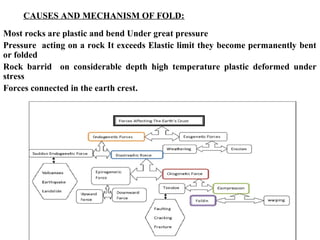
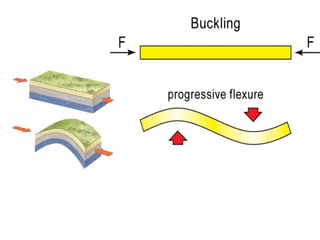
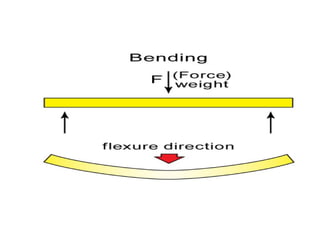
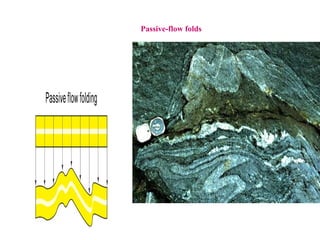
This document discusses various mechanisms of rock folding. It defines folding as the bending of rock strata due to compressional forces. There are several types of fold mechanisms including buckling, bending, flexure folding, flexural slip, flexural flow, passive flow, and kink folding. Each mechanism is influenced by factors like temperature, pressure, fluid properties, and the composition and texture of the rock. Buckling involves shortening of rock layers under lateral pressure. Bending involves applying force across layers to produce gentle folds. Flexural slip forms parallel concentric folds through buckling or bending with slip along layering.