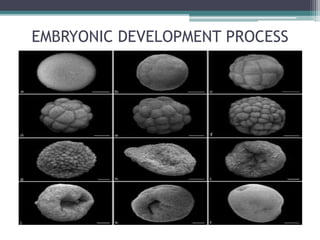
After fertilization, an embryo undergoes three main processes:
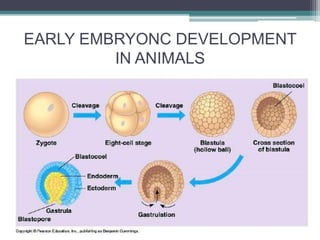
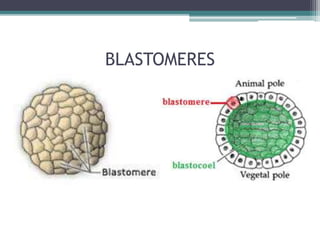
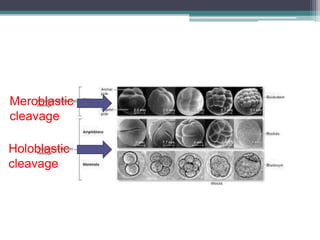
1) Cleavage - The zygote rapidly divides through holoblastic or meroblastic cleavage to form a hollow ball of cells called a blastula.
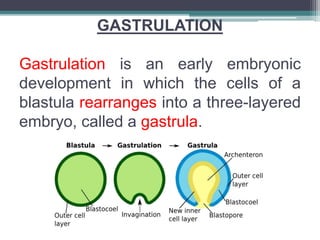
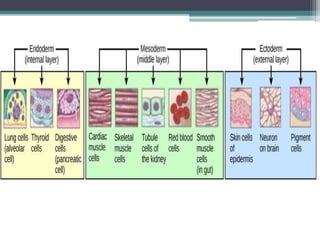
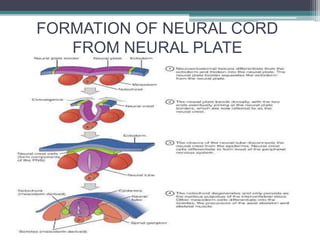
2) Gastrulation - The blastula cells rearrange to form the three germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
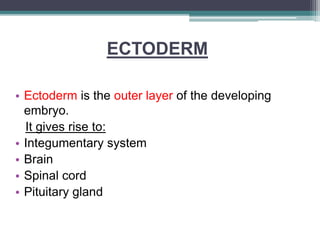
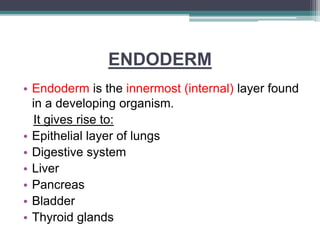
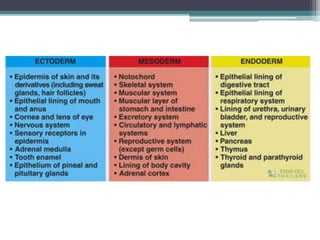
3) Organogenesis - The germ layers develop into organs, with the ectoderm forming skin and nervous system, endoderm forming lung, digestive, and glandular tissues, and mesoderm forming muscle and blood tissues.