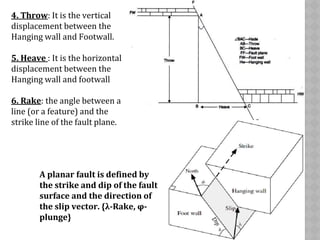
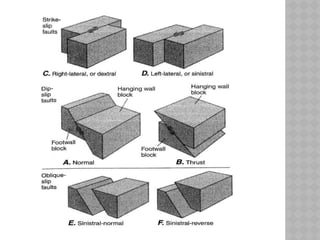
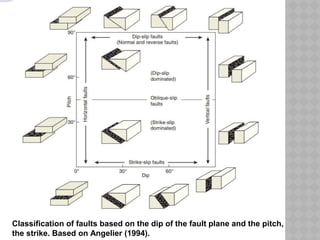
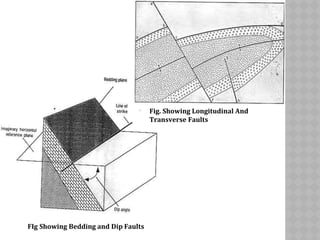
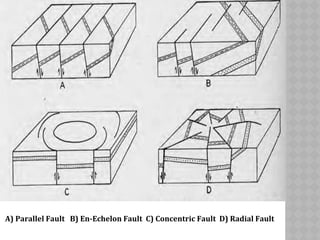
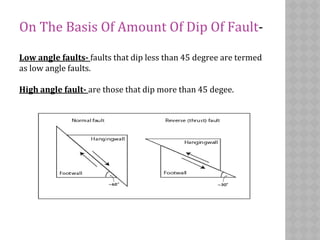
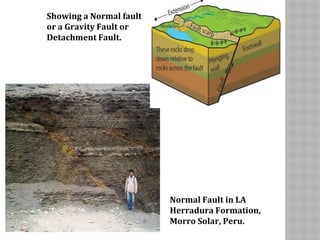
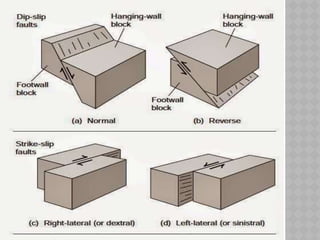
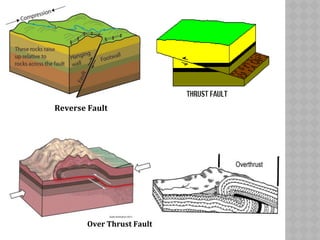
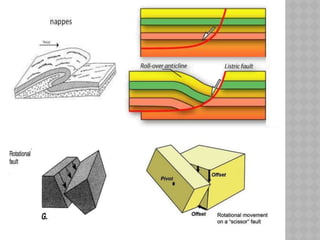
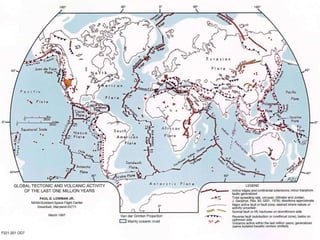
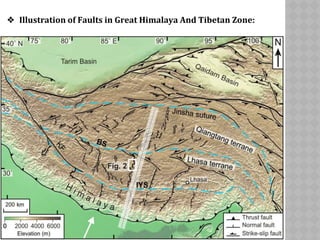
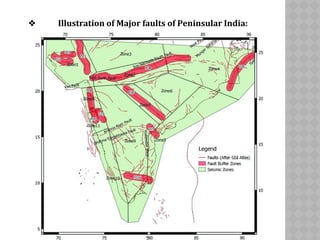
This document provides an overview of fault classification. It begins with definitions of fault geometry, including fault plane, dip, strike, hanging wall, footwall, throw, and rake. Faults can be classified geometrically based on attributes like rake, attitude relative to adjacent rocks, pattern, dip angle, and apparent movement. Major geometric types include strike-slip, dip-slip, and diagonal-slip faults. Genetic classification considers the relative movement, and identifies normal, reverse, thrust, strike-slip, and other fault types. Major faults in India are described along with the distribution of faults globally. In conclusion, the author emphasizes the geological and economic importance of studying faults, as well as their relevance to engineering and