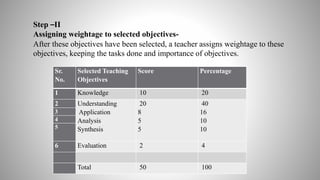
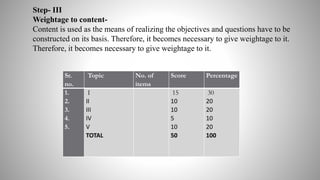
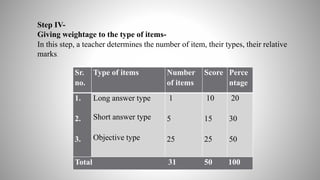
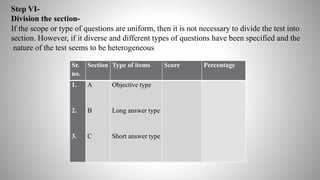
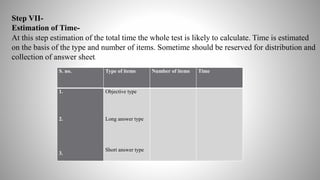
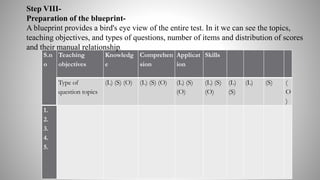
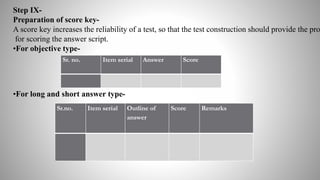
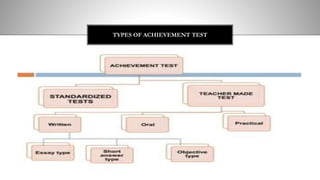
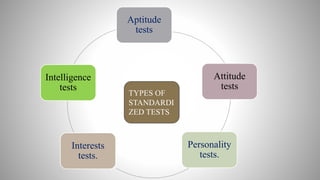
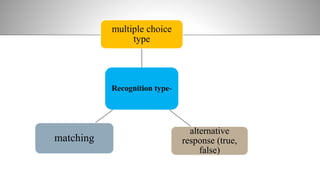
The document provides information on achievement tests. It begins with defining achievement test as a test used to measure what students have learned through instruction. It then outlines the key components of achievement tests, including their definition, functions, characteristics, types, and the steps involved in constructing them. Specifically, it discusses standardized tests versus teacher-made tests, and the different question formats used in achievement tests like essay questions, short-answer questions, and objective questions.