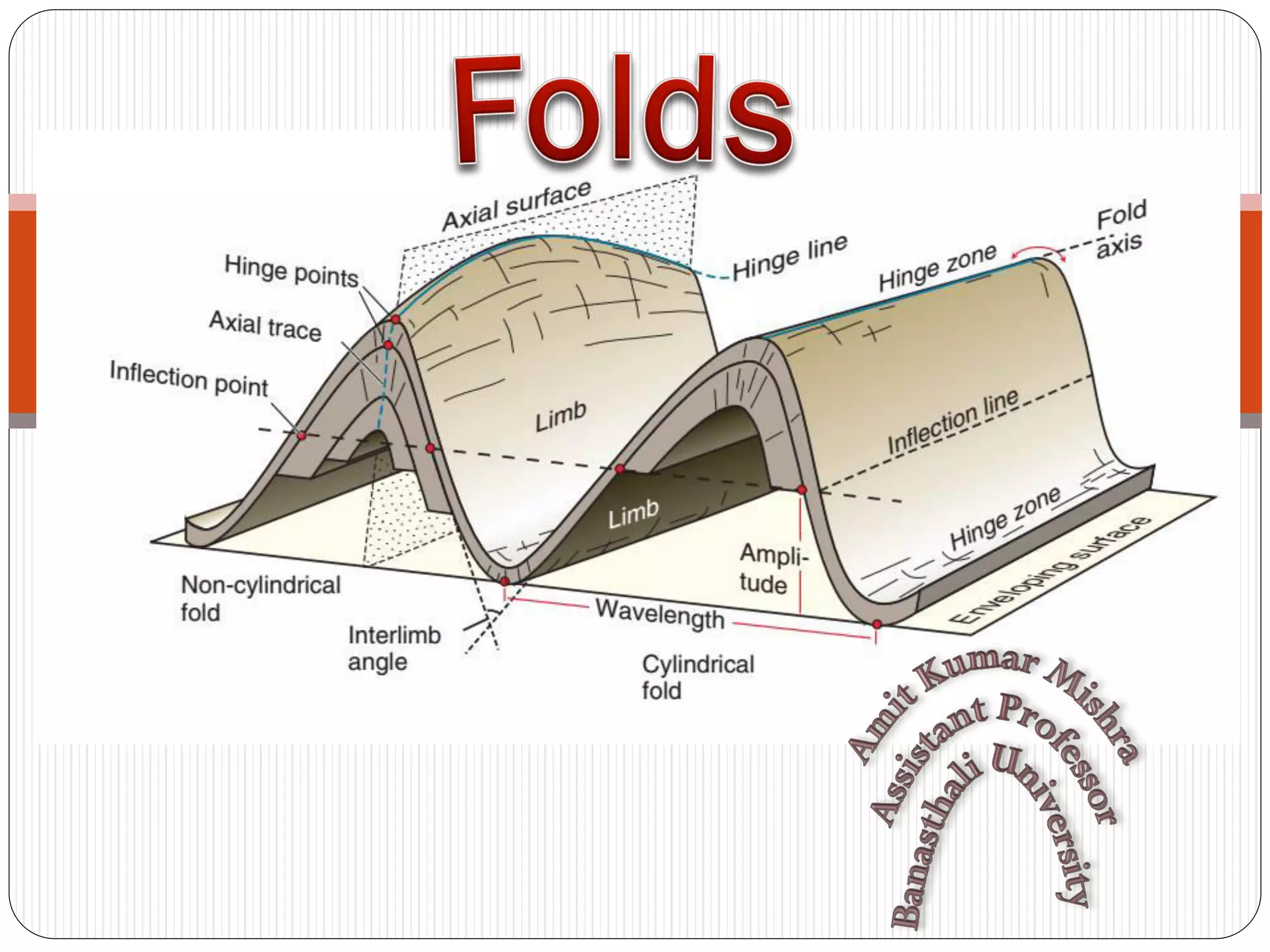
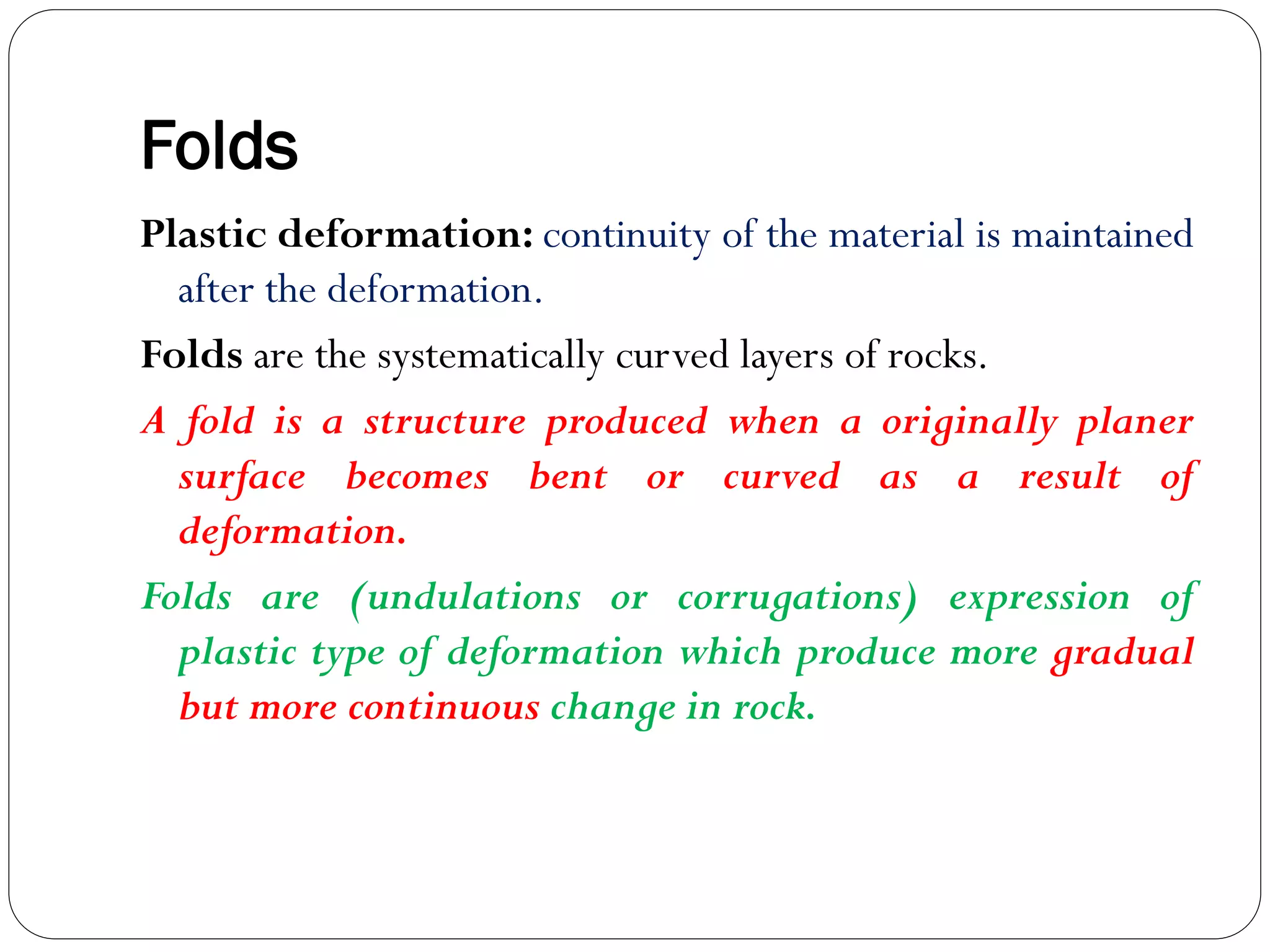
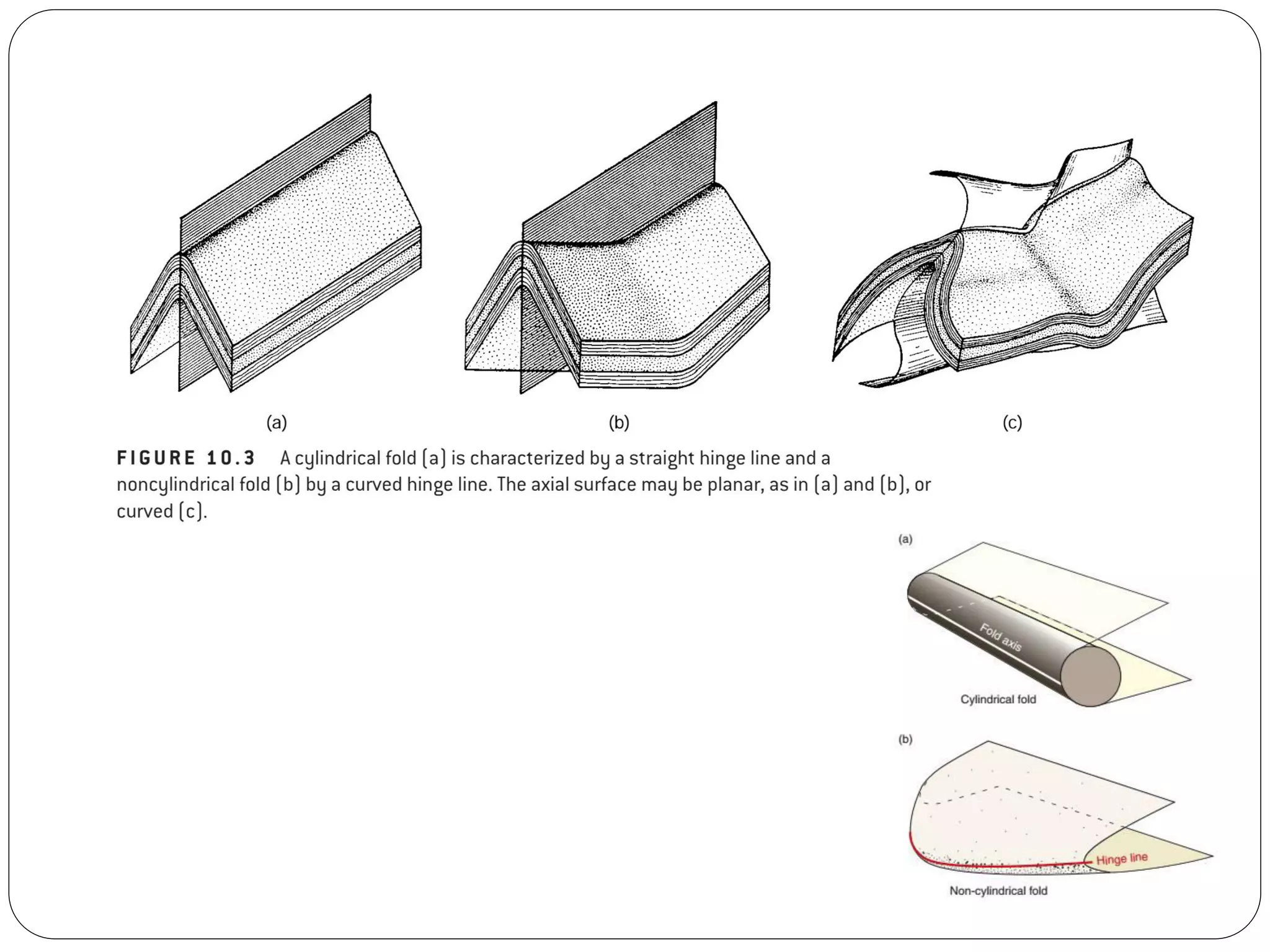
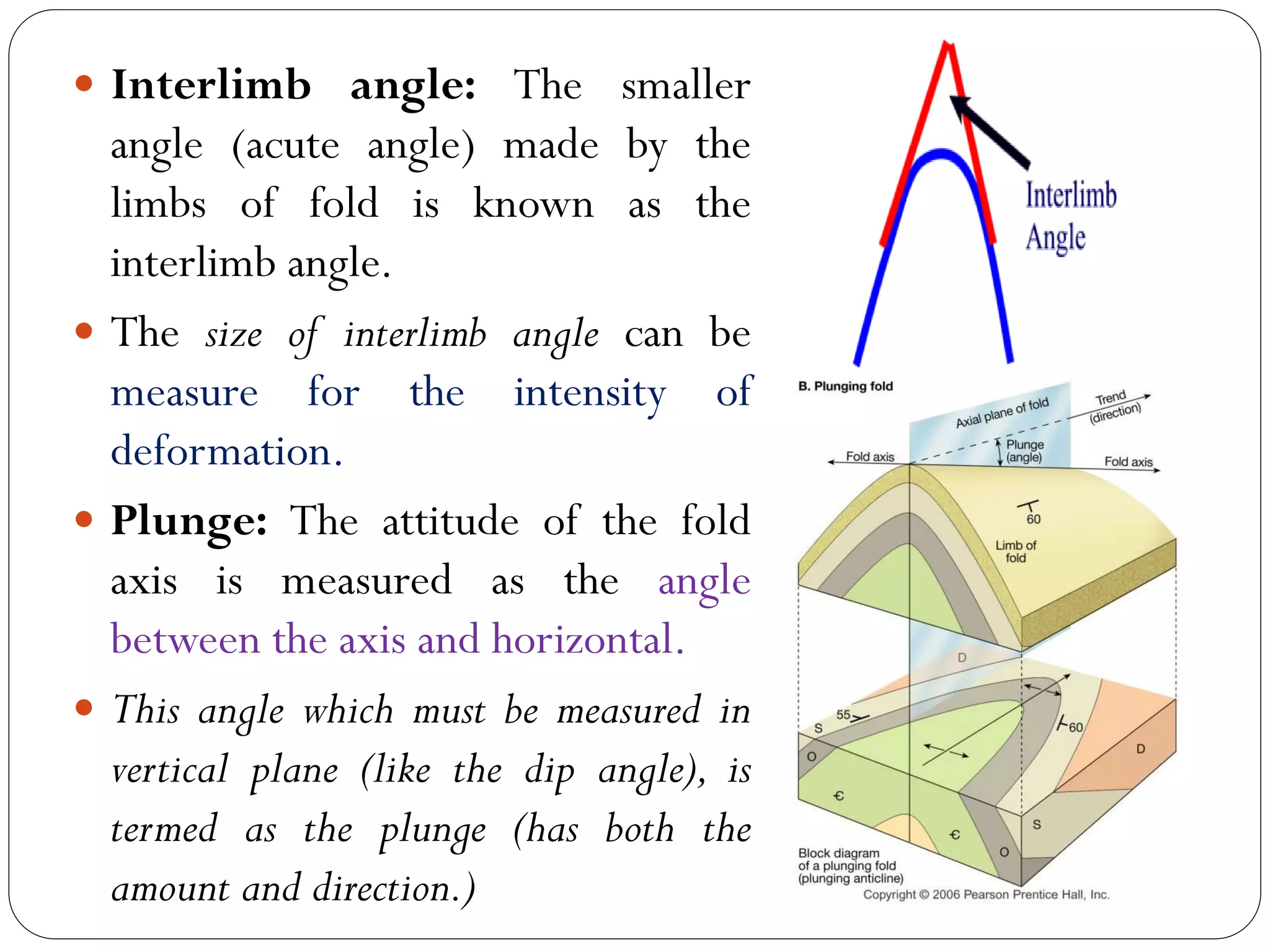
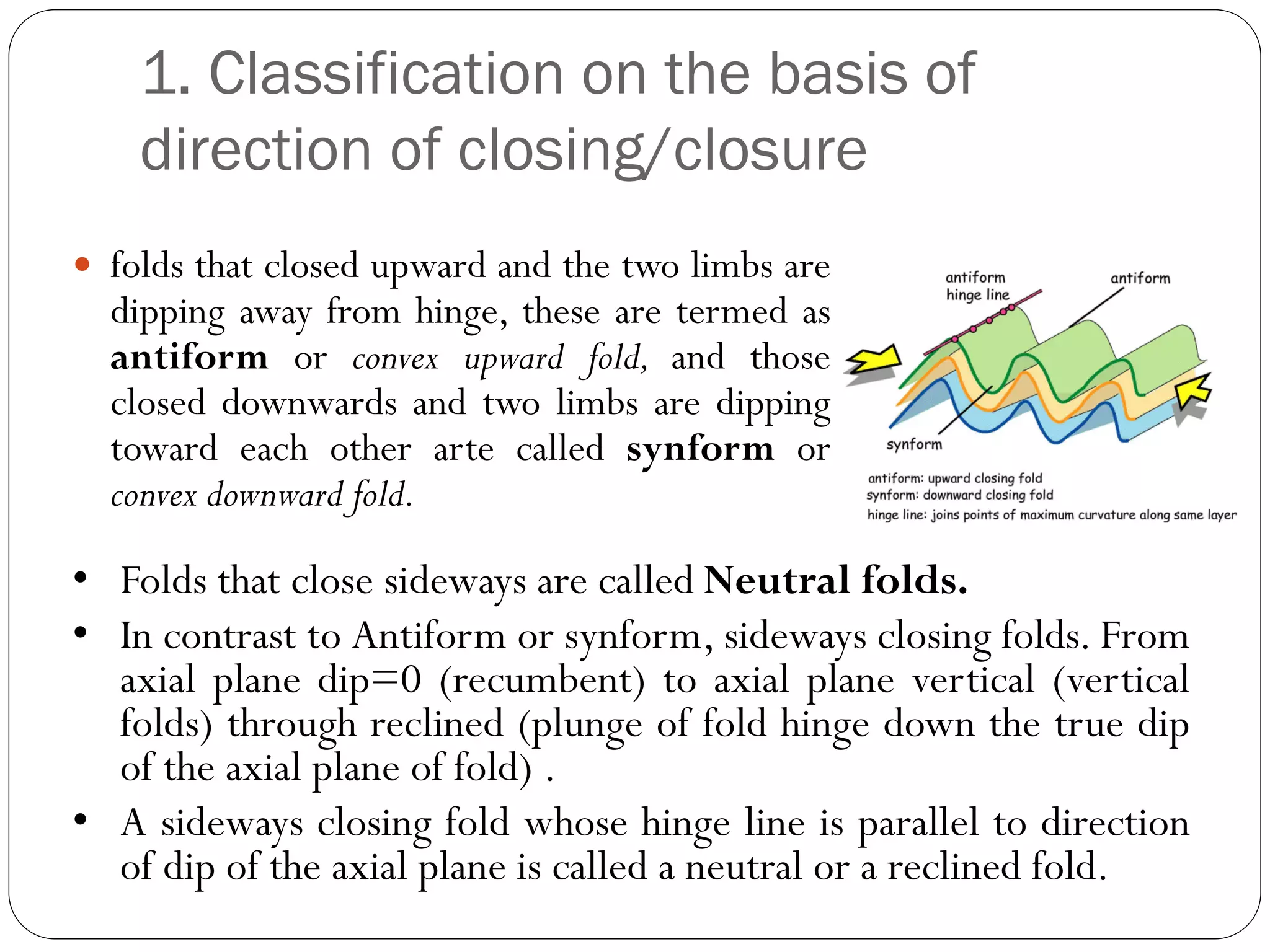
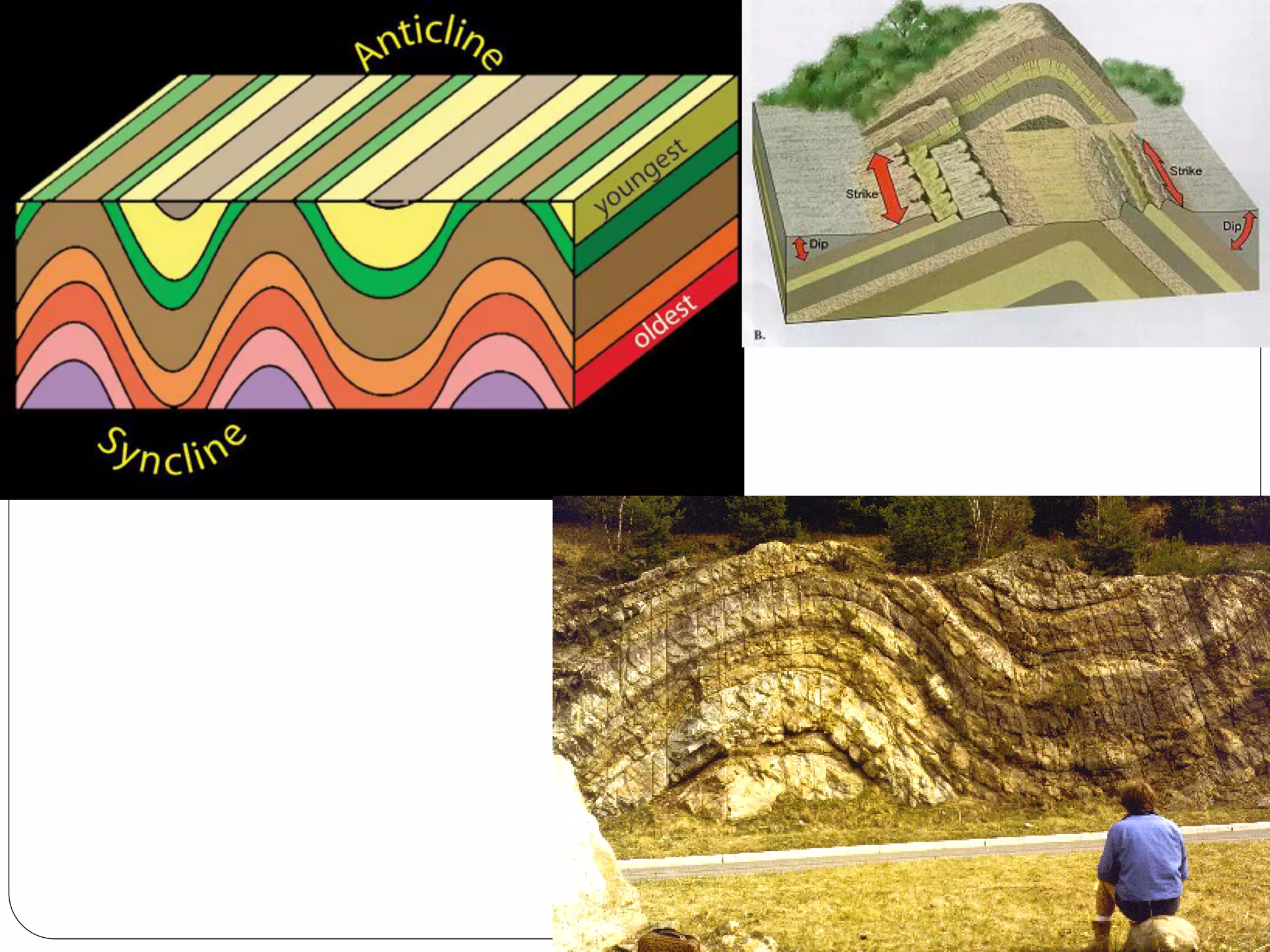
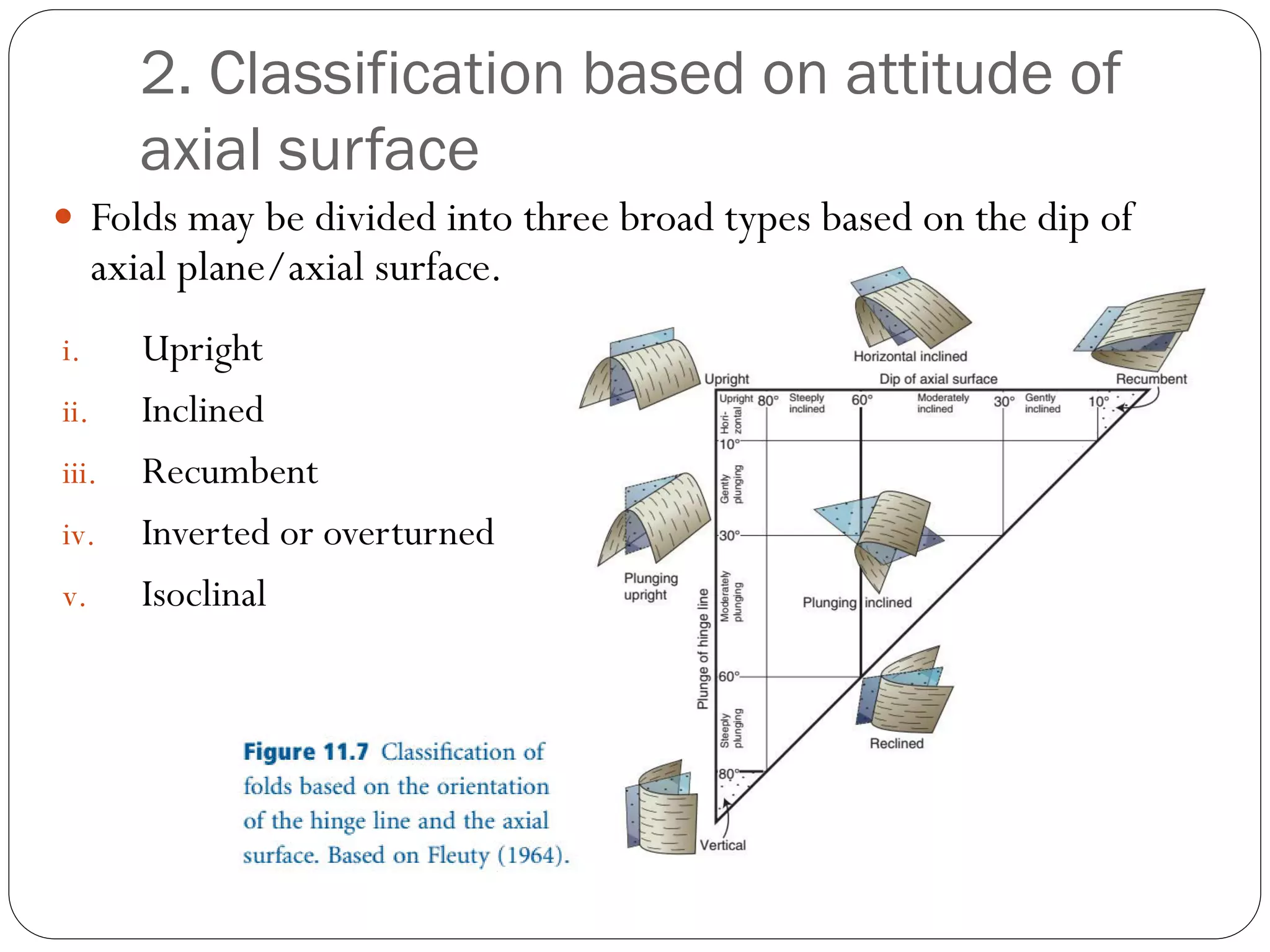
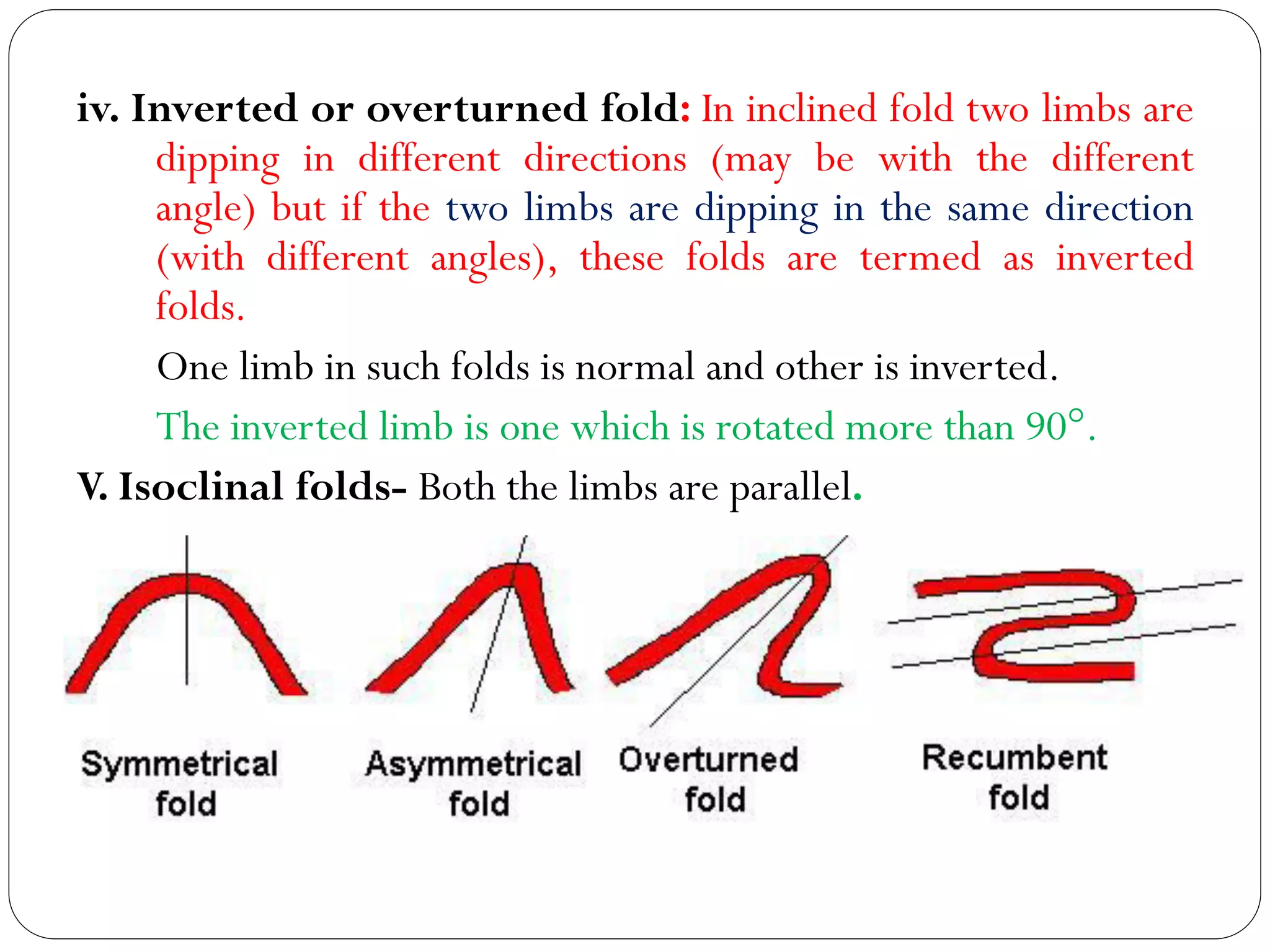
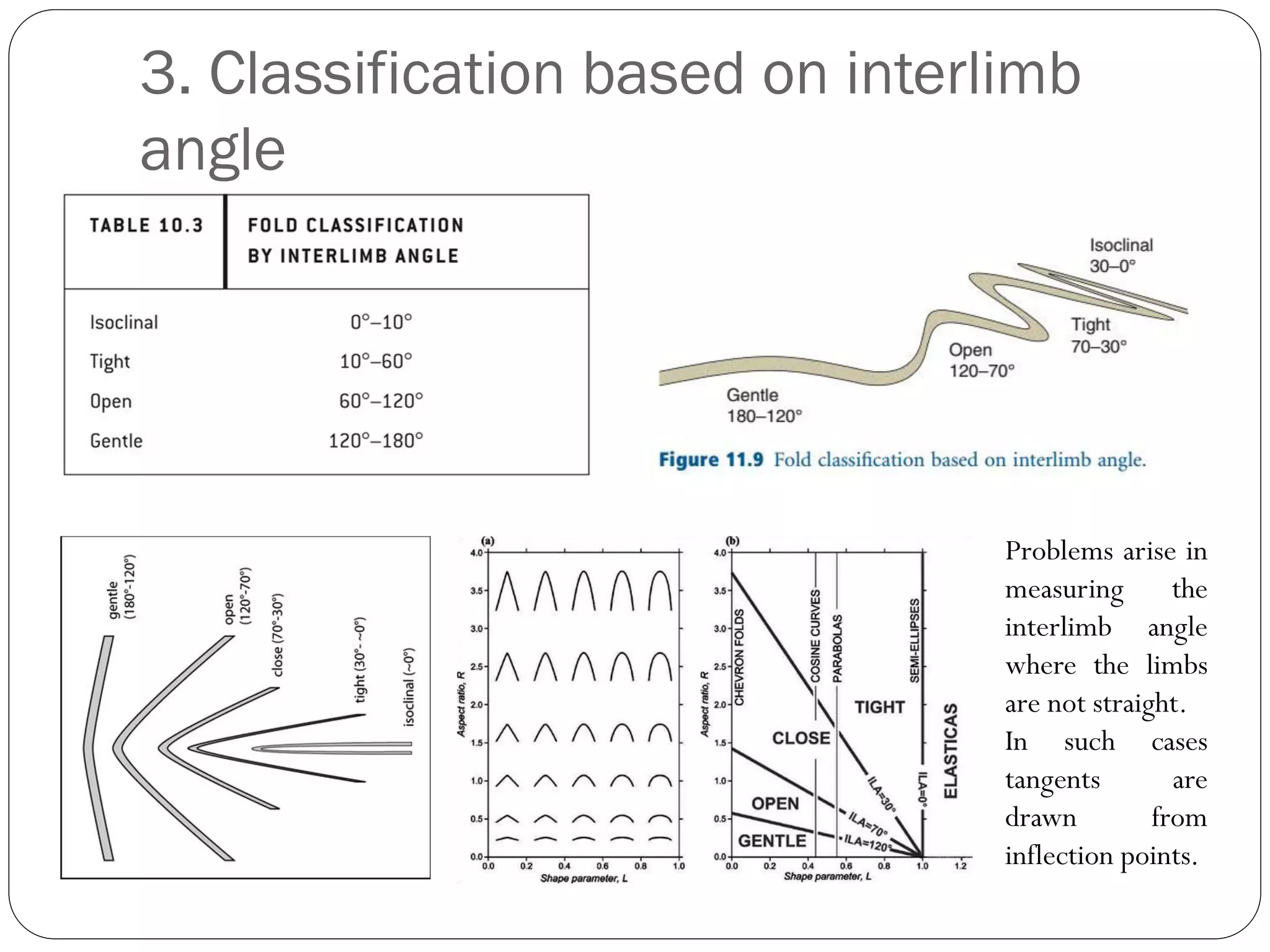
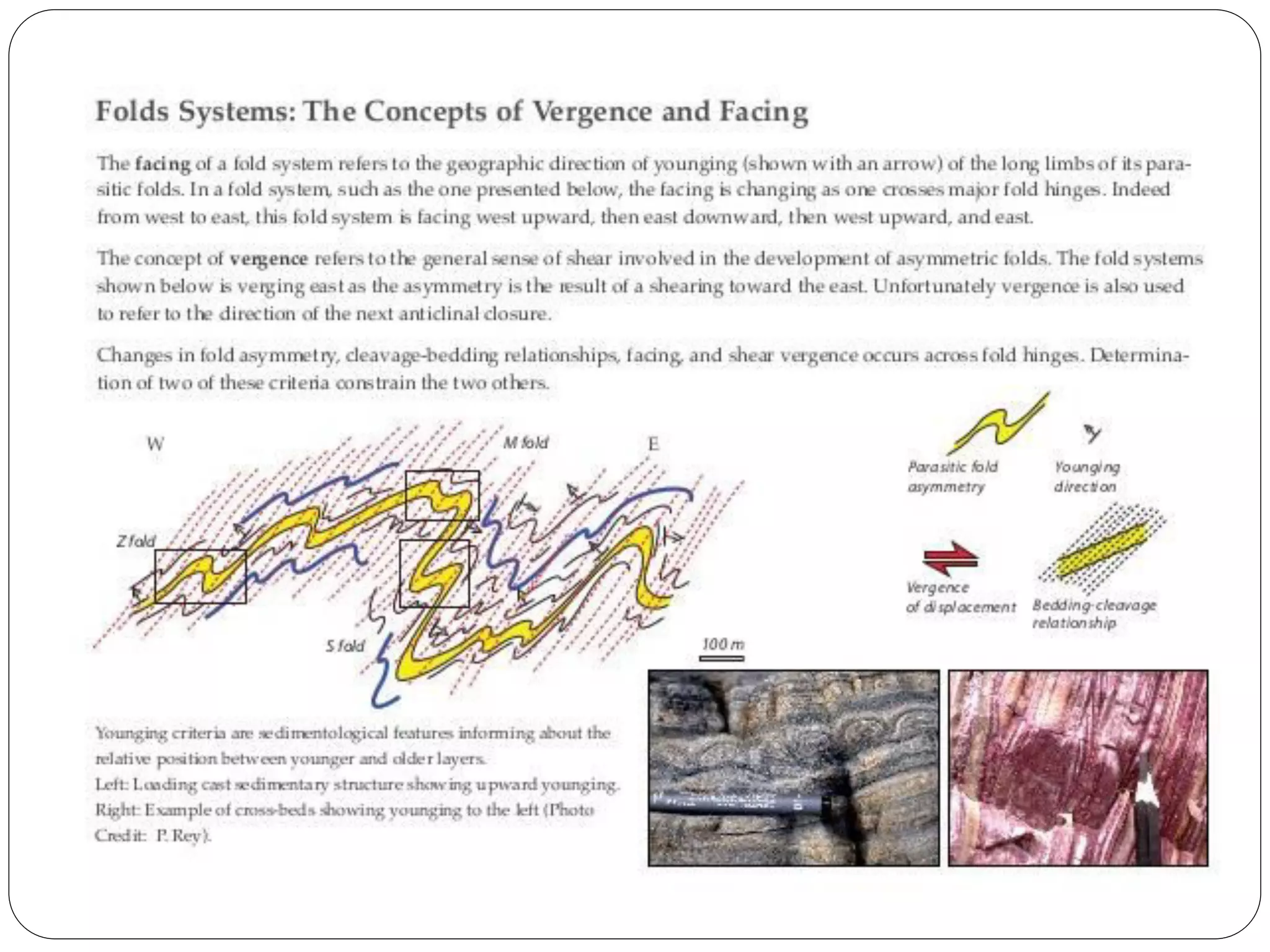
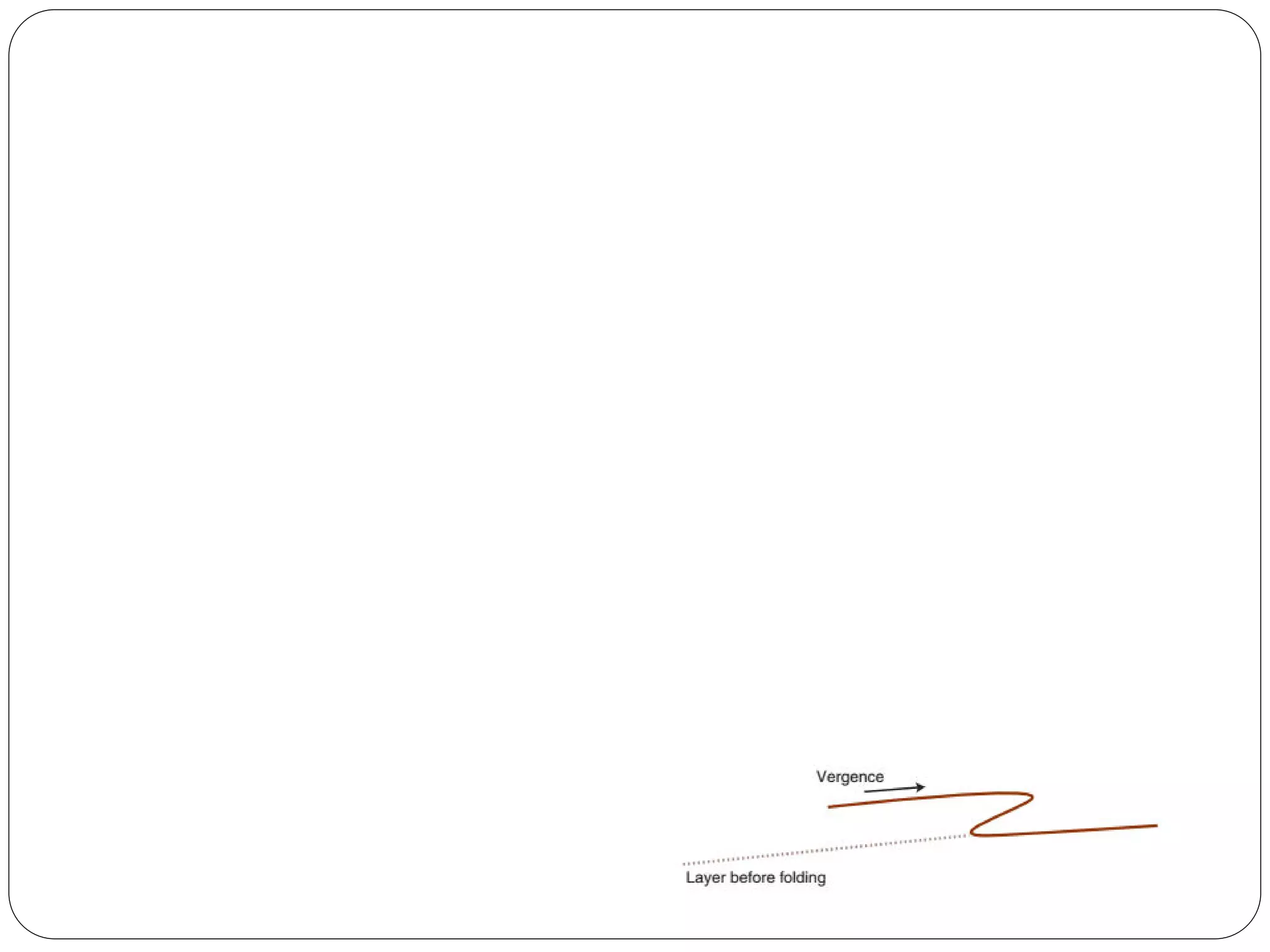
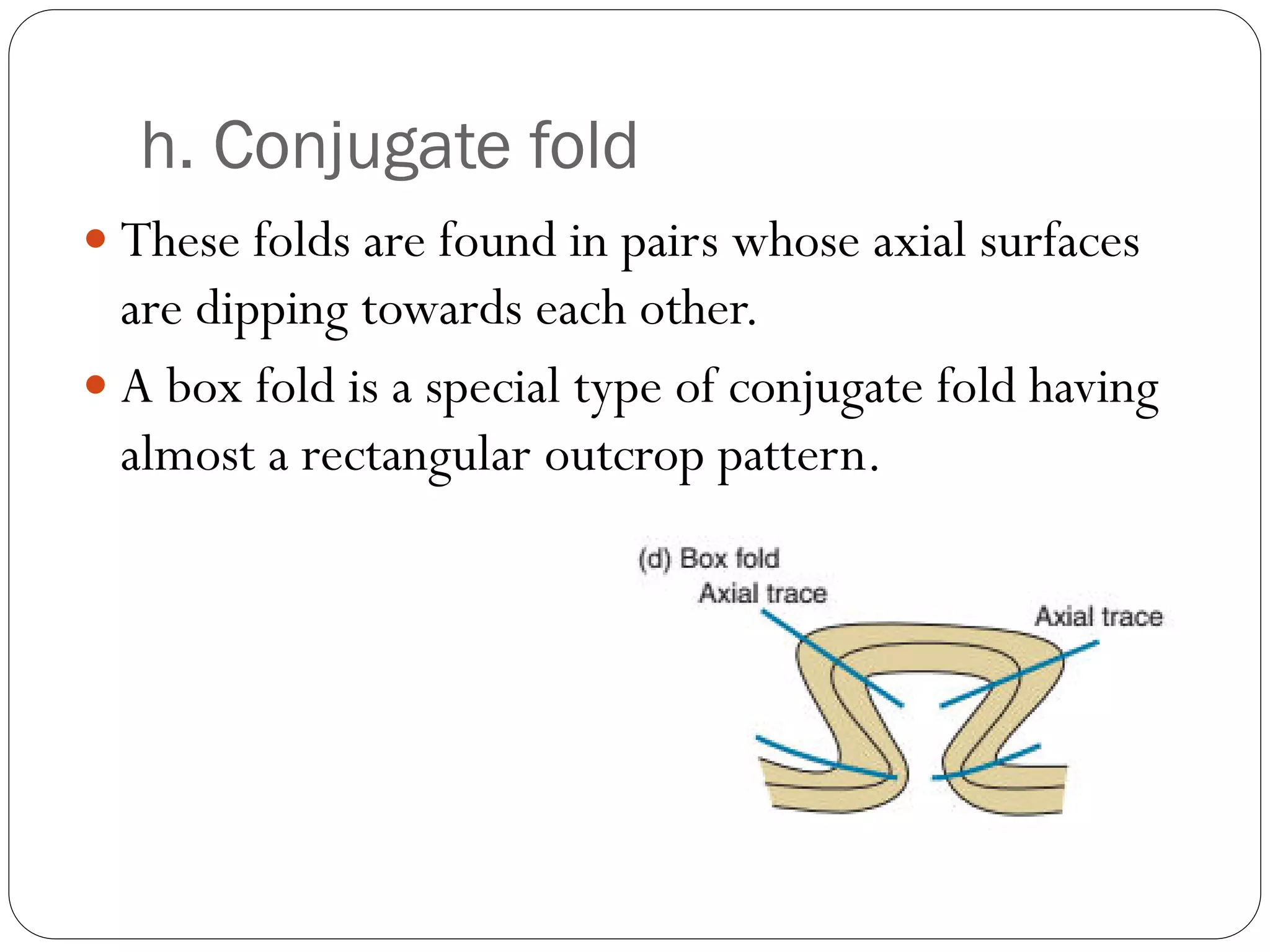
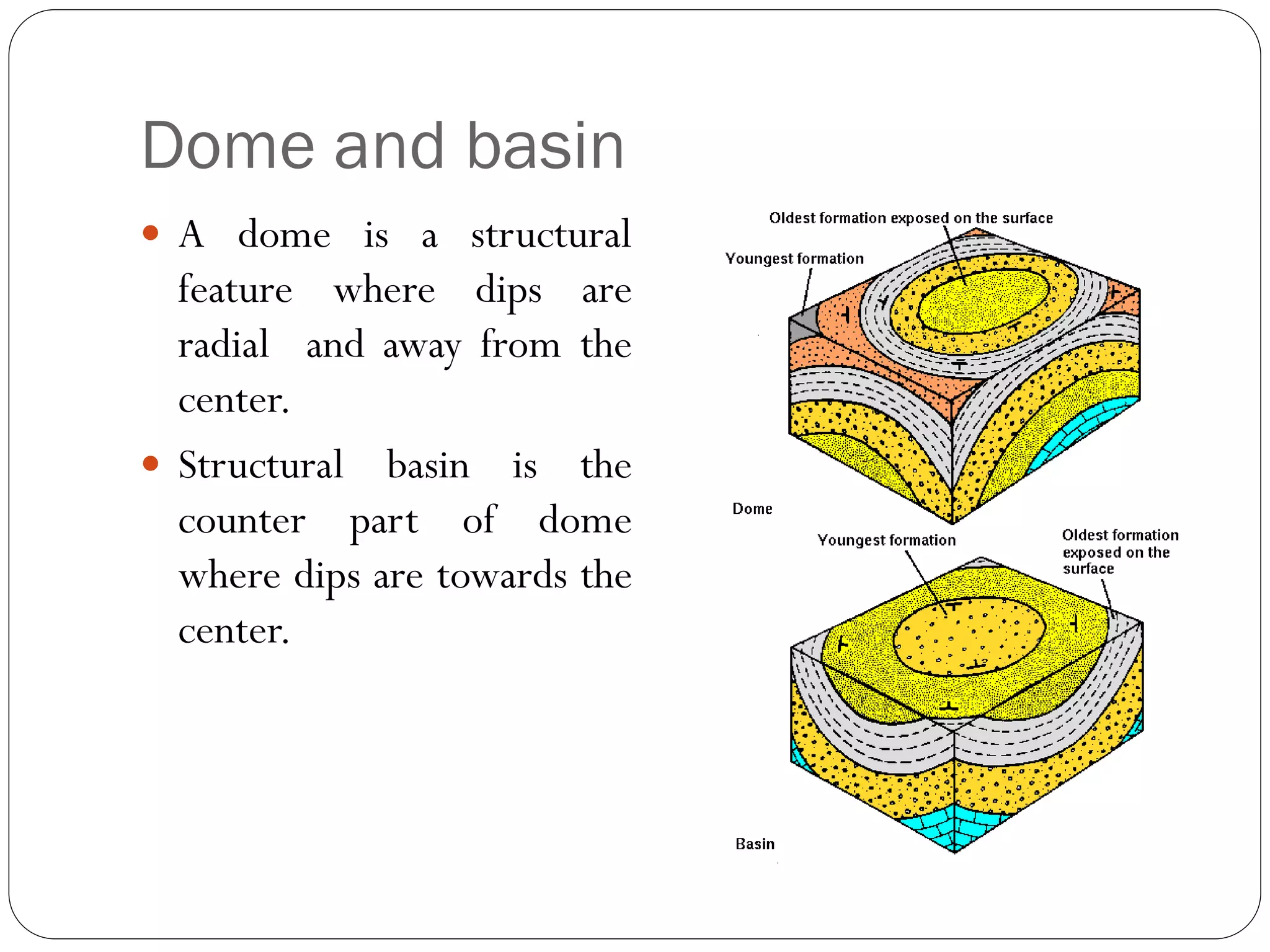
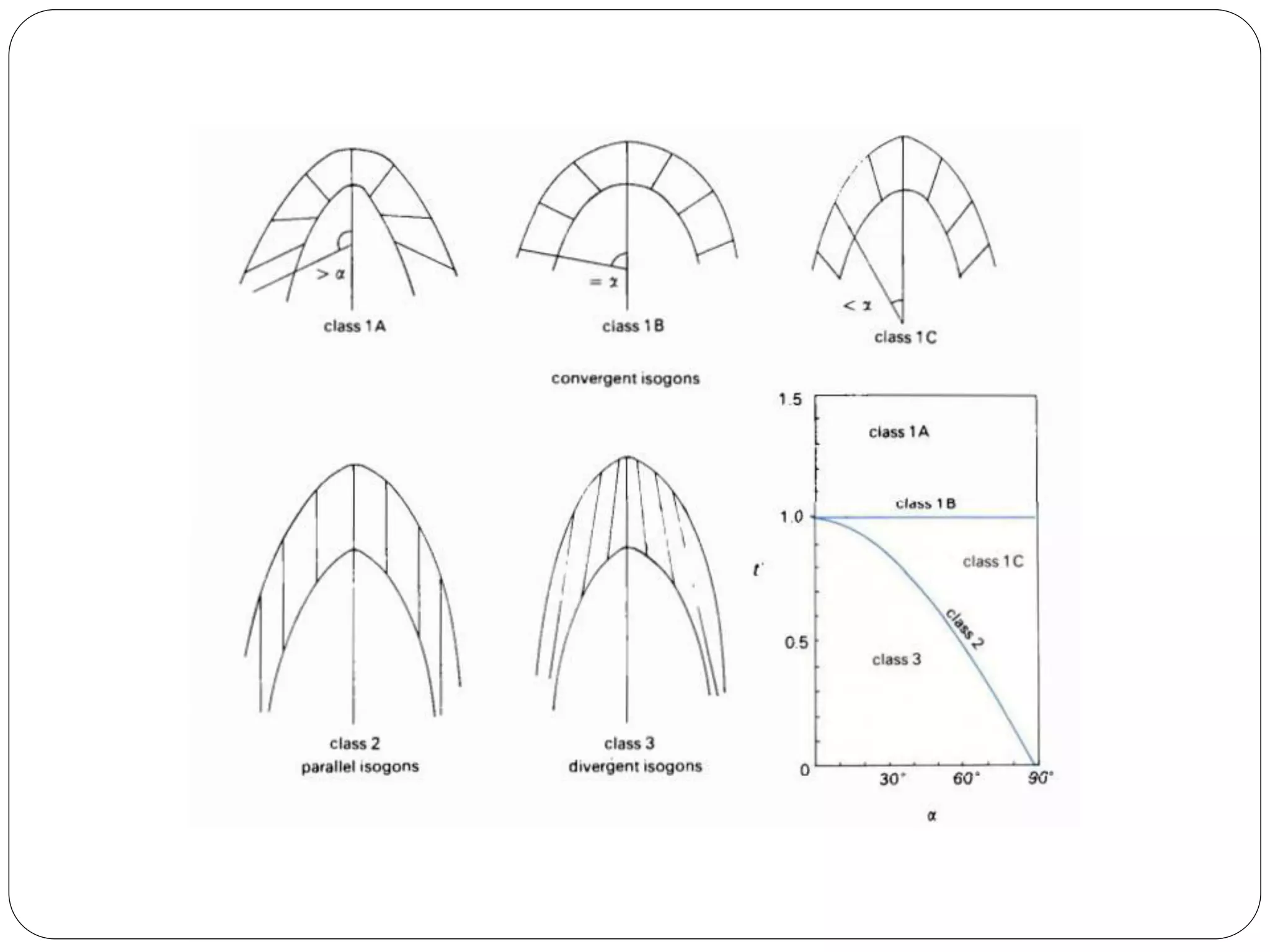
The document discusses the concept of folds in geology, describing their characteristics, classifications, and components such as hinges, limbs, and axial planes. It details the various types of folds classified by direction of closing, attitude of the axial surface, and interlimb angles, as well as specific examples like anticlinal and synclinal folds. Additionally, it explains geometric classifications based on dip isogons and highlights different fold styles and their features.