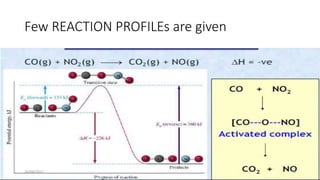
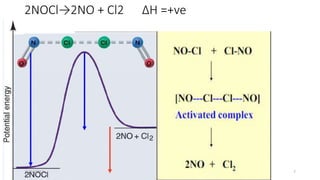
1) Transition state theory (TST) explains reaction rates by assuming a special type of equilibrium between reactants and unstable transition state complexes that have partially formed bonds between reactants and products.
2) TST can be used to calculate activation parameters like enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs energy of activation based on experimentally determined rate constants.
3) According to TST, a reaction will occur if the concentration of the transition state complex is high enough and if the complex breaks apart to form products rather than reverting back to reactants.