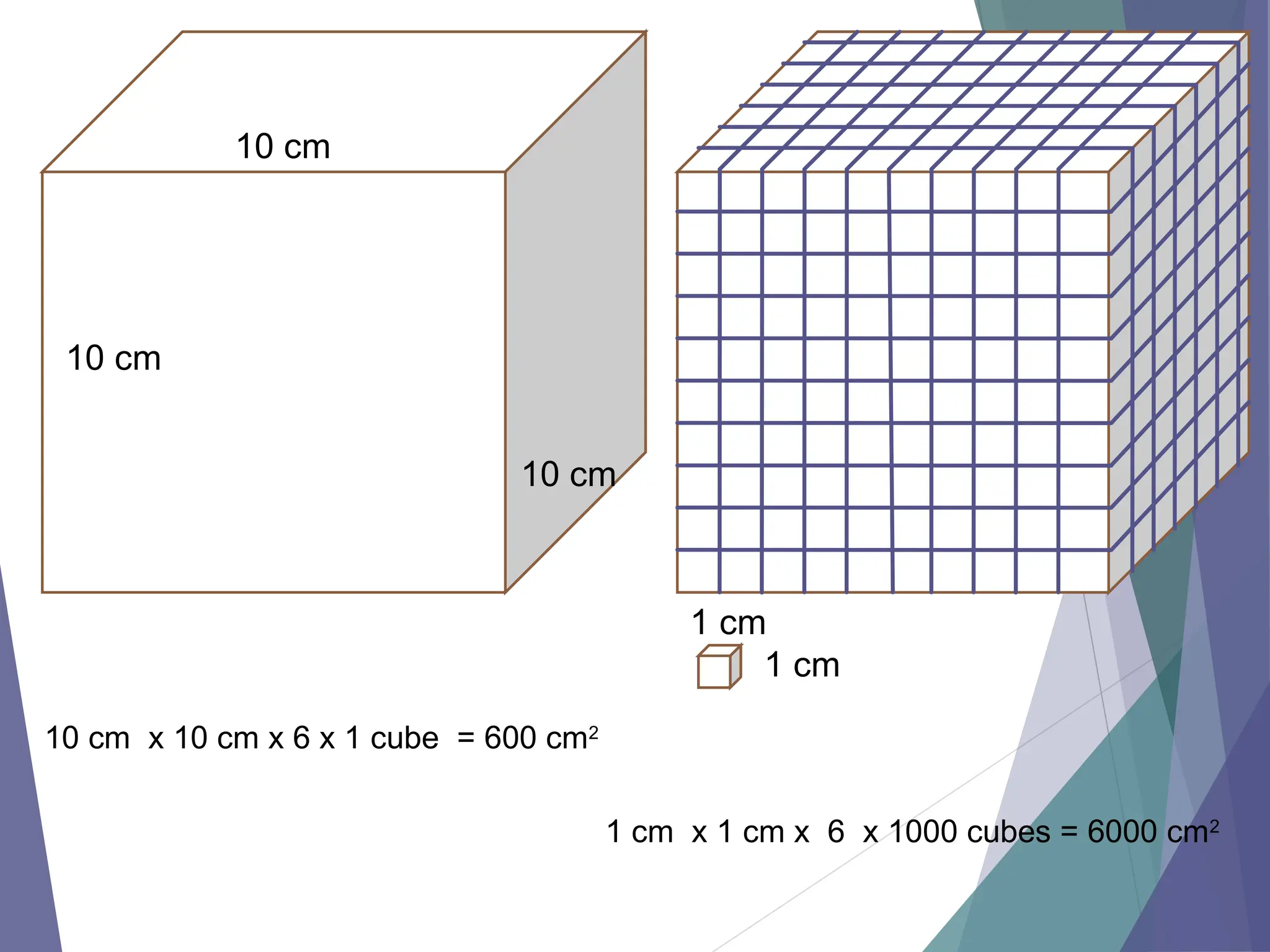
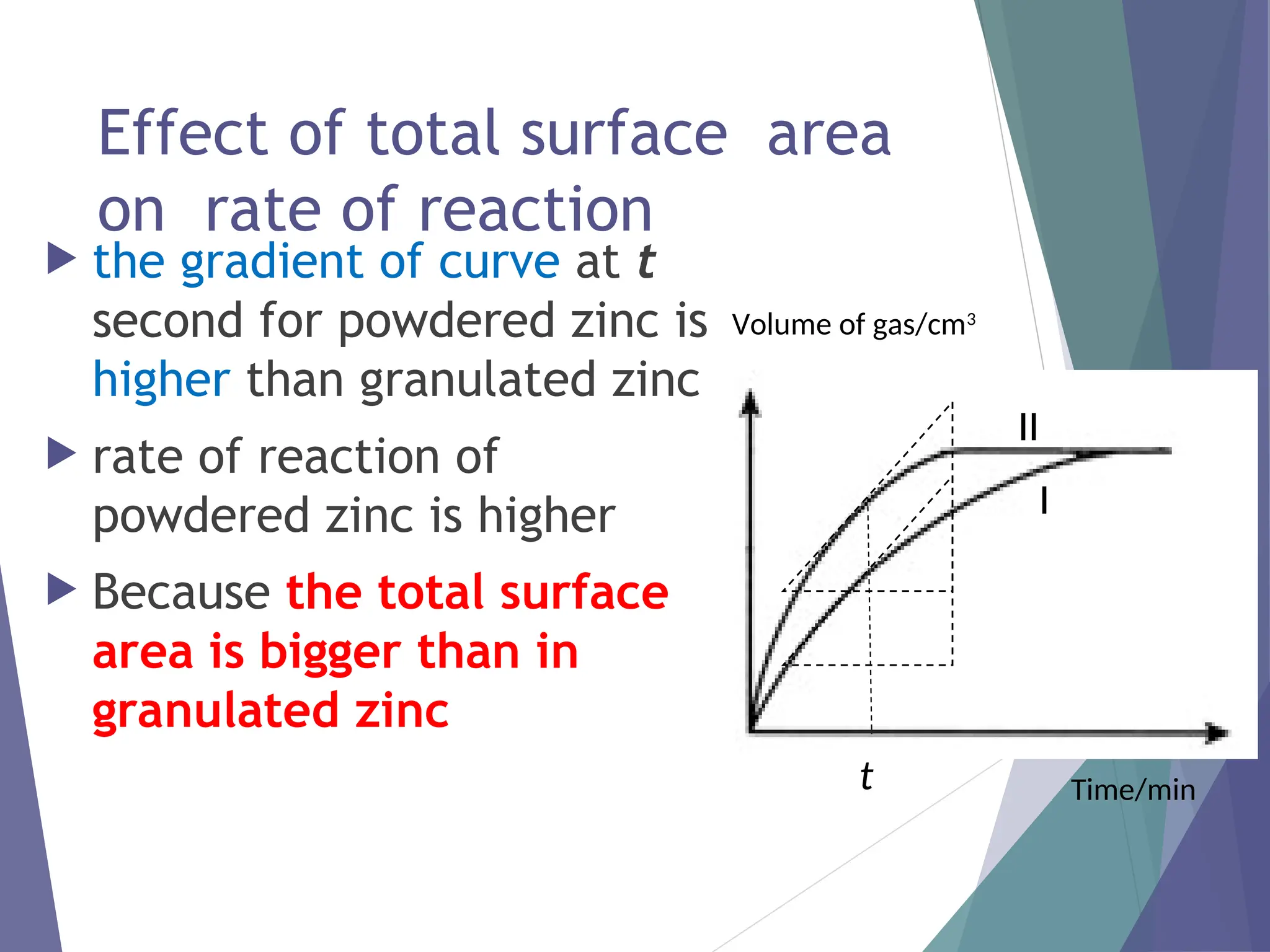
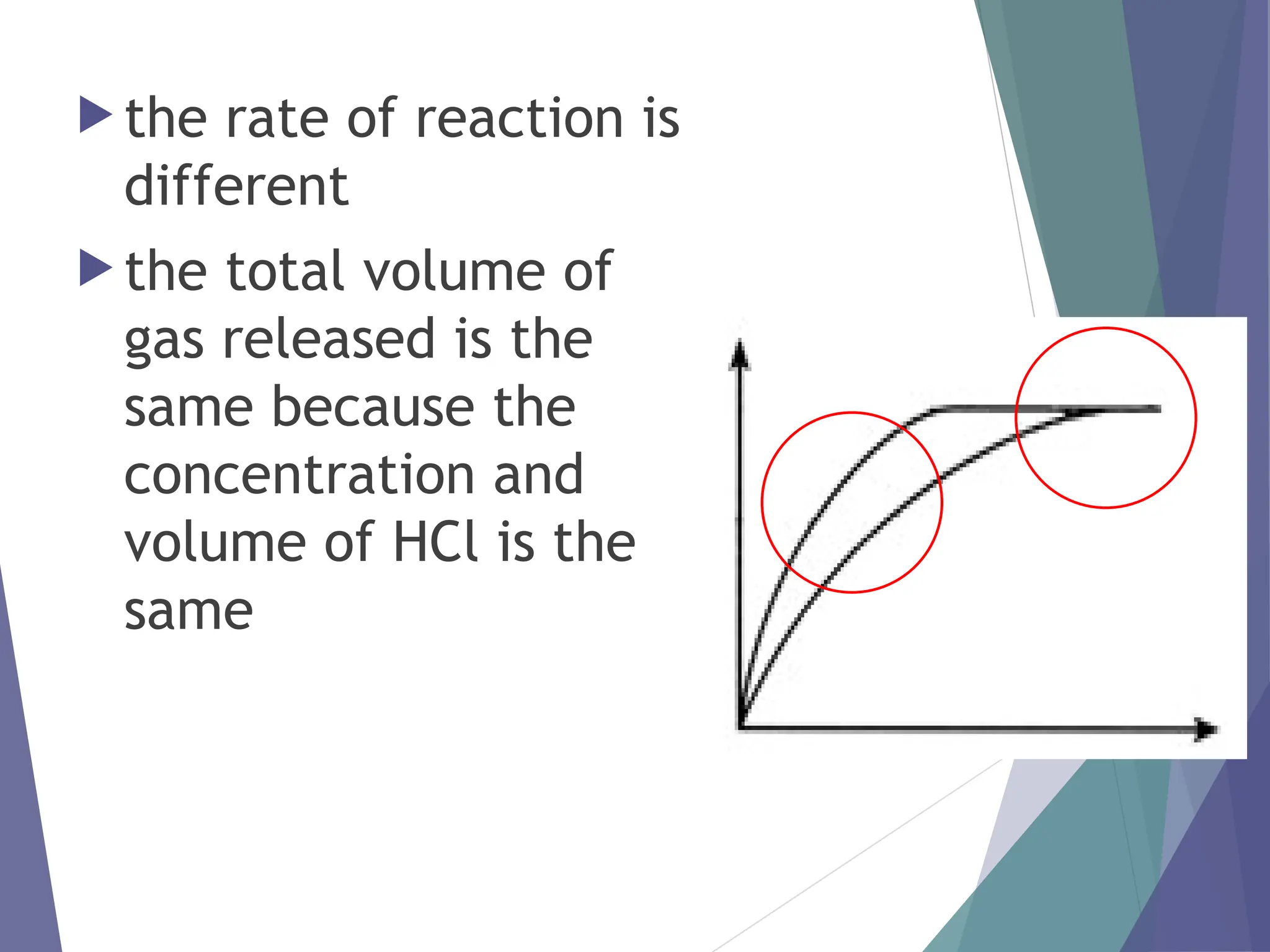
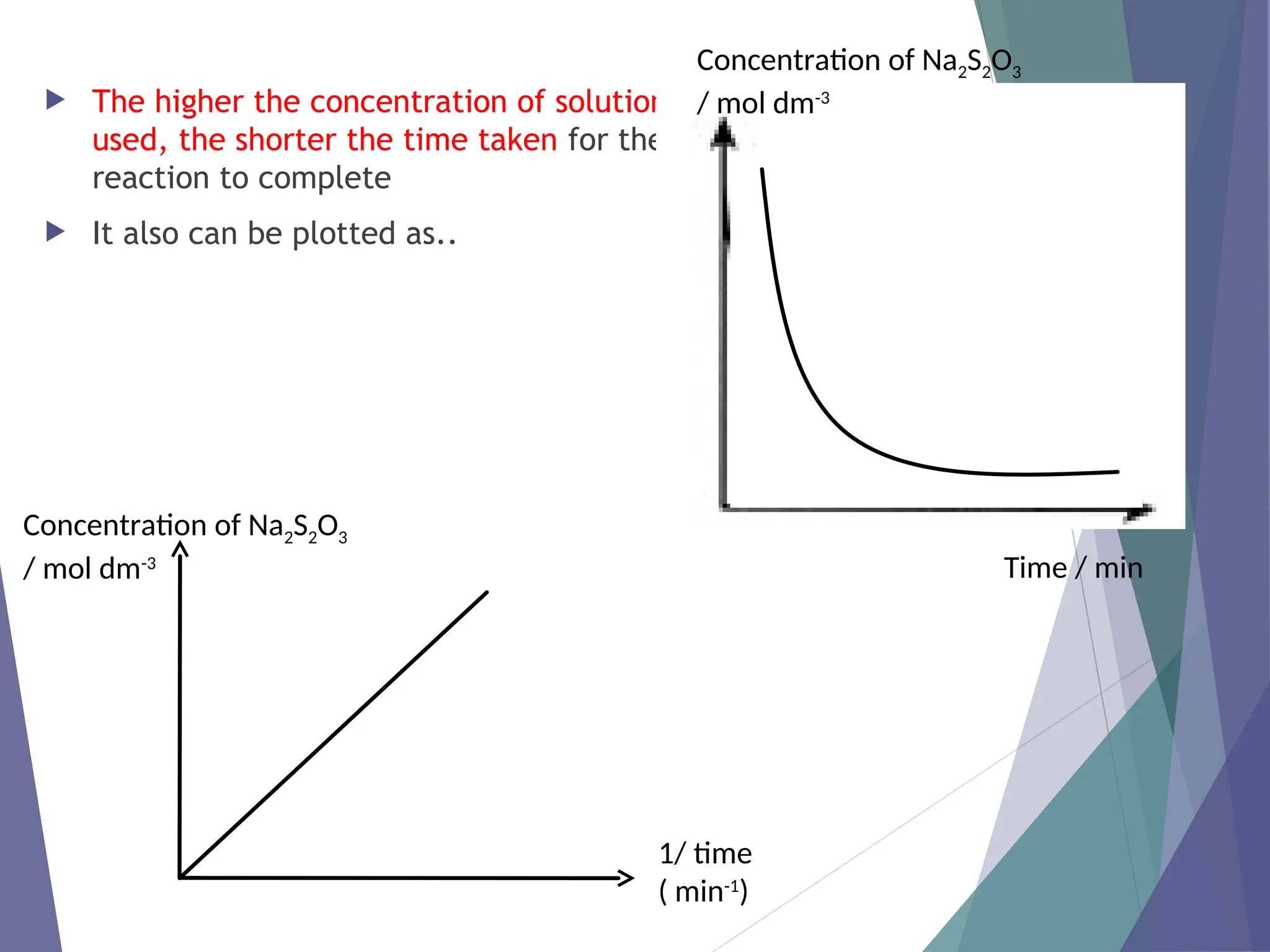
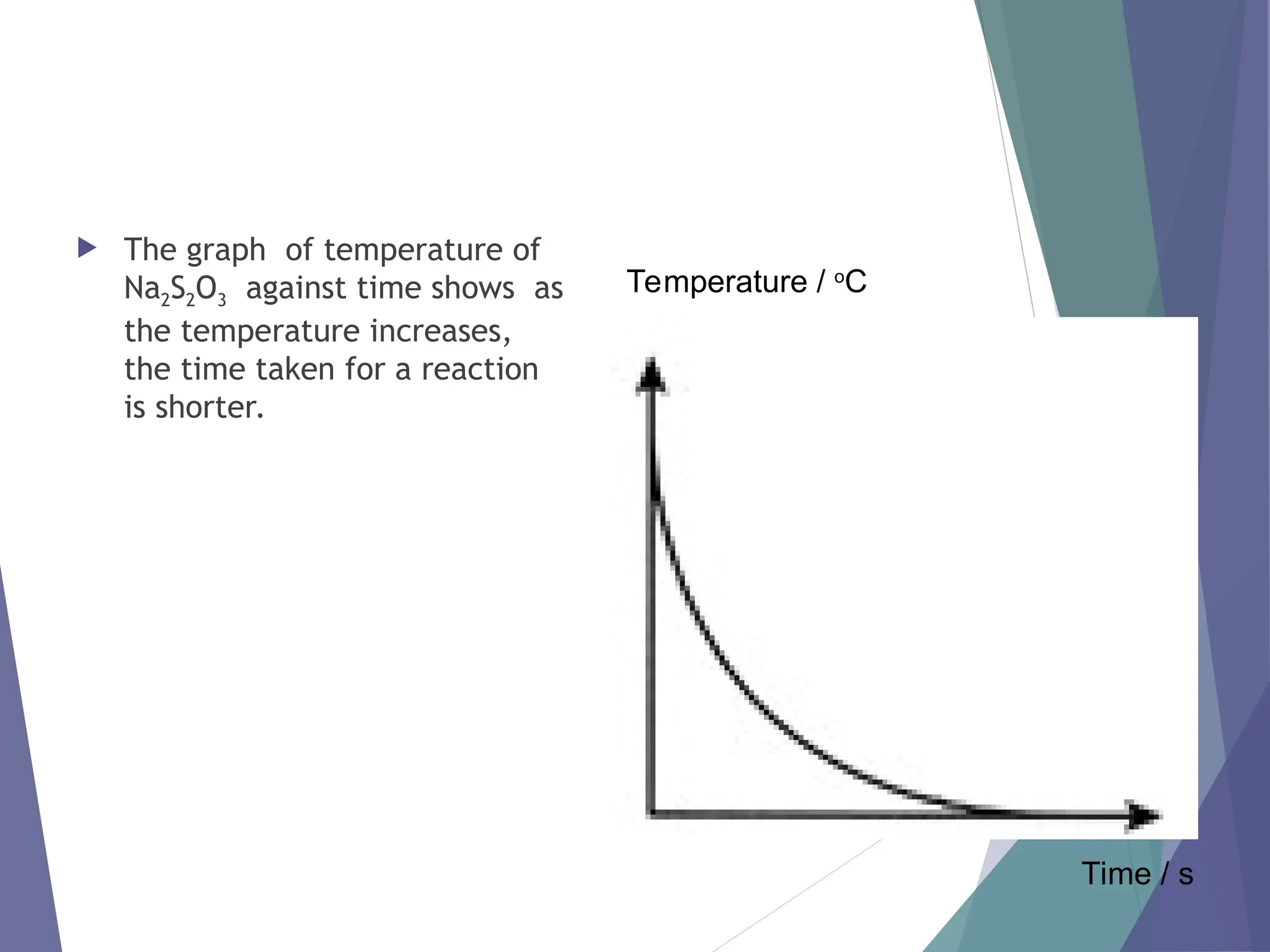
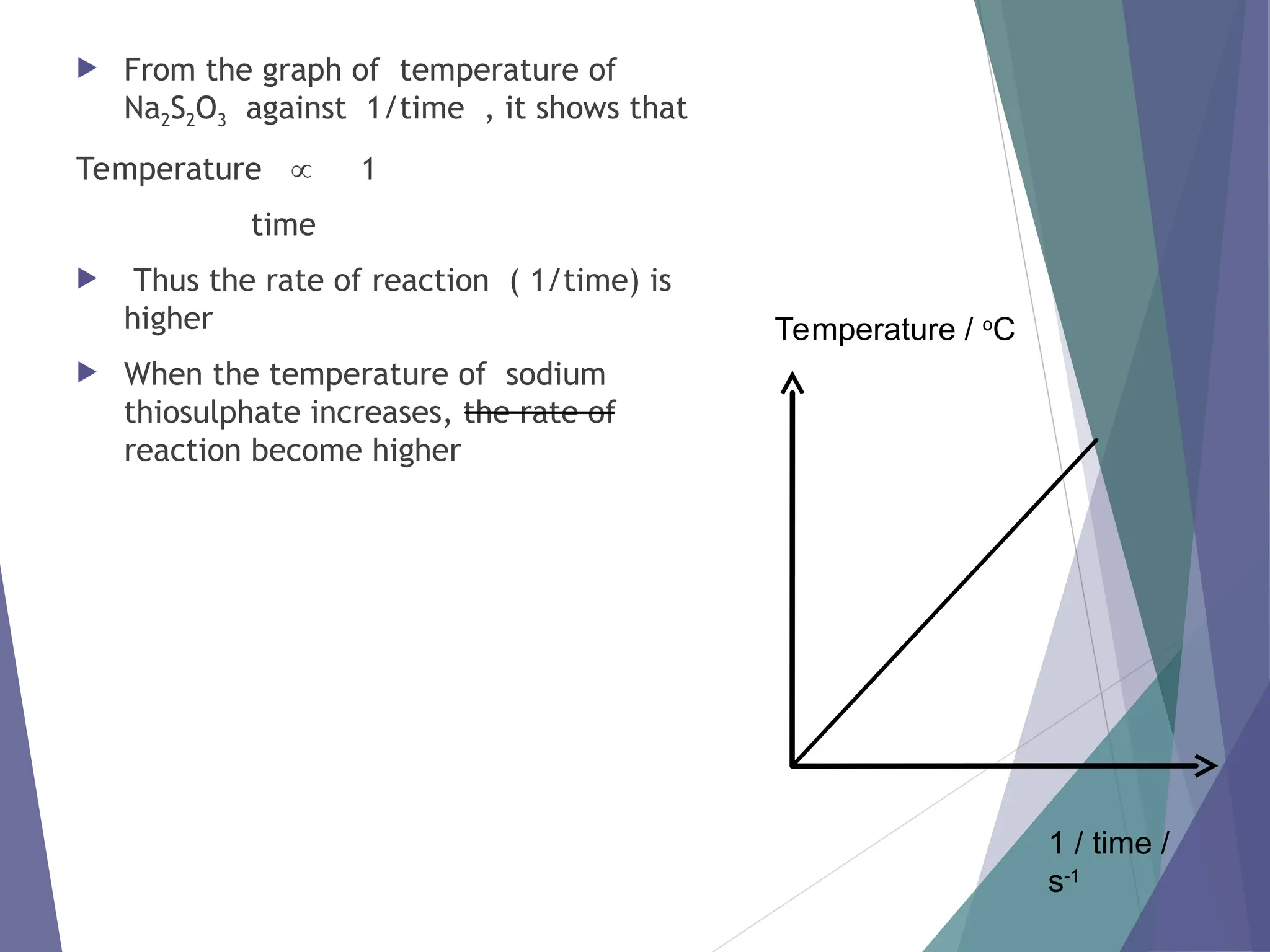
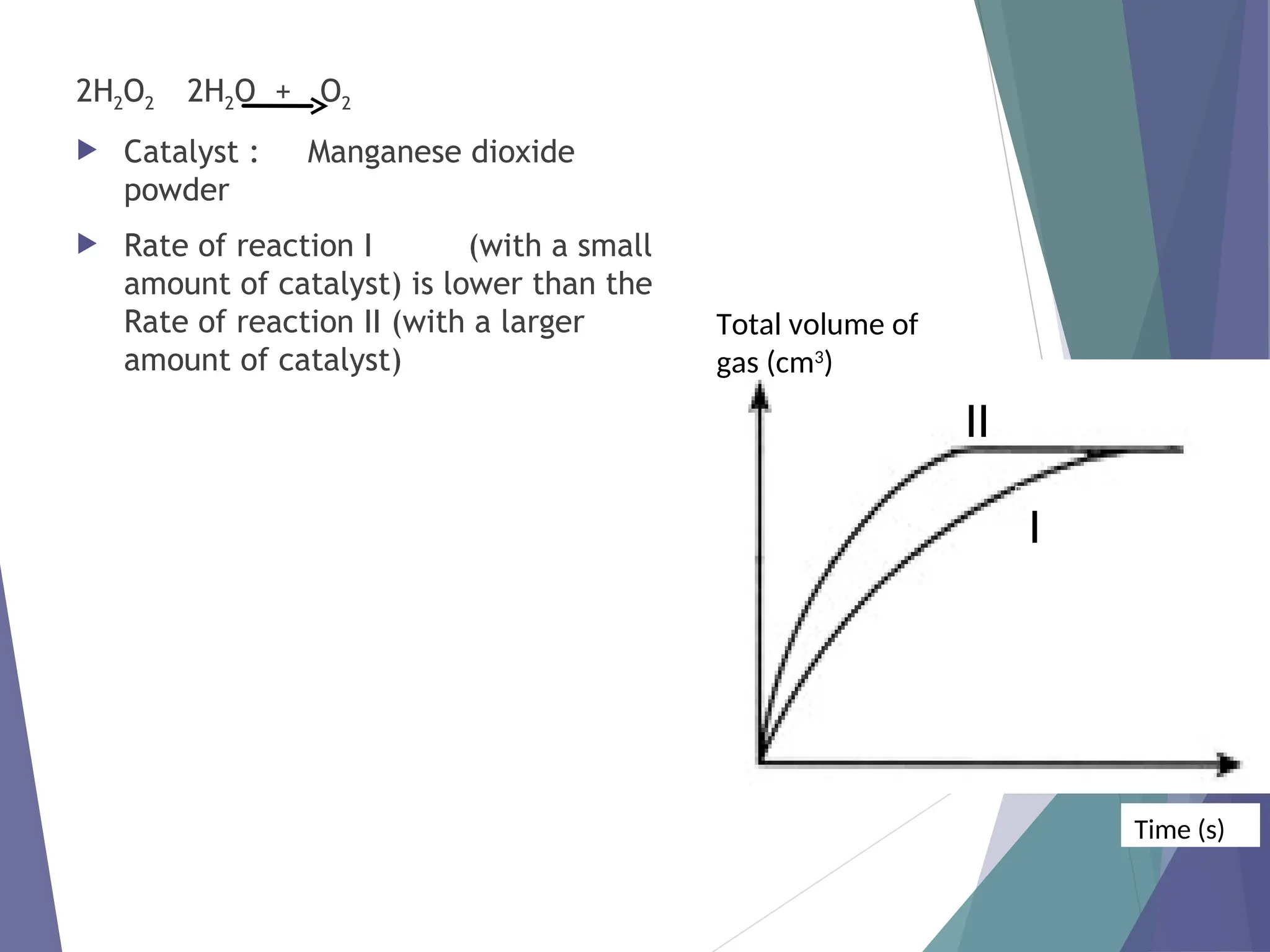
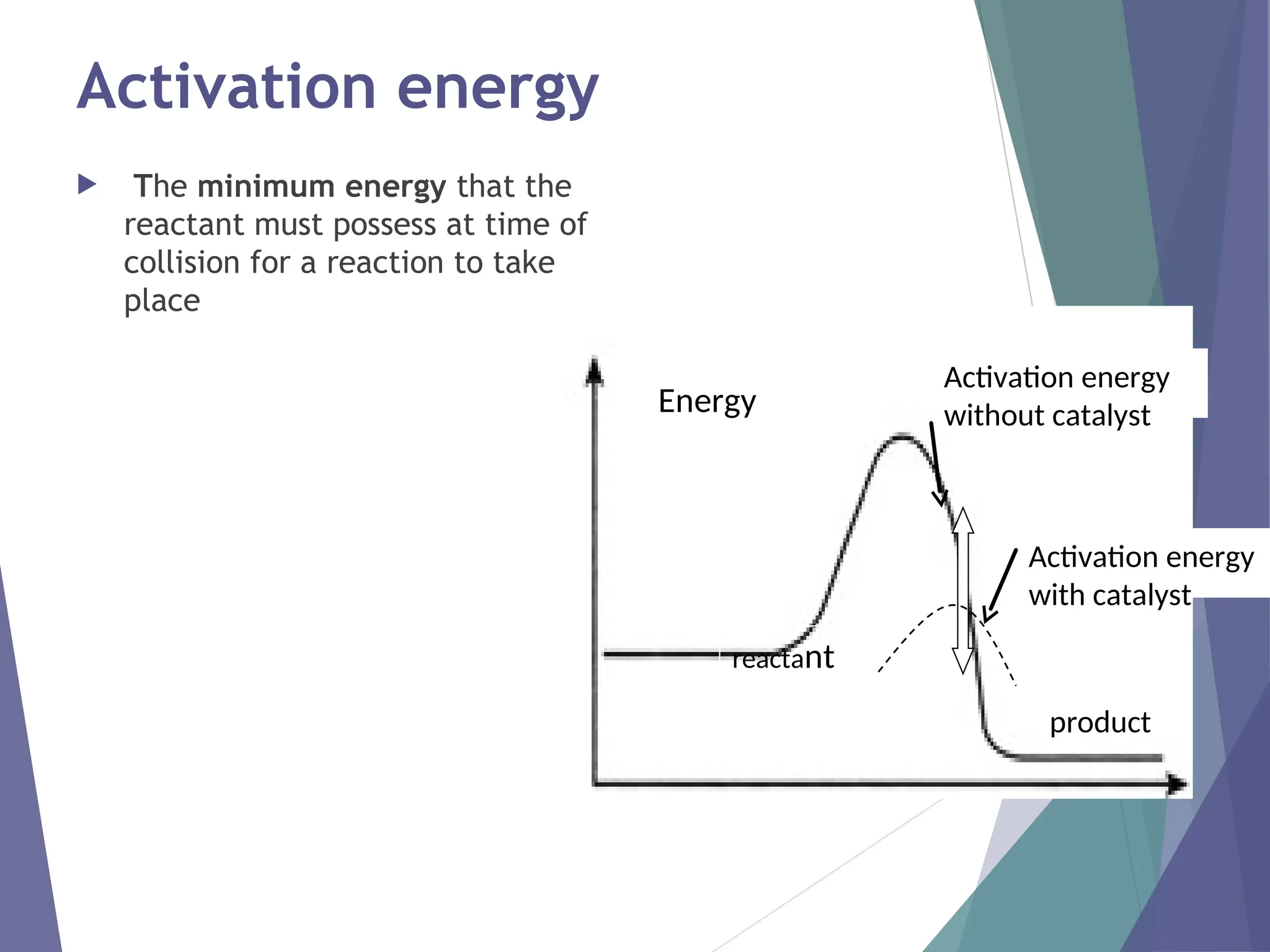
The document discusses factors affecting the rate of chemical reactions including surface area, temperature, concentration, catalysts, and pressure. It illustrates how each factor influences the rate of reaction, with examples like powdered zinc reacting faster than granulated zinc due to greater surface area, and heightened temperatures resulting in quicker reactions. Additionally, it highlights the role of catalysts in accelerating reactions and the effect of pressure on gaseous reactions.