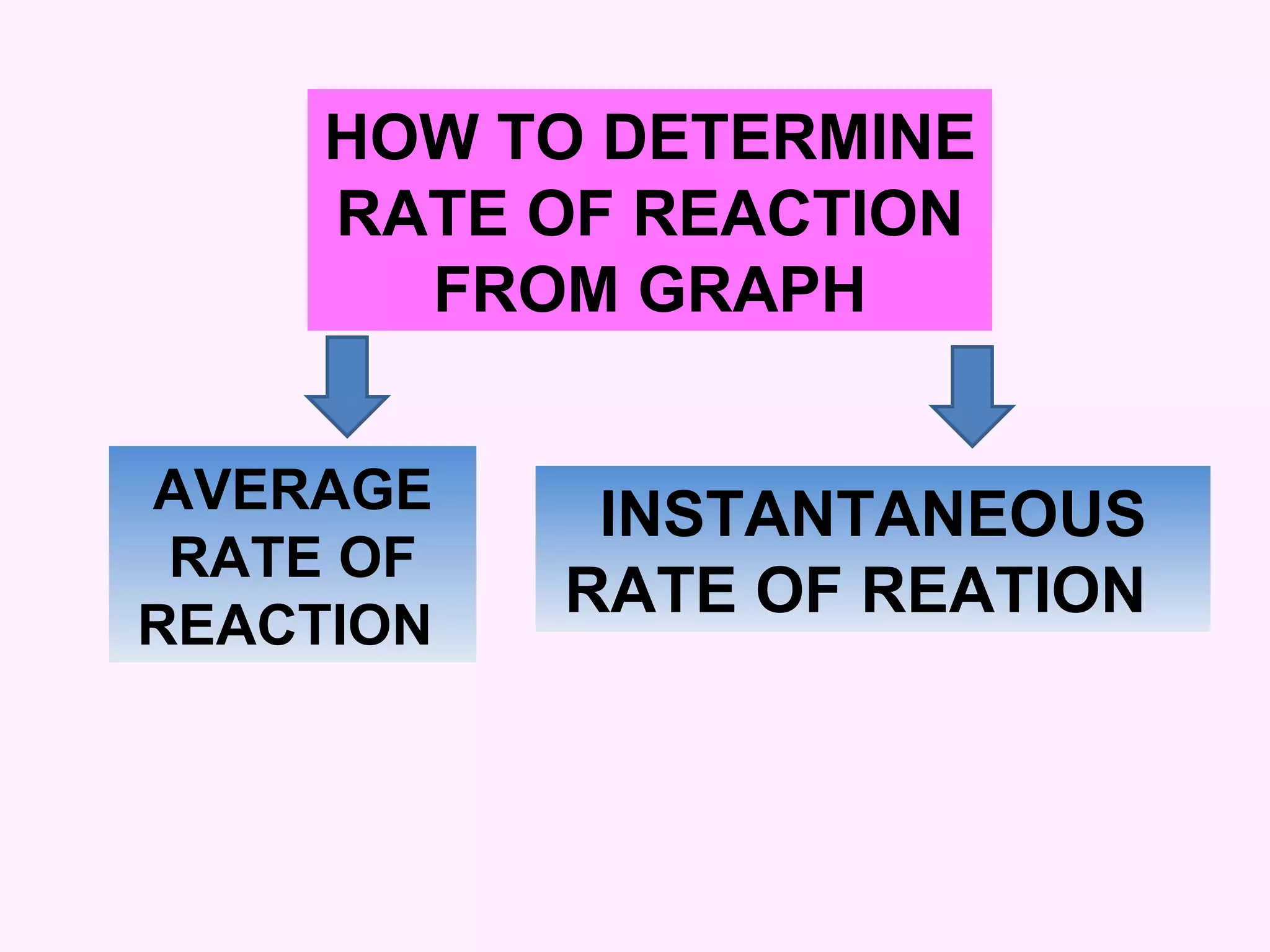
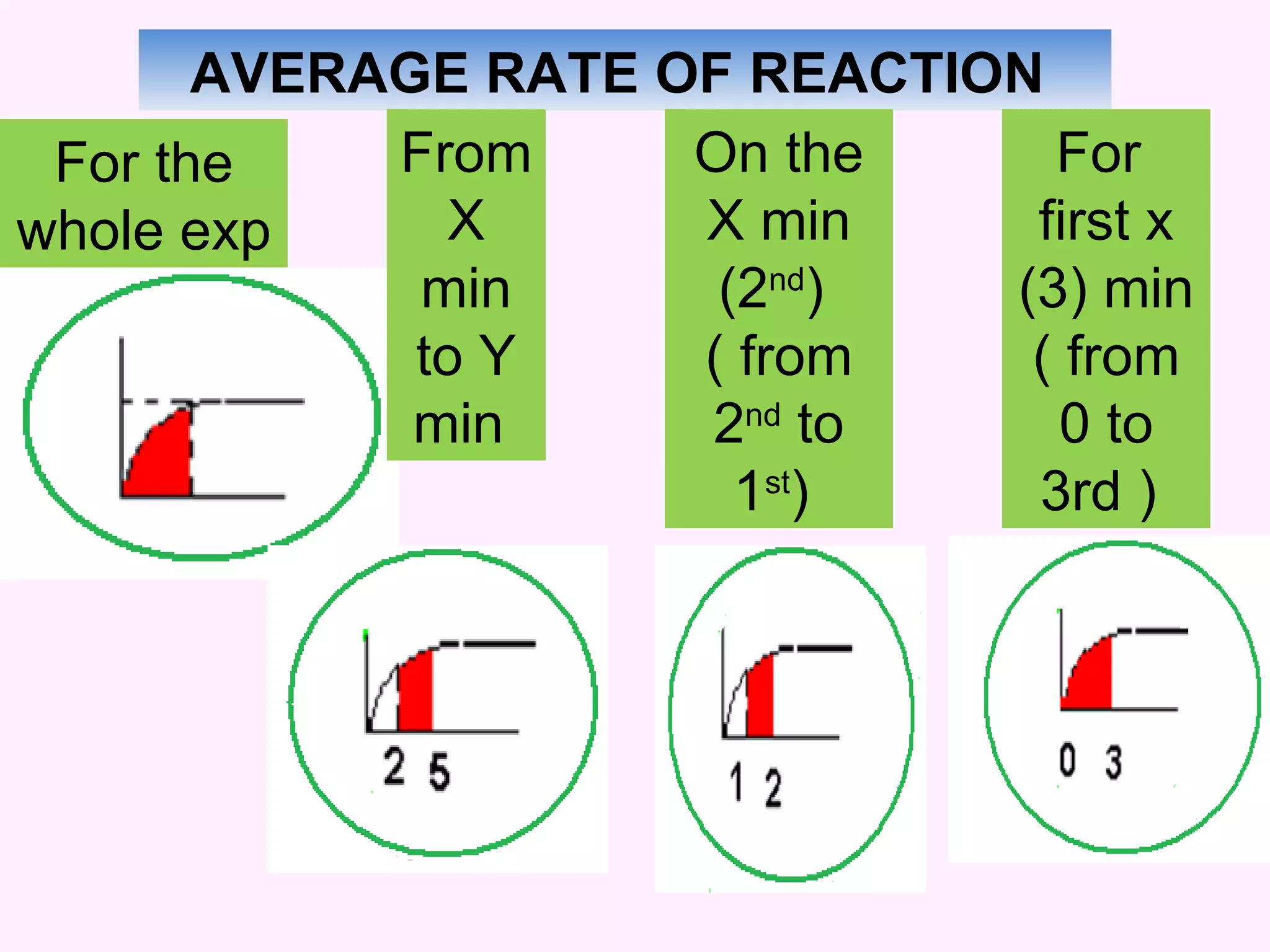
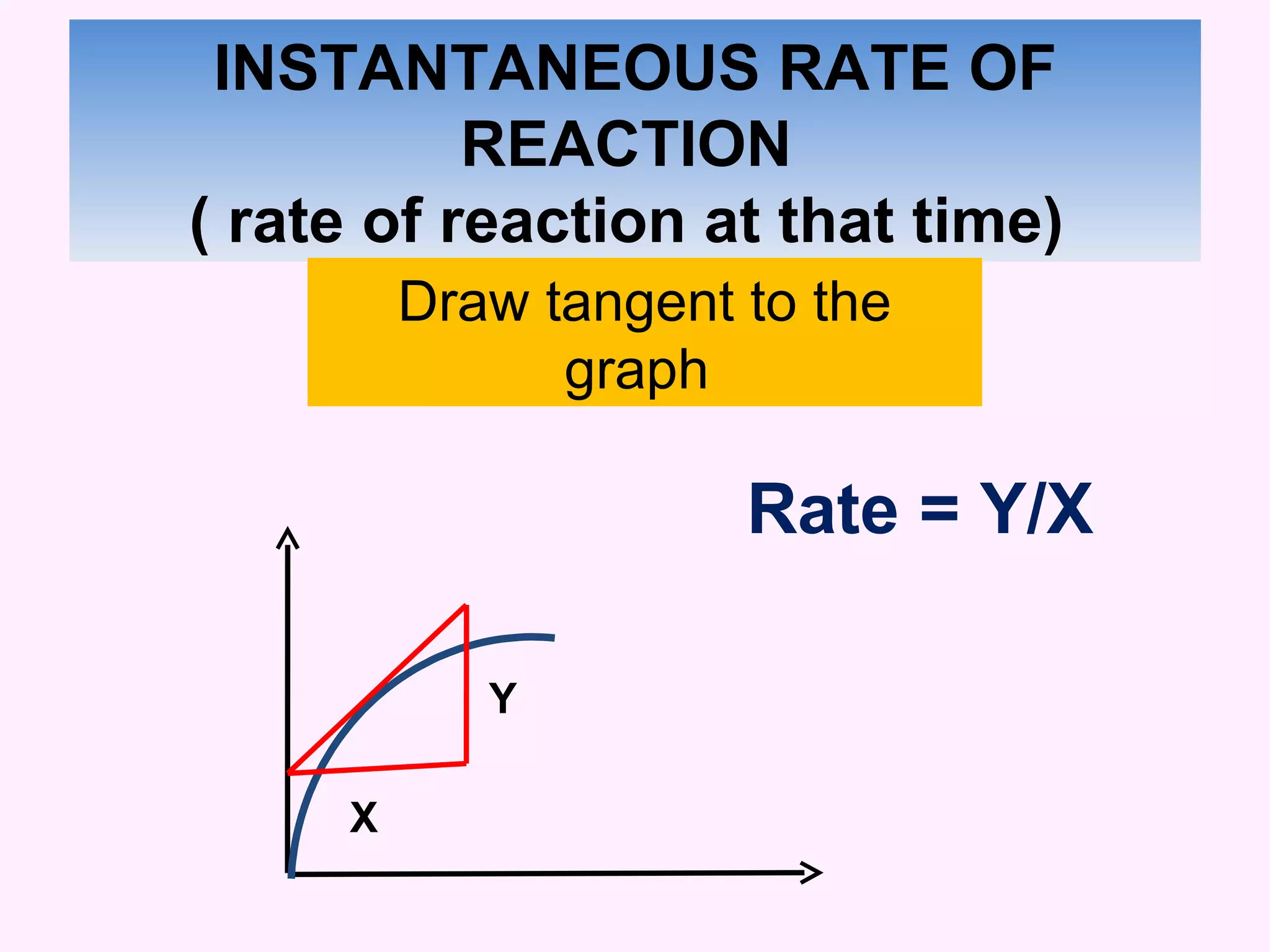
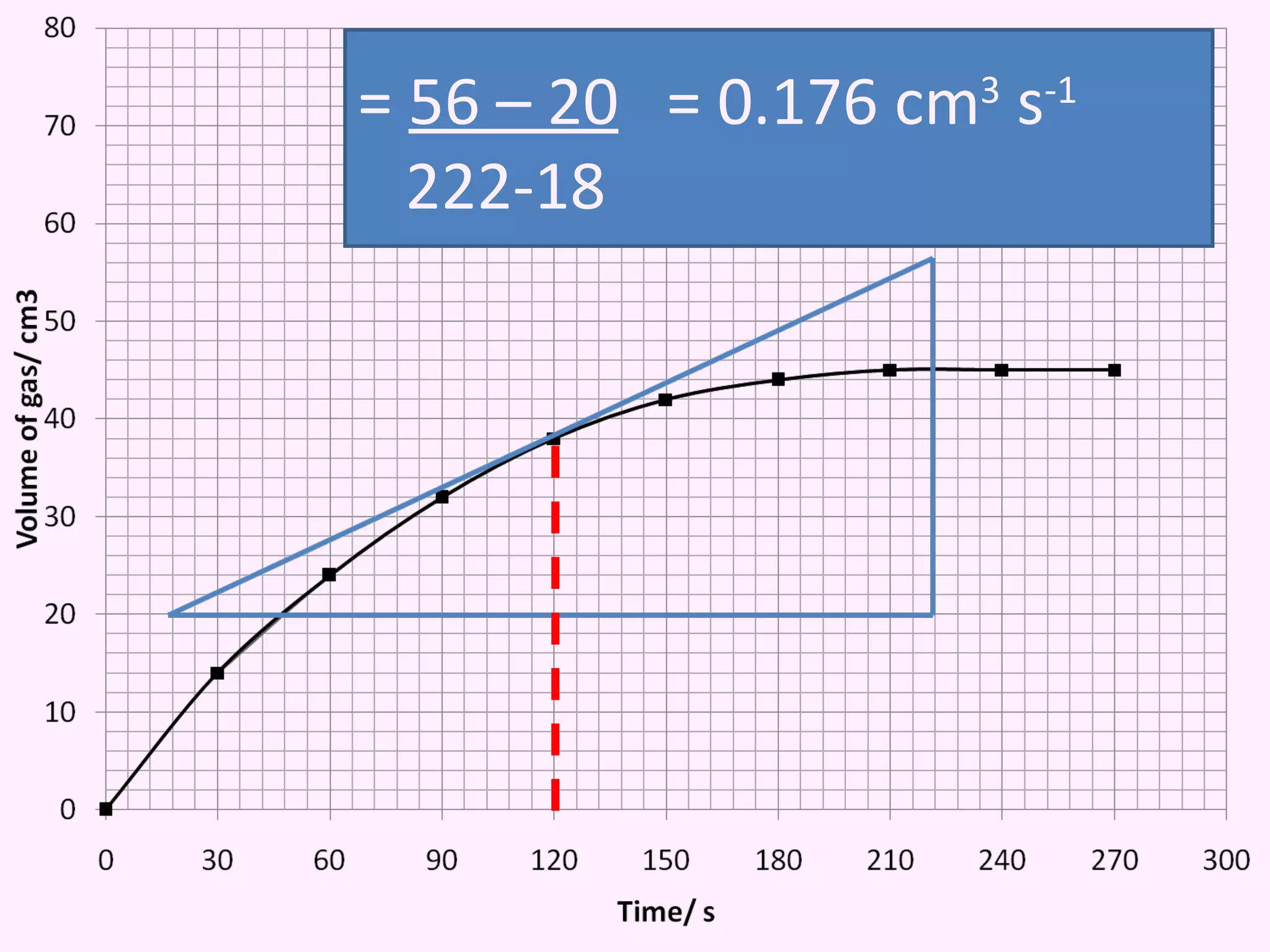
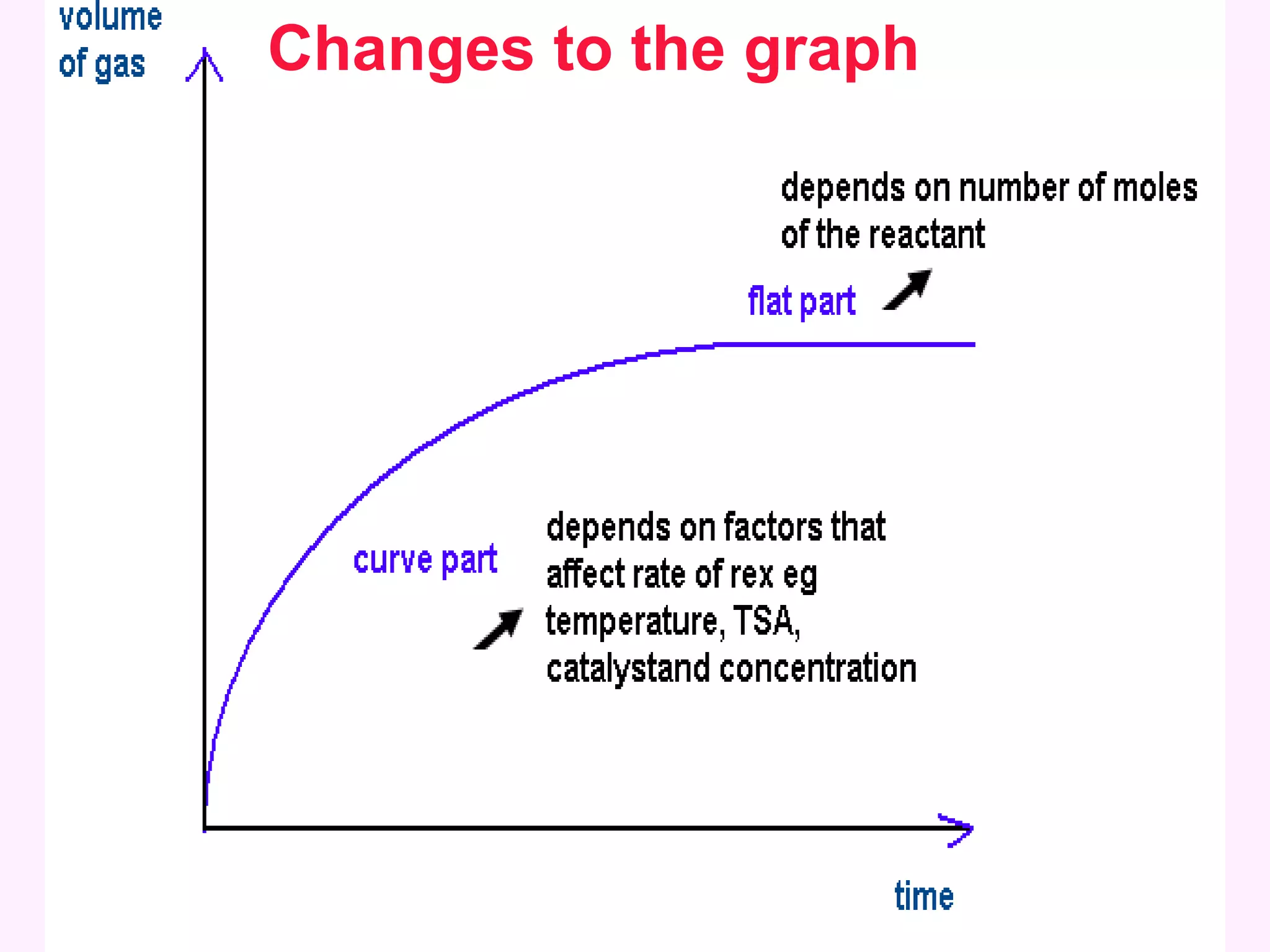
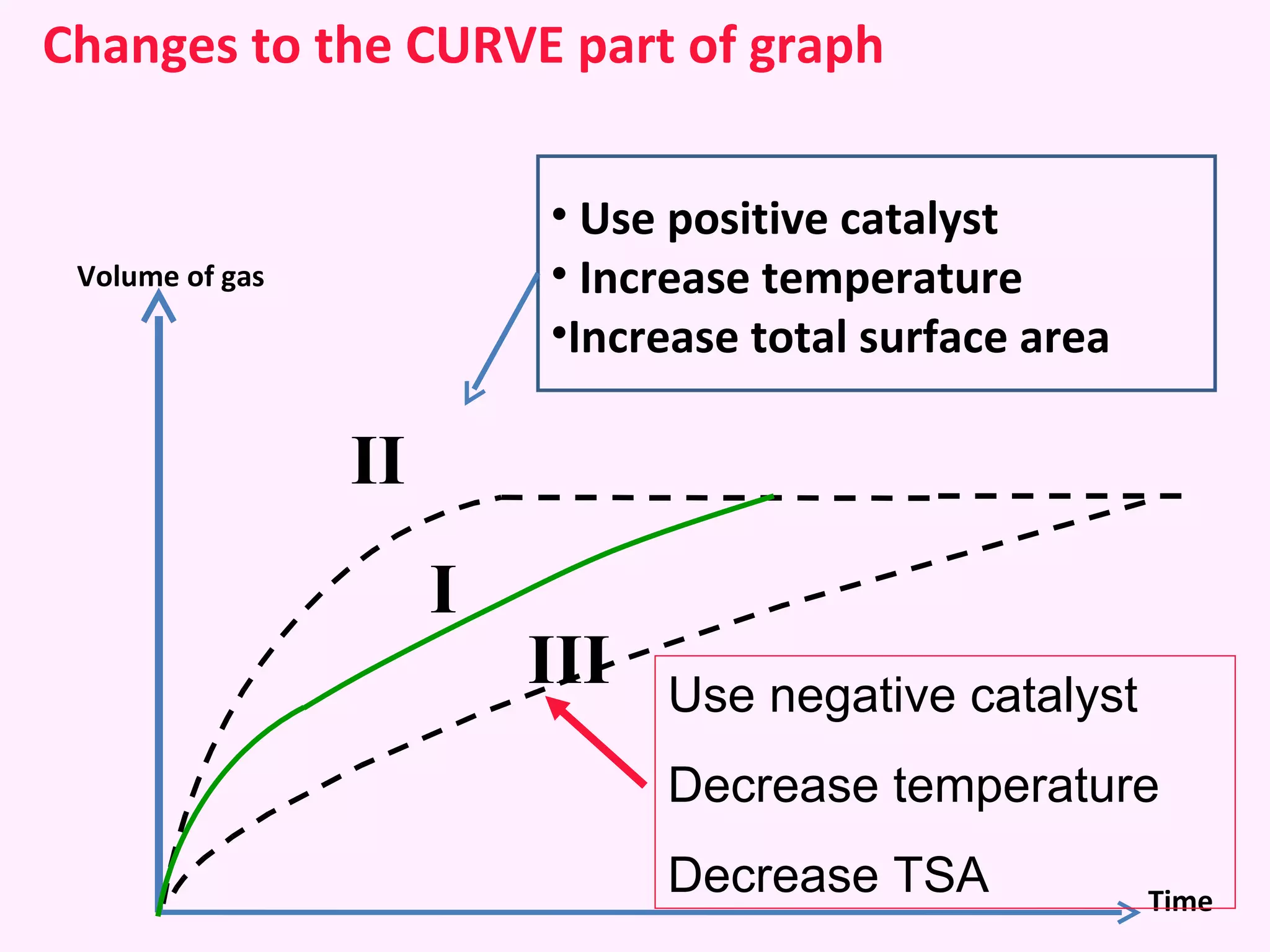
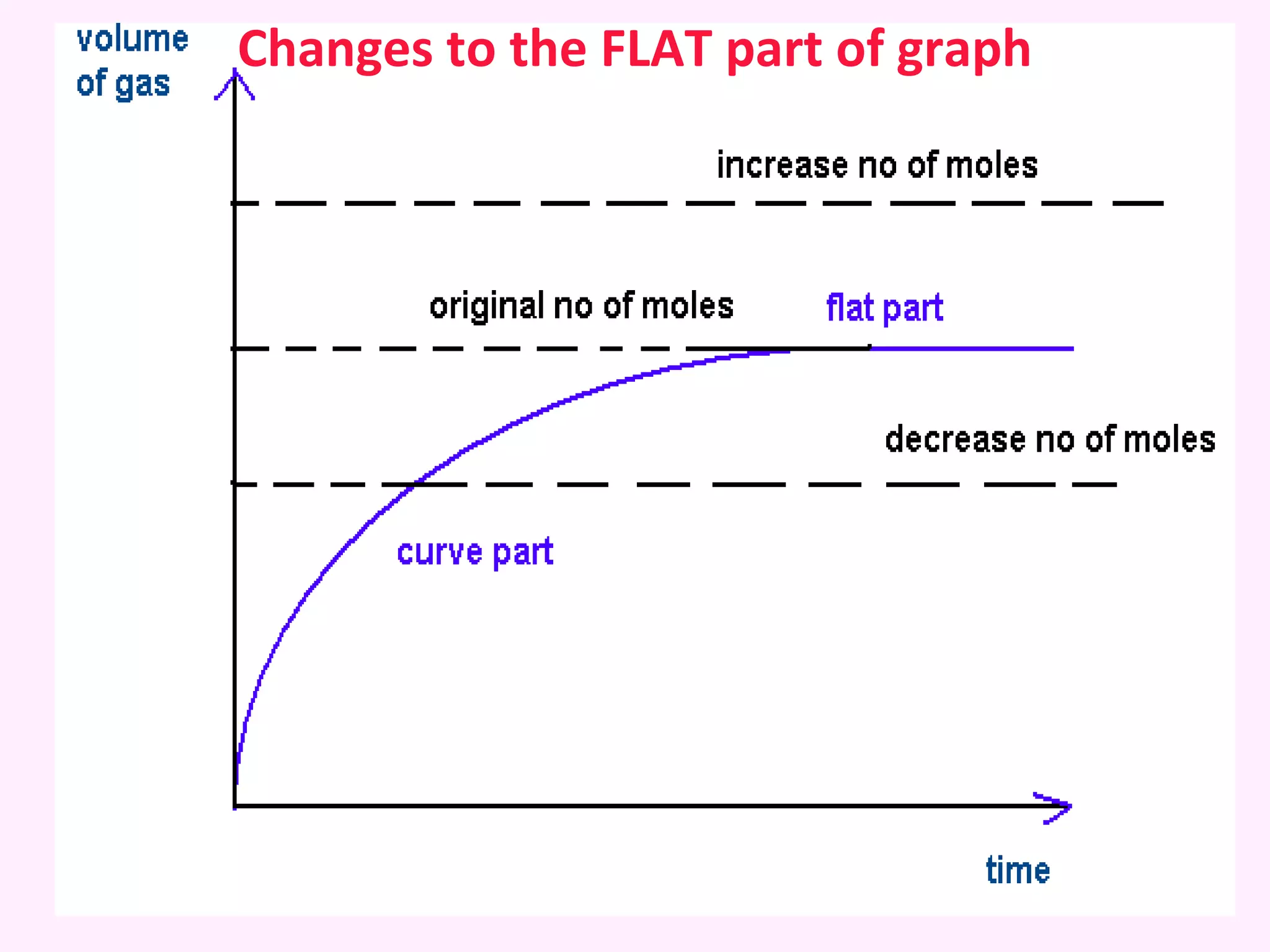
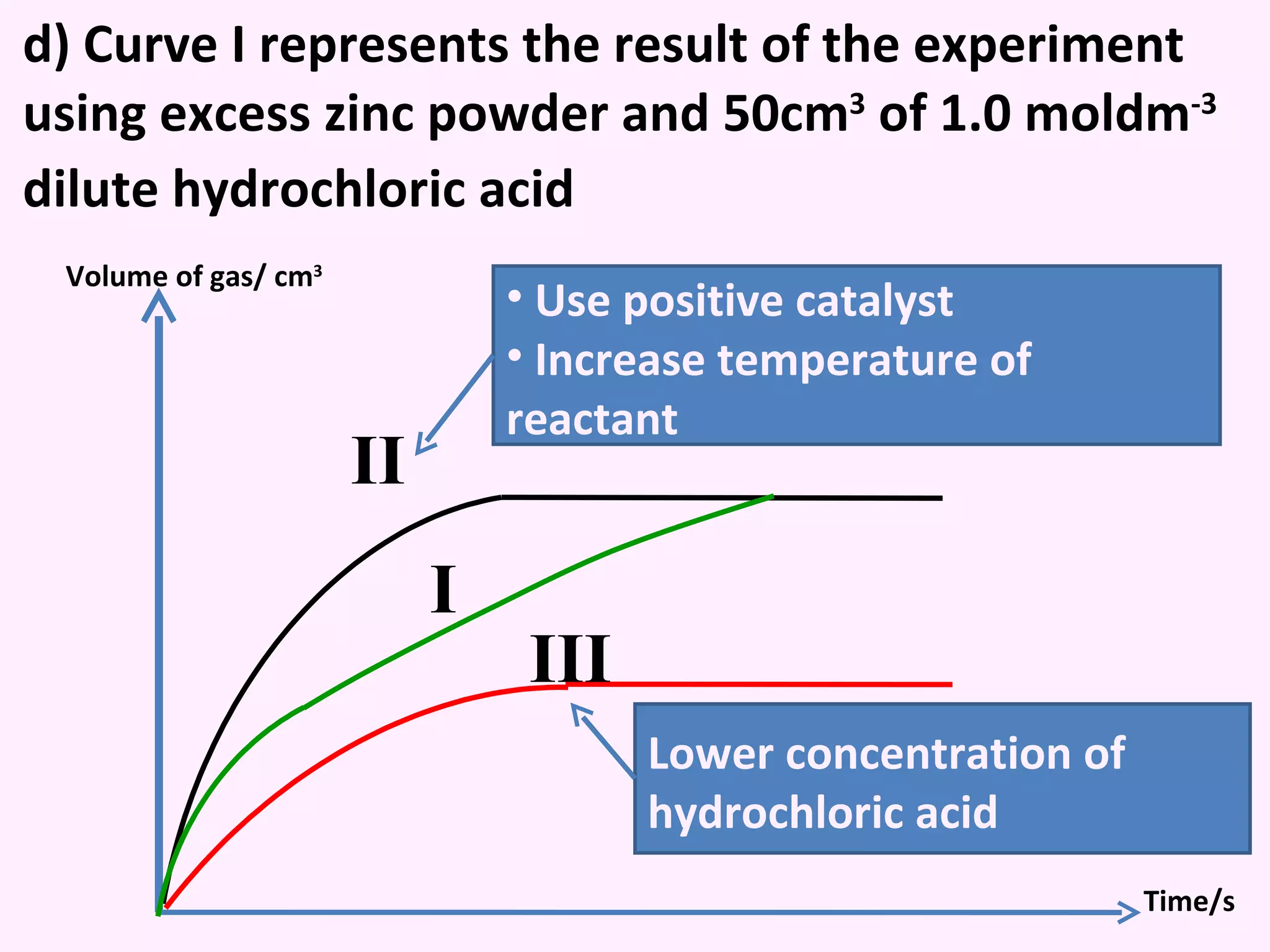
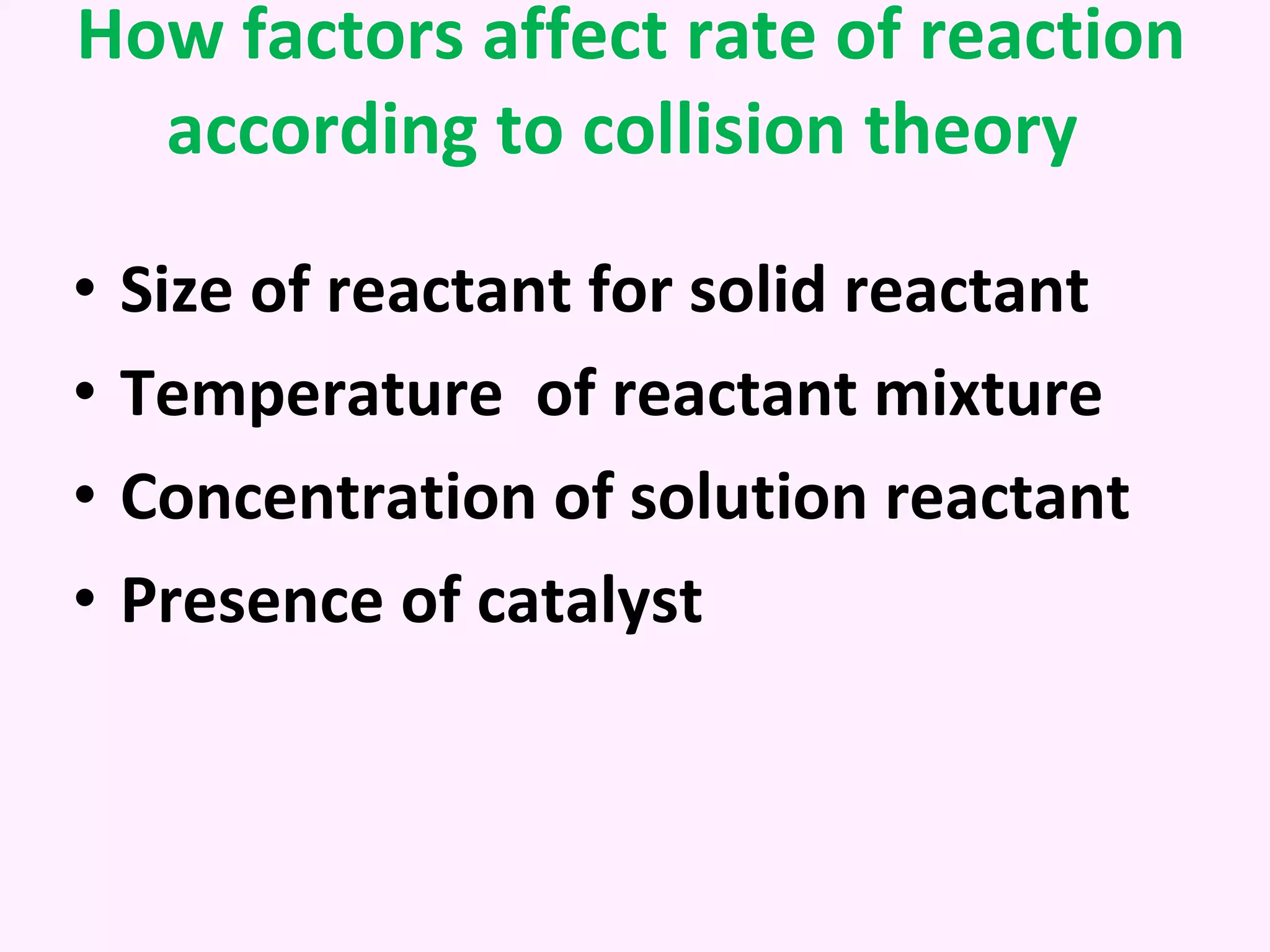
This document discusses average and instantaneous rates of reaction and how to determine them from a graph. It also discusses collision theory and how factors like temperature, concentration, particle size, and catalysts affect the rate of a reaction according to this theory. Collision theory states that for a reaction to occur particles must collide with enough energy to overcome the activation energy barrier. These factors influence the rate by increasing the frequency and effectiveness of collisions between reacting particles.