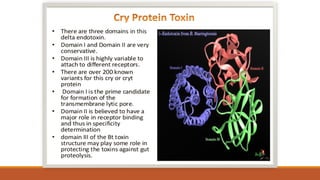
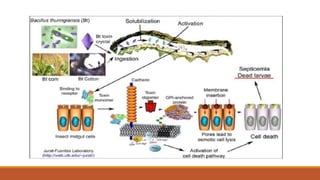
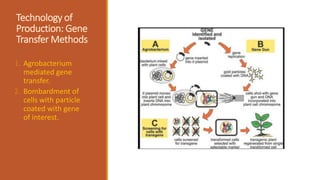
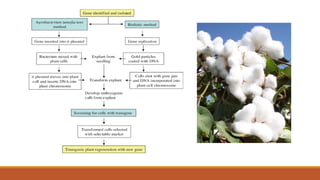
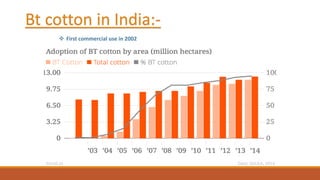
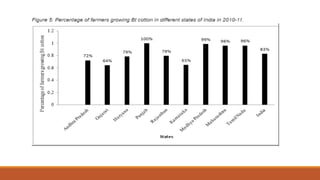
Bt cotton is a genetically modified cotton plant that produces an insecticide to combat pests like bollworms. It contains a gene from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), a soil bacterium that produces crystal proteins that are toxic to the larvae of moths and butterflies but harmless to other organisms. The Bt protein is activated in the alkaline environment of the insect's gut and makes holes in the lining, killing the insect. Bt cotton provides benefits like increased yields, reduced insecticide use, and lower costs, but also has disadvantages like higher seed prices and concerns about its effects on human and environmental health. India was an early adopter of Bt cotton in 2002.