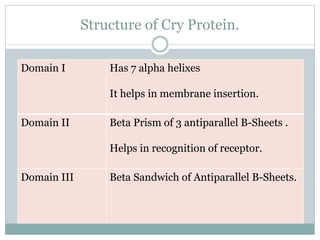
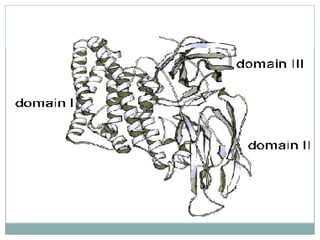
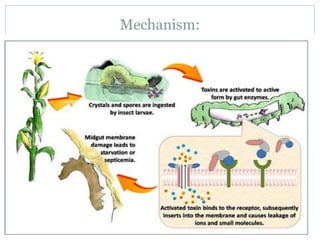
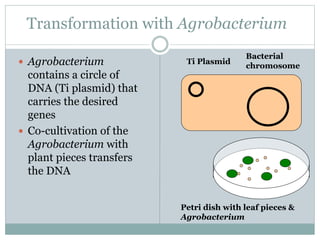
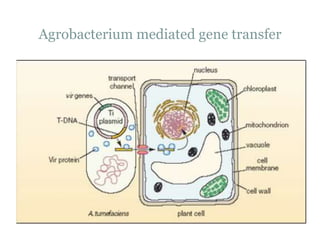
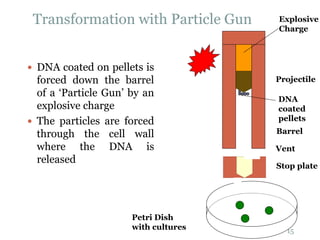
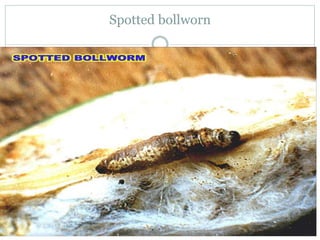
This document provides an overview of BT cotton, including its history, mechanism, pros, cons, and future perspectives. BT cotton is a genetically modified cotton variety that produces insecticides to protect against bollworms. It was first developed in 1996 and introduced commercially. The document discusses how BT cotton provides insect resistance through cry proteins that target the larvae of moths and butterflies. It notes several pros, such as increased yields and reduced environmental pollution from pesticides, but also some cons like high costs and potential issues from overuse. The future of BT cotton appears promising with new hybrids in development that address additional issues like drought tolerance.