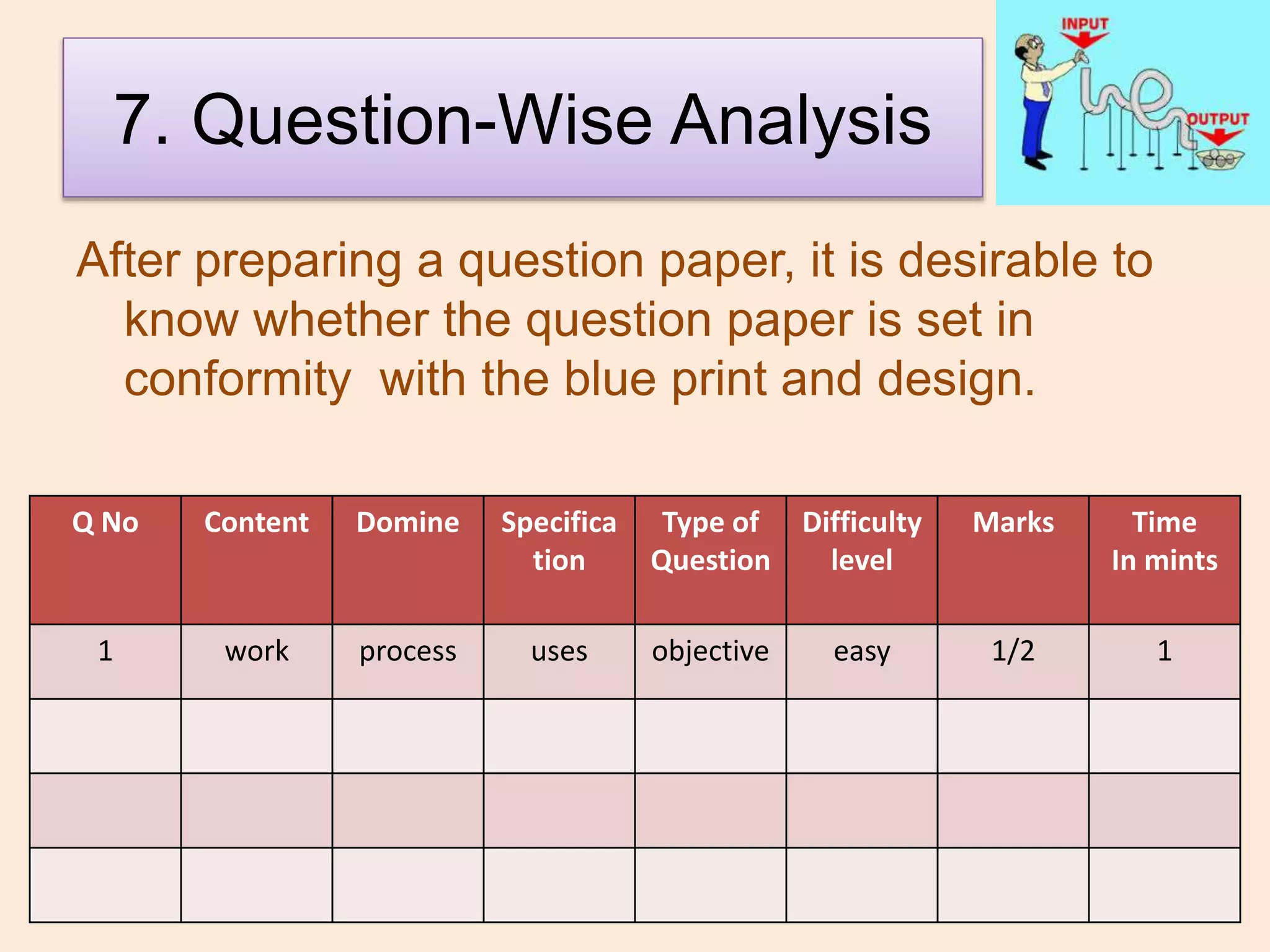
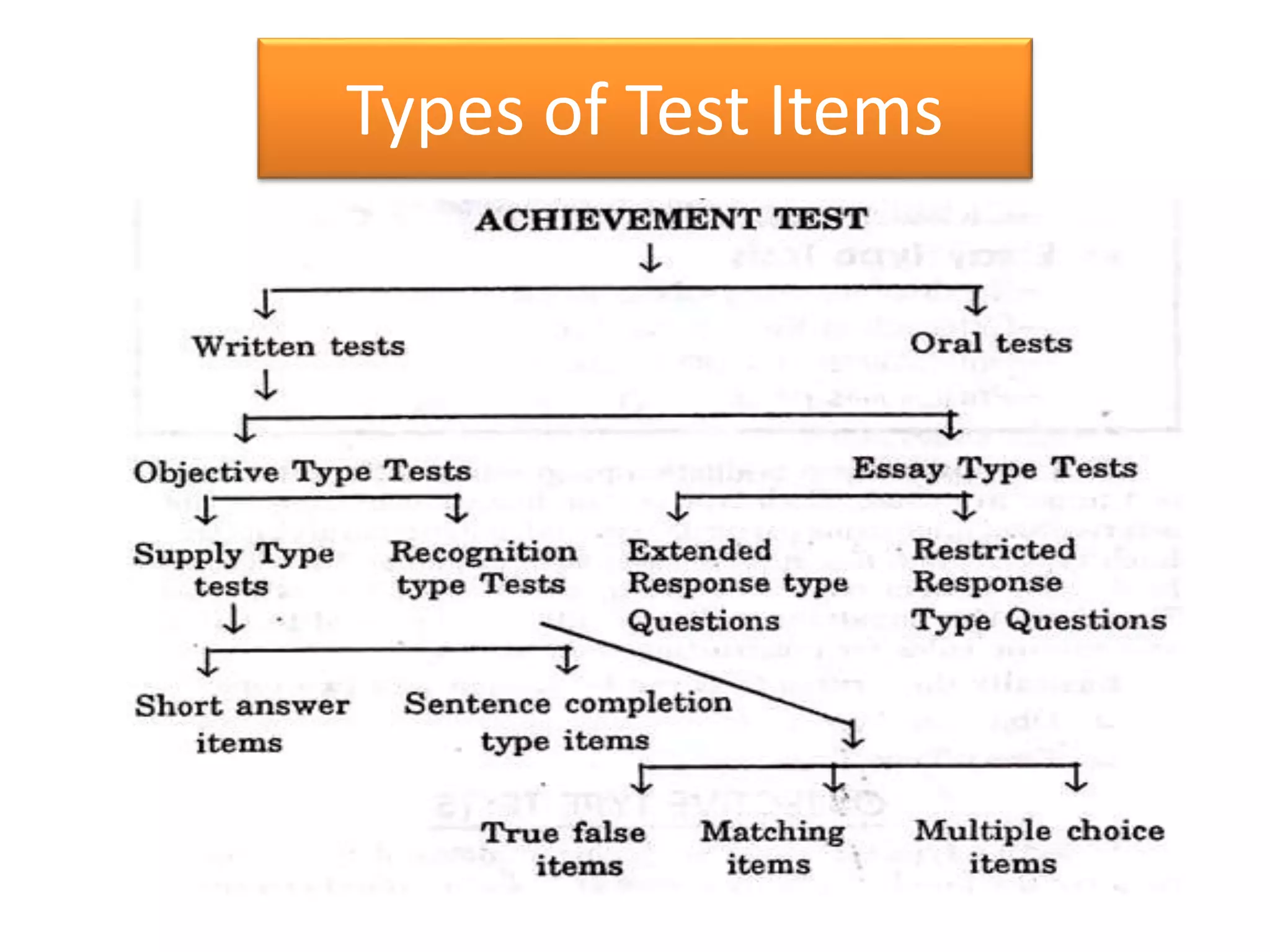
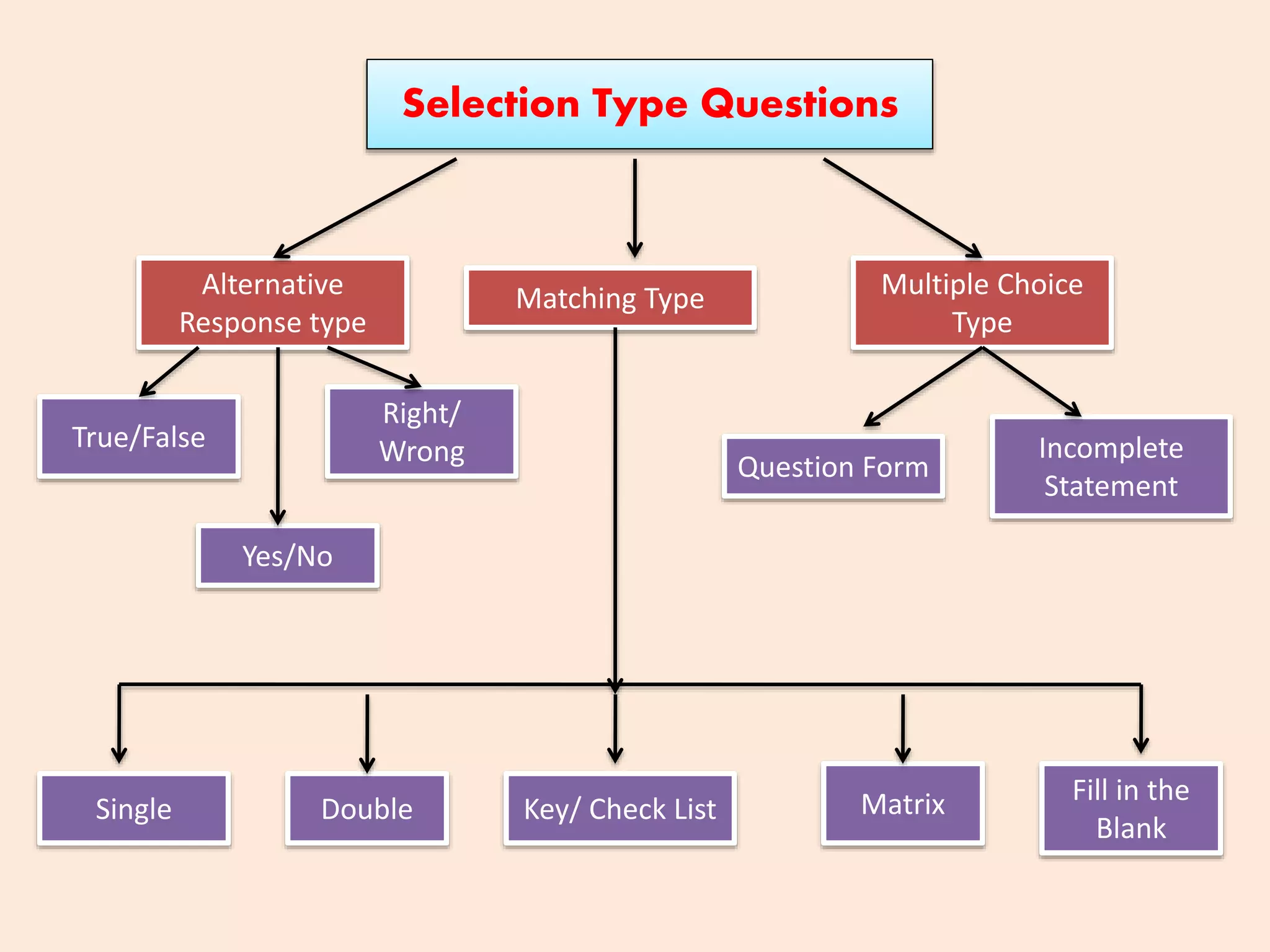
The document discusses achievement tests, emphasizing their role in measuring students' proficiency and mastery in various subjects as well as their application in educational settings. It differentiates between teacher-made tests and standardized tests, outlining their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Additionally, the document details the construction process of achievement tests, including planning, design, question formulation, and types of test items.