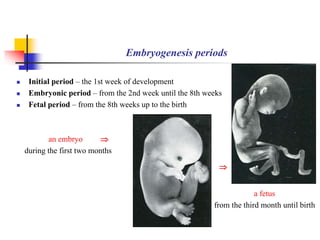
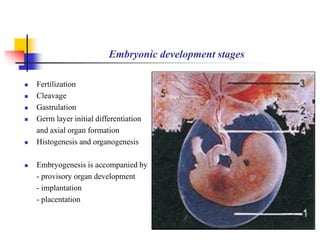
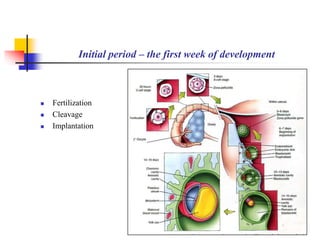
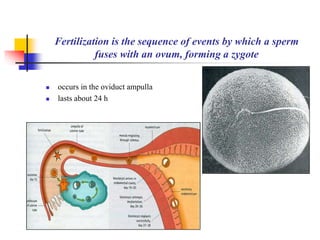
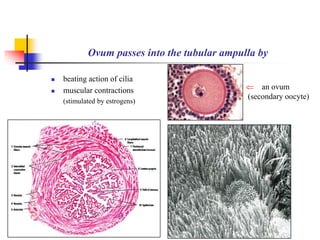
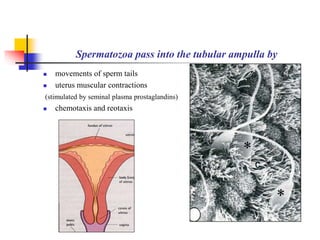
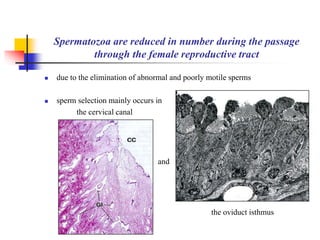
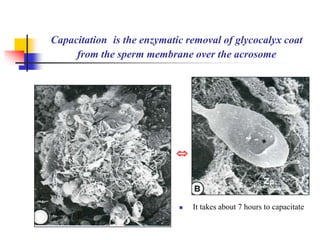
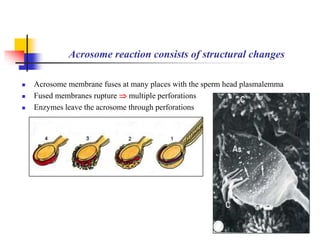
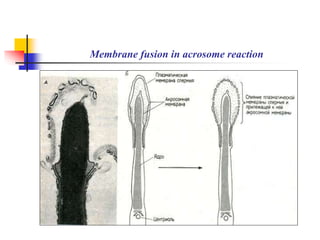
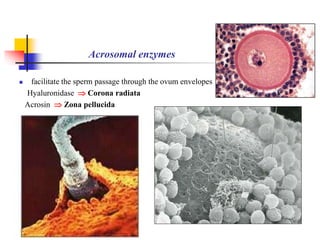
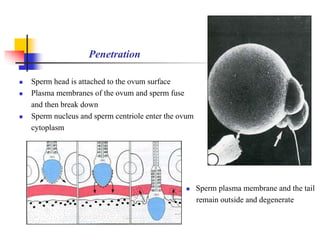
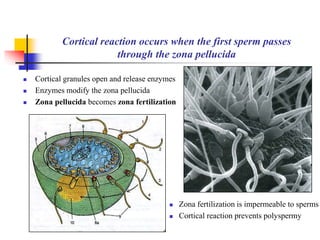
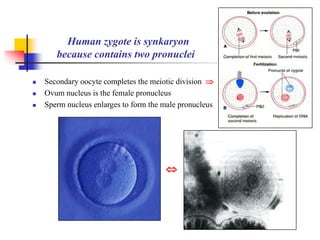
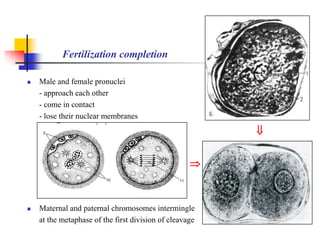
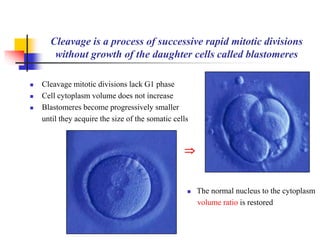
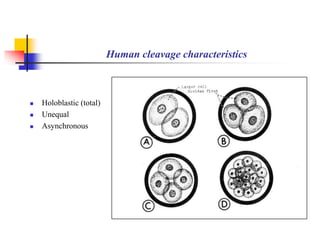
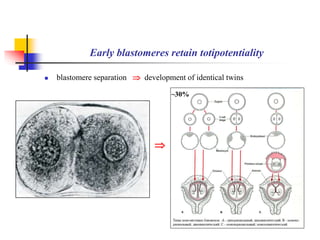
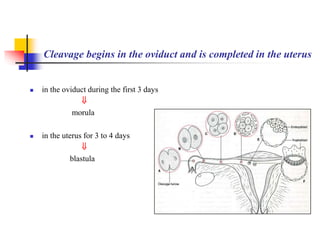
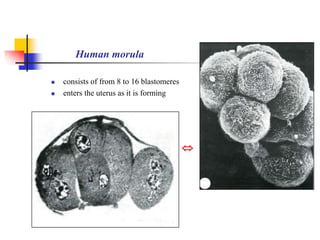
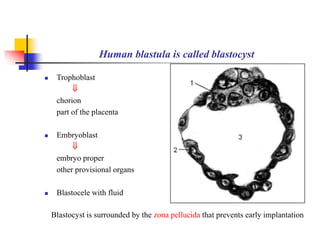
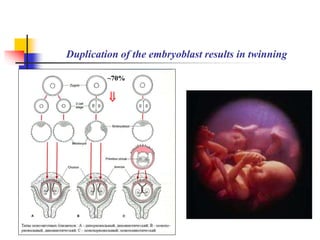
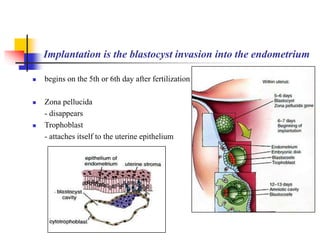
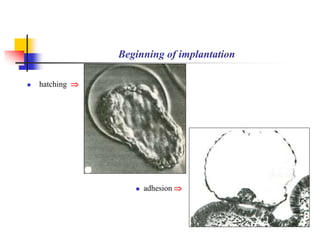
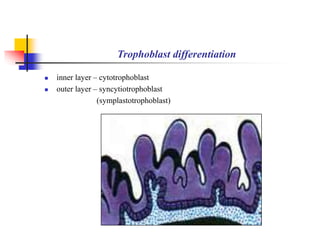
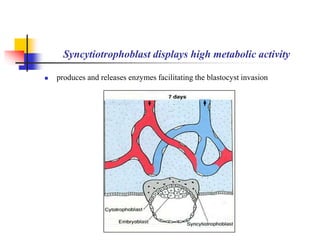
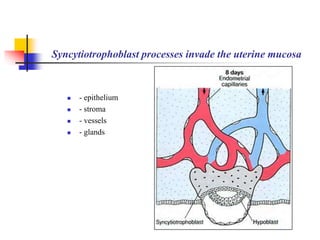
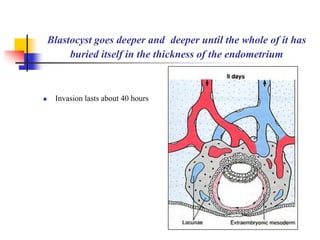
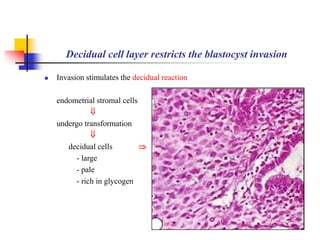
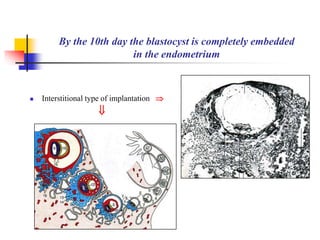
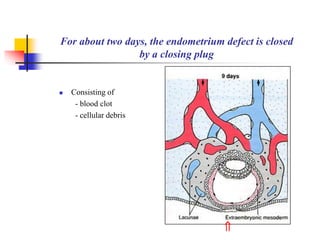
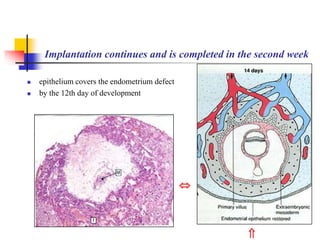
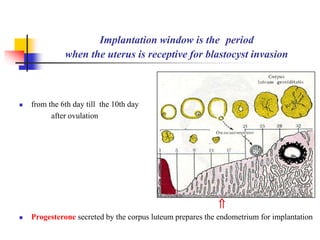
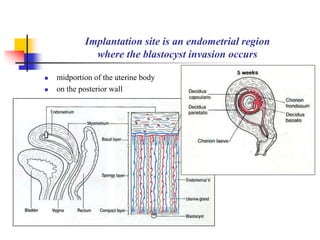
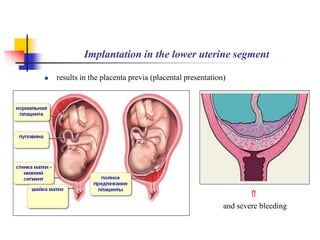
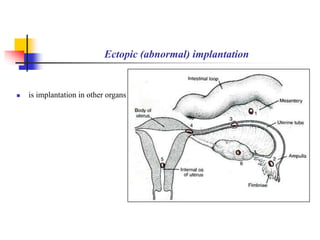
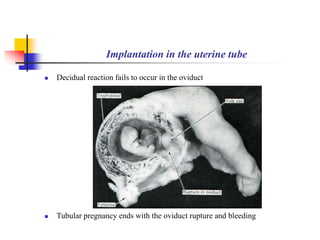
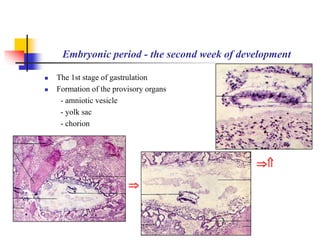
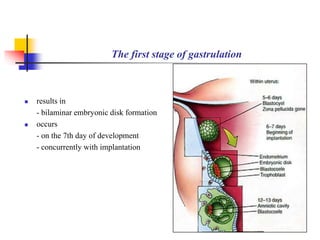
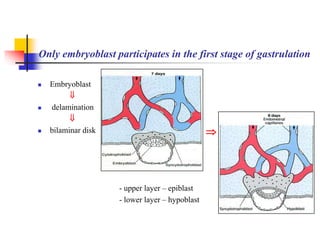
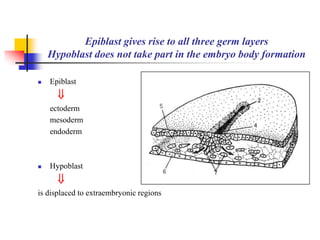
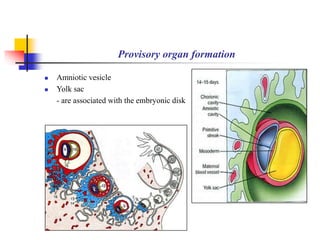
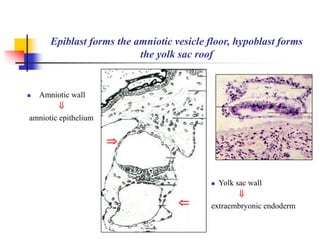
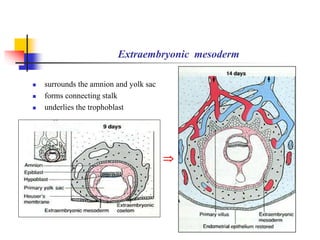
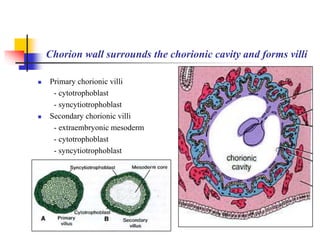
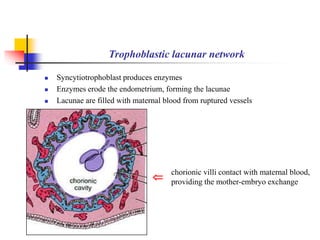
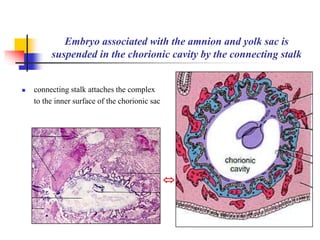
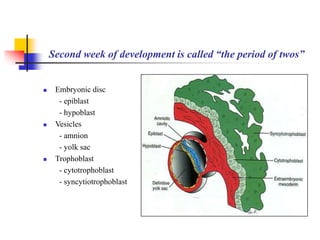
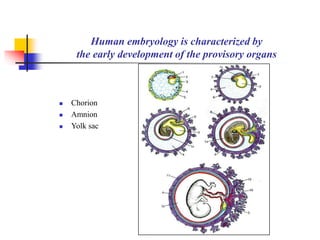
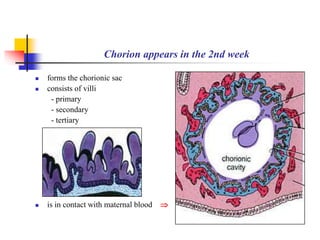
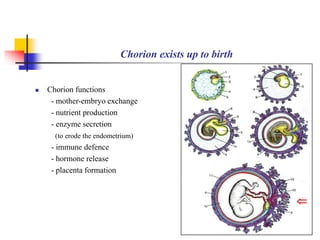
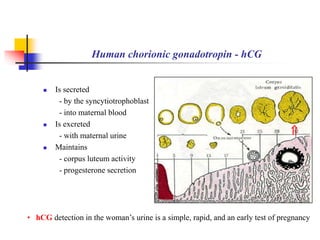
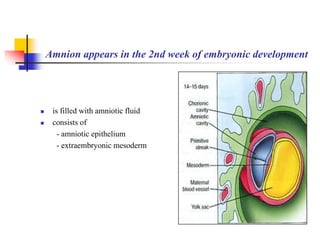
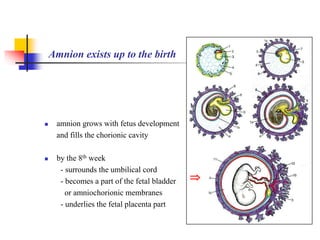
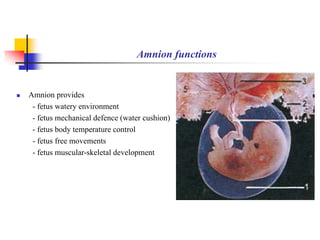
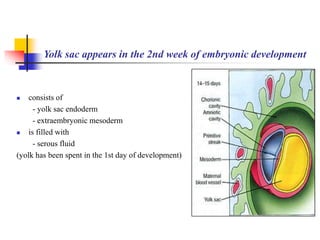
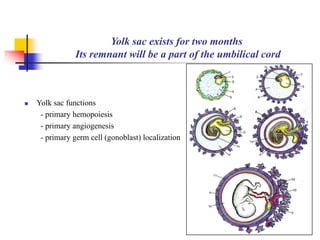
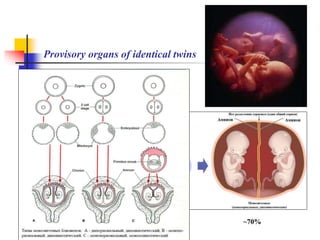
The document provides an in-depth overview of human embryology, detailing the prenatal period from fertilization to birth which spans 280 days. It outlines the stages of embryonic development, including fertilization, cleavage, implantation, and the formation of provisional organs such as the chorion, amnion, and yolk sac. Key processes such as the acrosome reaction during fertilization, the changes in the zygote, and the stages of gastrulation and implantation are also discussed.