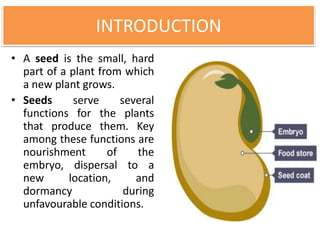
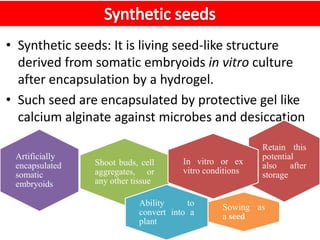
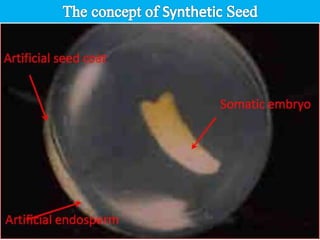
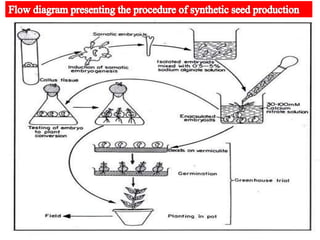
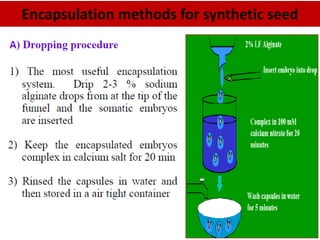
Synthetic seeds are encapsulated somatic embryos or shoot buds that can be used for planting like traditional seeds. They allow for clonal propagation of plants that are difficult to reproduce through traditional seeds, including some fruit crops. The production of synthetic seeds involves inducing somatic embryogenesis in callus cultures, maturing the embryos, and encapsulating them in a protective gel before planting. This allows genetic material to be stored and dispersed while avoiding issues with seed-borne diseases, low seed viability, and difficulties reproducing species that lack traditional seeds.