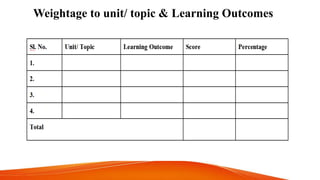
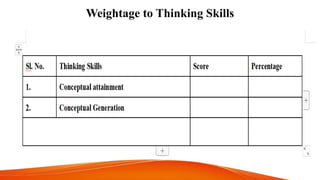
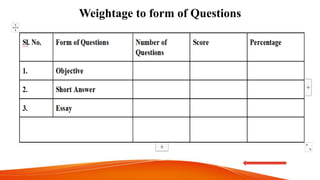
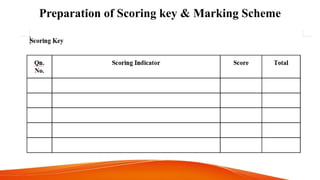
Achievement tests are designed to measure students' knowledge and academic progress over time in the subjects and skills learned in school. They evaluate the effectiveness of schools, teachers, and help determine appropriate course placement for students. Achievement tests are "backward-looking" in that they assess how well students have learned expected material. Characteristics of a good achievement test include reliability, validity, ease of administration, cost, time, acceptability, specificity, and being precise and clear. The construction of an achievement test involves planning, designing, preparing items and scoring keys, and analyzing questions.