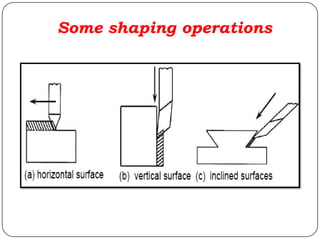
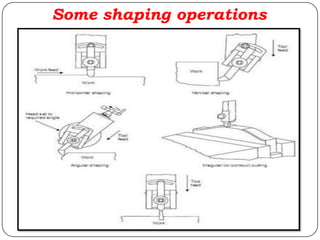
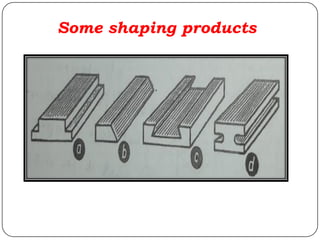
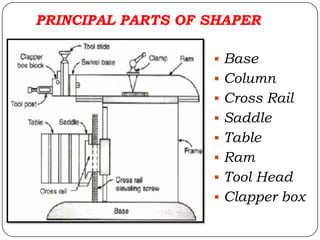
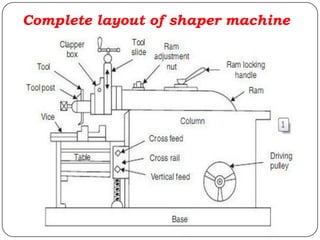
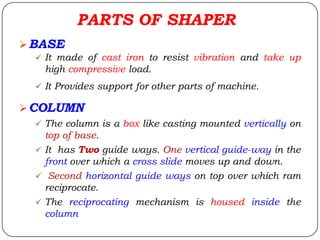
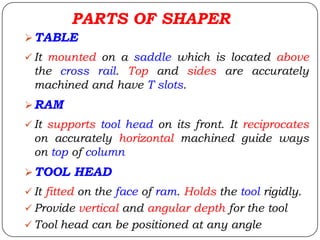
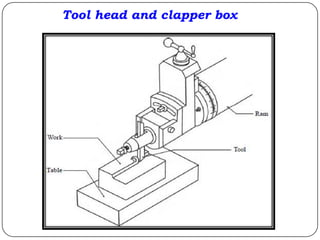
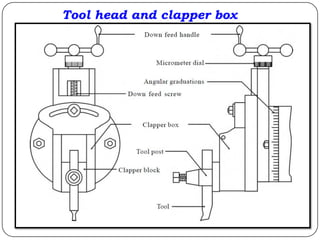
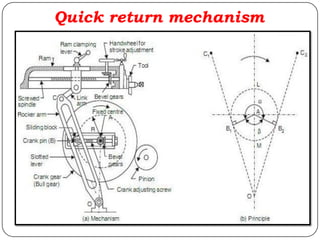
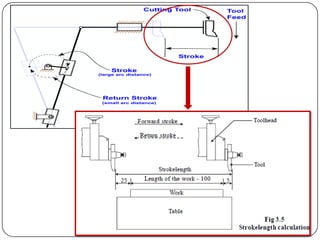
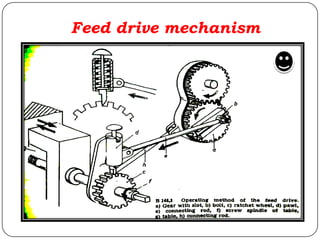
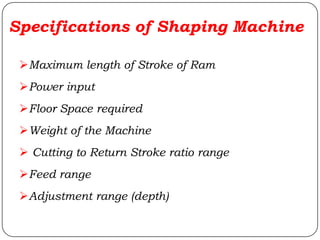
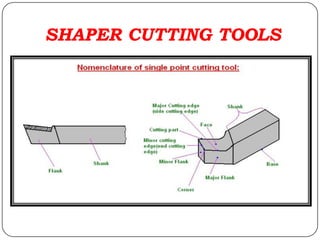
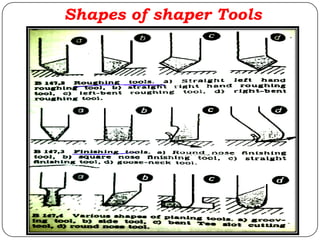
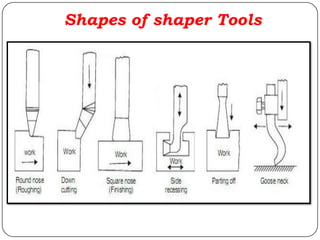
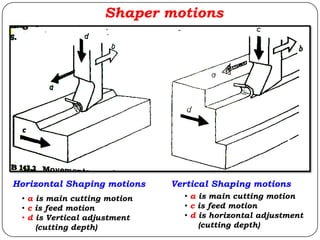
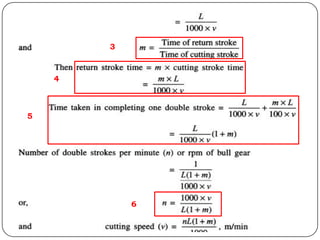
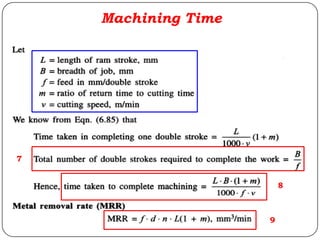
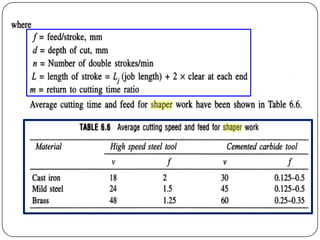
The document provides information about shaping and planing processes. It discusses the shaping machine, including its principal parts like the base, column, ram and tool head. It describes the shaping operations of producing flat surfaces, slots and contours. The quick return mechanism is explained, along with specifications, tool materials and cutting motions. Formulas for cutting speed, feed, depth and machining time calculations are also presented.