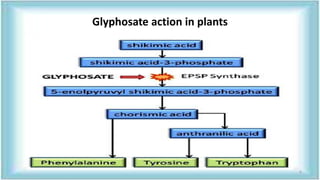
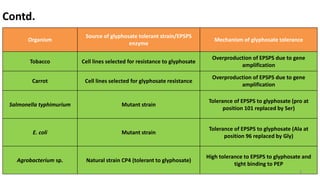
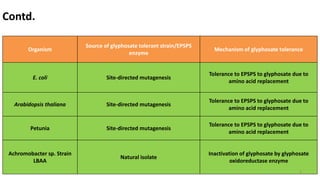
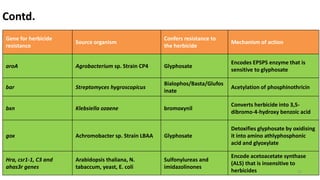
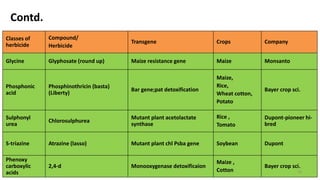
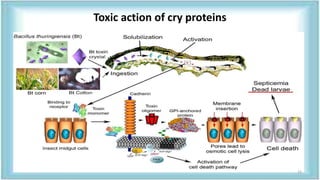
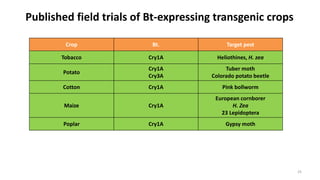
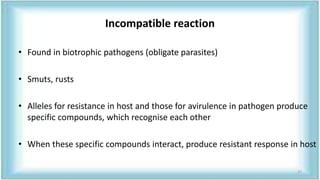
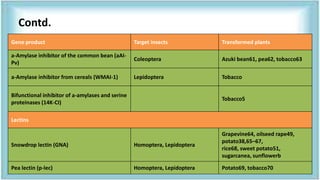
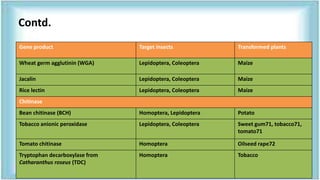
This document discusses genetic engineering approaches for improving biotic stress tolerance in plants. It focuses on engineering resistance to herbicides, insects, fungi and bacteria. For herbicide resistance, genes have been introduced that encode herbicide-insensitive versions of the EPSPS enzyme or enzymes that can degrade herbicides. For insect resistance, genes from Bacillus thuringiensis encoding cry toxins have been widely used, as well as genes encoding protease inhibitors, lectins, and chitinases. For resistance to fungi and bacteria, genes involved in the plant's incompatible hypersensitive response have potential for engineering resistance.