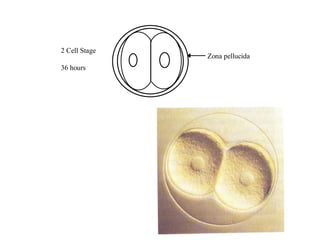
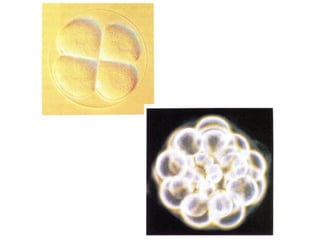
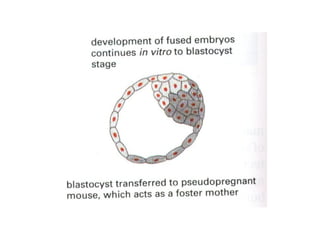
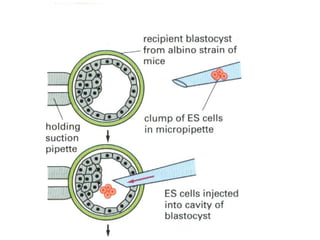
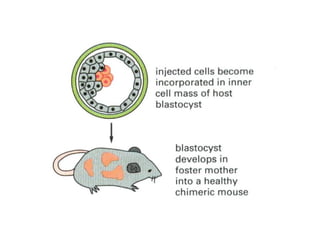
1) Early mammalian embryonic development involves cleavage divisions that result in a solid ball of cells called a morula.
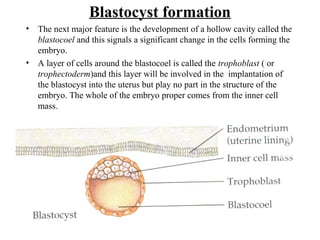
2) The morula develops into a blastocyst containing an inner cell mass and outer trophoblast layer.
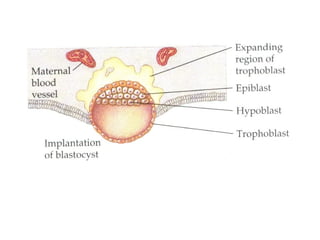
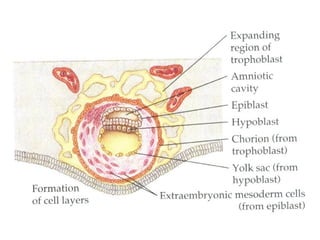
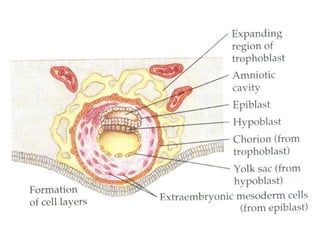
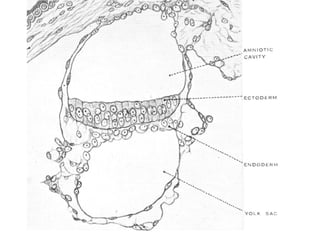
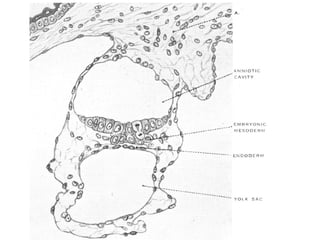
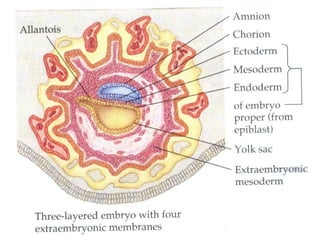
3) Around 7-10 days, the blastocyst implants into the uterine wall and the trophoblast penetrates the lining, forming finger-like villi that will become the placenta. Extra-embryonic tissues including the amnion, yolk sac, and allantois develop to support the growth of the embryo.